高级语言程序设计课程第八次个人作业
这个作业属于哪个课程:https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/fzu/2024C
这个作业要求在哪里: https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/fzu/2024C/homework/13307
学号:<102400227>
姓名:<谭培>
//11.1:一来没看懂返回地址是啥,后面结合书上自定义函数前带星号想到指针类型
#include<stdio.h>
#define size 100
char *read(char *, int );
int main(){
char str[size];
read(str,size);
puts(str);
}
char *read(char *st, int n){
int i=0;
do{
st[i]=getchar();
}while(st[i]!=EOF&&++i<n);
return st;
}

11.2:重新回顾了一下第七章ctype里的函数
#include<stdio.h>
#include<ctype.h>
#define size 100
//假定题目中的n为100
char *read(char *, int );
int main(){
char str[size];
read(str,size);
puts(str);
}
char *read(char *st, int n){
int i=0;
do{
st[i]=getchar();
if(isblank(st[i])) break;
}while(st[i]!=EOF&&++i<n);
return st;
}
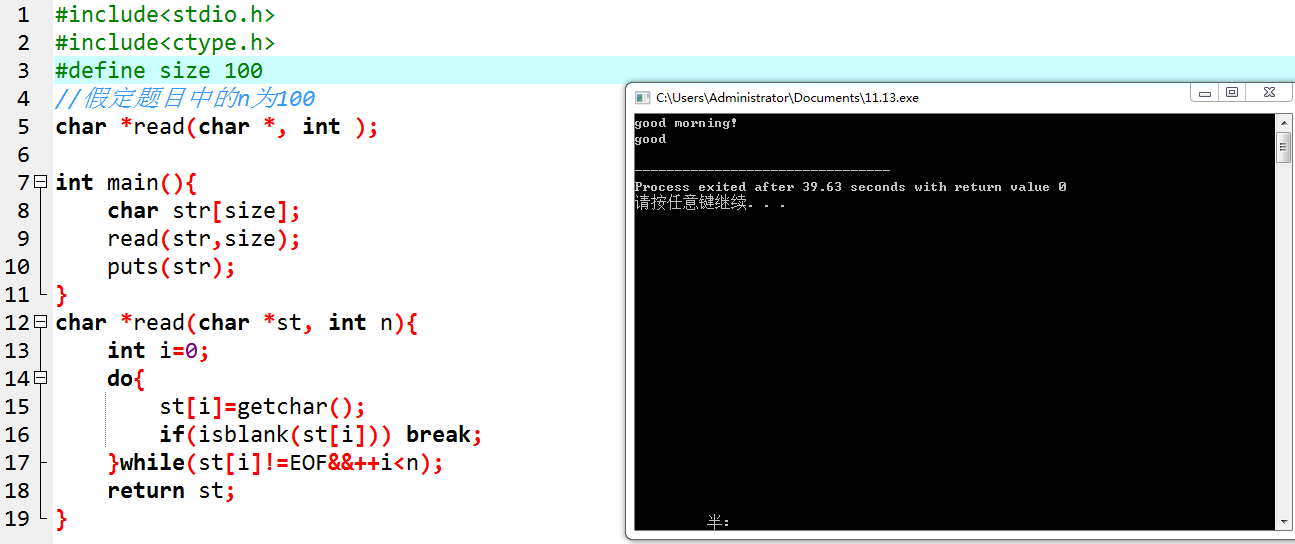
//11.3:一直在处理怎么判别是否已经有一个单词了,注意到可以分别讨论
#include<stdio.h>
#include<ctype.h>
#define size 100
//假定题目中的n为100
char *read(char *, int );
int main(){
char str[size]=" ";
read(str,size);
puts(str);
}
char *read(char *st, int n){
int i=0;
char ch;//临时存储
do{
ch=getchar();
if(isblank(ch)&&i==0) continue;
if(isblank(ch)&&!isblank(st[i-1])) break;
st[i++]=ch;
}while(ch!=EOF&&i<size);
return st;
}
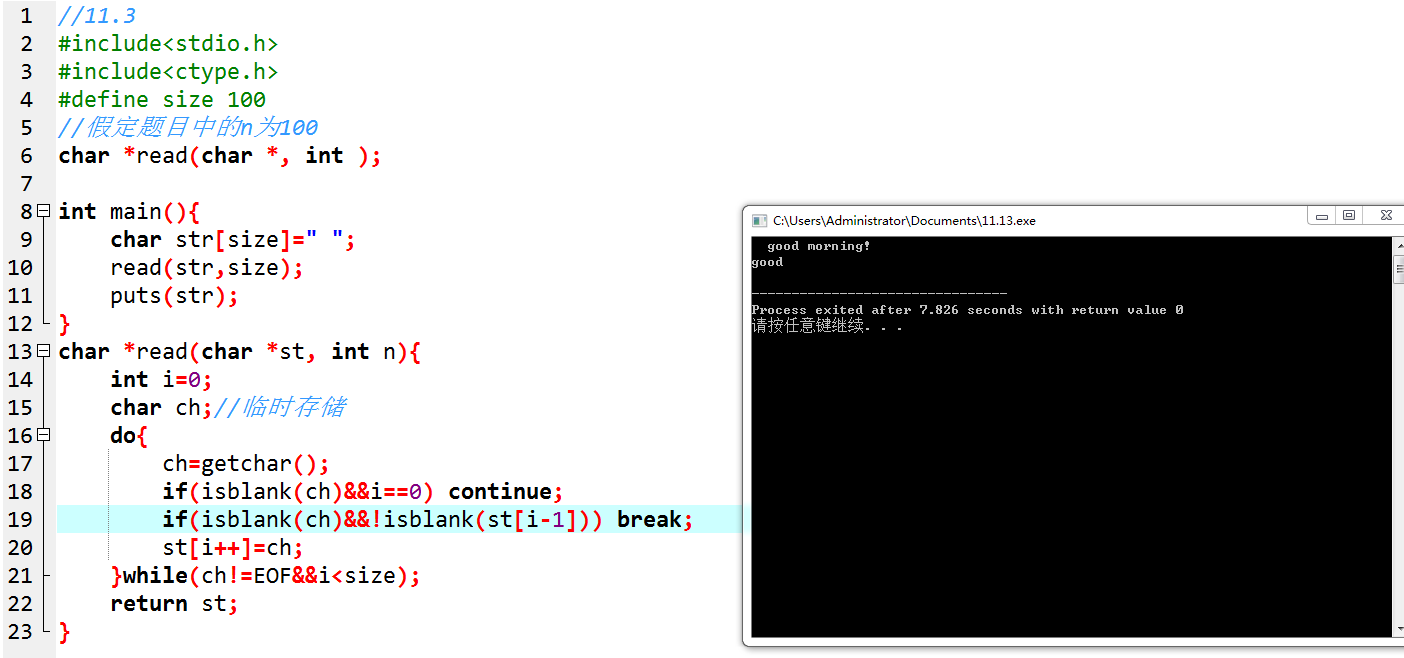
//11.6:一来在自定义函数中用了sizeof,但这里数组已经退化为指针了,并不能反映出实际数量,使用strlen才对。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int is_within(char ch, char *str){
int length=strlen(str);
int find=0;
for(int i=0; i<length; i++){
if(ch==*(str+i)) {
find=1;
break;
}
}
return find;
}
int main() {
char str[100];
char ch;
int i=0;
while((str[i]=getchar())!=EOF){
i++;
if(i+1==100||str[i-1]=='\n') break;
}
str[i]=='\0';
ch=getchar();
int result=is_within(ch,str);
printf("%d",result);
return 0;
}
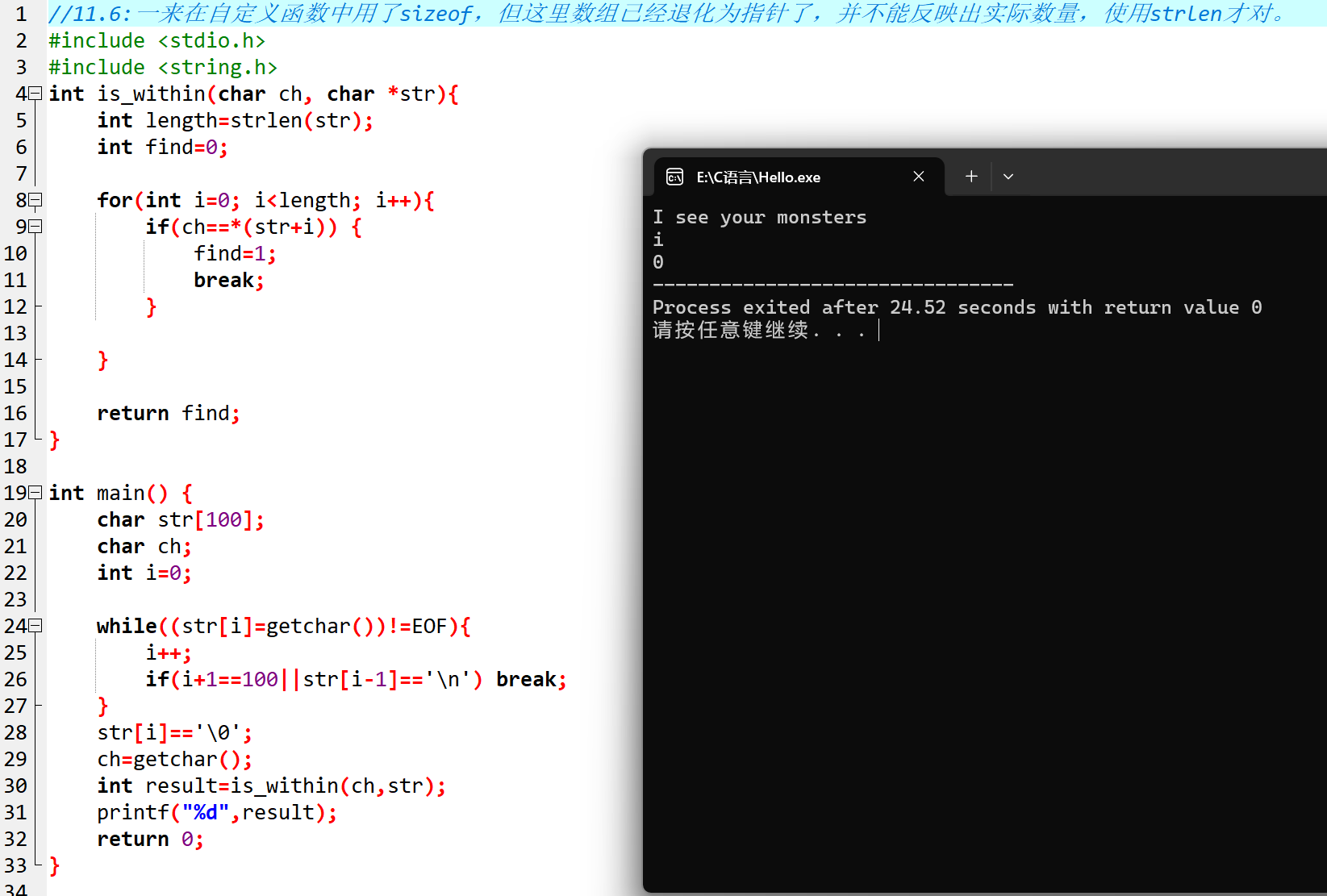
//11.7
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
char* mystrncpy(char *s2, char *s1, int n) {
int cnt = 0;
while (*s1!= '\0' && cnt < n) {
*(s2 + cnt++) = *s1++;
}
while (cnt < n) {
*(s2 + cnt++) = '\0';
}
return s2;
}
int main() {
char str1[100];
char str2[100];
int n = 0;
printf("输入一个字符串:(回车结束)\n");
fgets(str1, 100, stdin);
str1[strcspn(str1, "\n")] = '\0';
printf("复制长度:\n");
scanf("%d", &n);
do {
if (mystrncpy(str2, str1, n)!= NULL) {
puts(str2);
} else {
printf("复制失败!\n");
}
// 清空输入缓冲区
int c;
while ((c = getchar())!= '\n' && c!= EOF) {}
printf("输入新的字符串:(回车结束)\n");
fgets(str1, 100, stdin);
str1[strcspn(str1, "\n")] = '\0';
printf("复制长度:\n");
scanf("%d", &n);
if (n > strlen(str1)) {
n = strlen(str1);
}
} while (strcmp(str1, "")!= 0);
return 0;
}
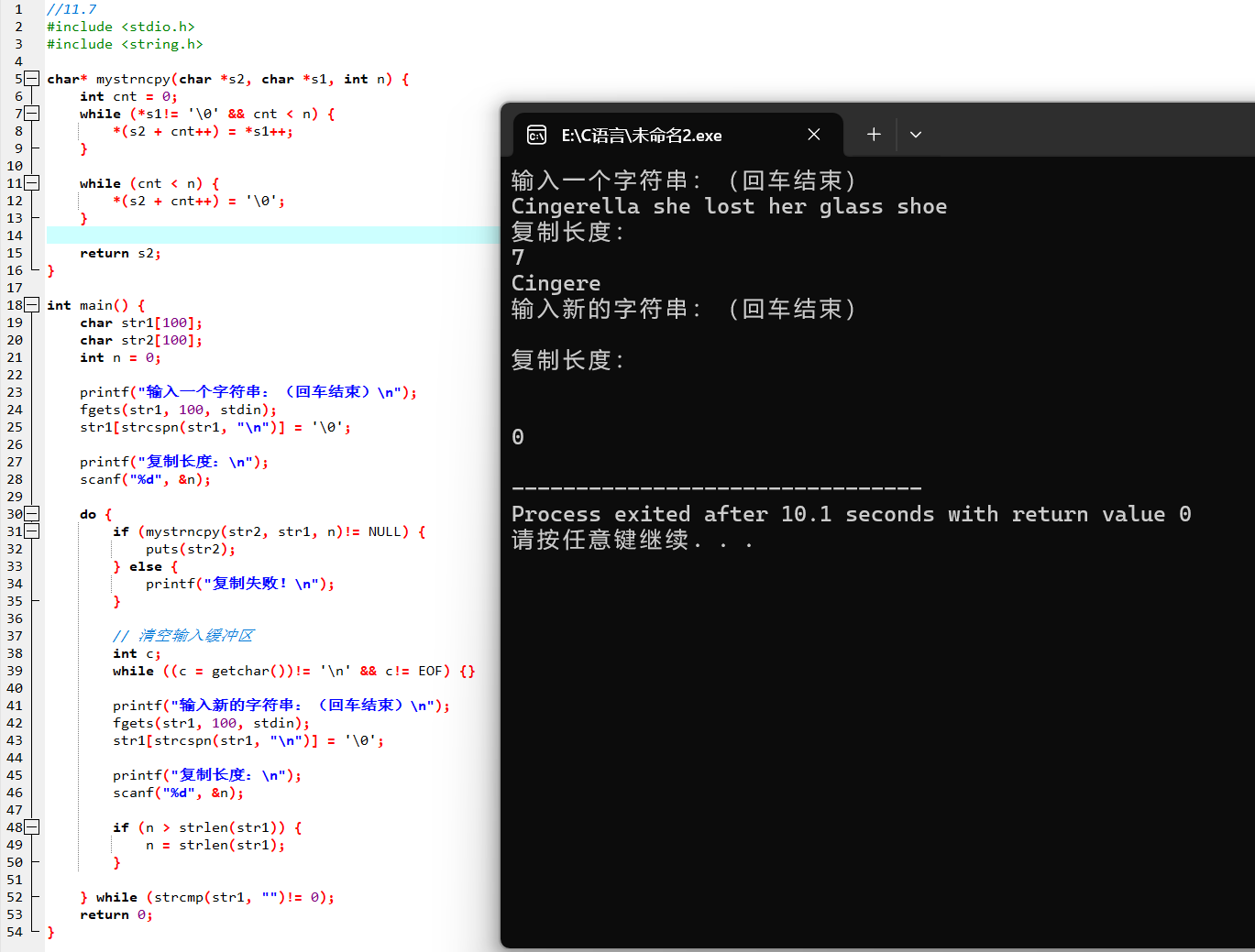
//12.1 :自定义函数中scanf函数中units本身就是地址
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
void critic(int *units){
printf("No luck,my friend. Try again.\n");
scanf("%d",units);
}
int main() {
int units=0;
printf("How many pound to a firkin of butter?\n");
scanf("%d",&units);
while(units != 56)
critic(&units);
printf("You must have looked it up!\n");
return 0;
}
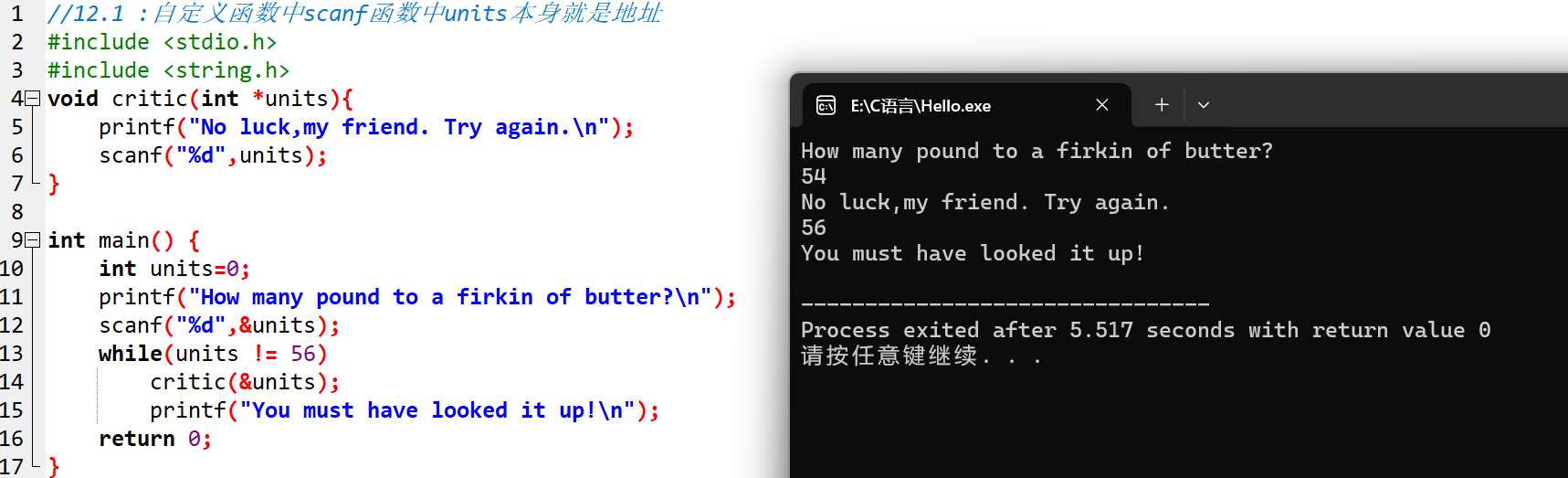
12.2:第一次编译多文件,有点难度,问了佬
#include <stdio.h>
#include "pe12_2a.c"//这里名称和原题不一样
int main(void)
{
int mode;
printf("Enter 0 for metric mode, 1 for US mode: ");
scanf("%d", &mode);
while (mode >= 0)
{
set_mode(mode);
get_info();
show_info();
printf("Enter 0 for metric mode, 1 for US mode (-1 to quit): ");
scanf("%d", &mode);
}
printf("Done.\n");
return 0;
}
//这里是pe12_2a.c的代码
#include <stdio.h>
int g_mode;
double g_distance;
double g_fuel;
void set_mode(int mode)
{
if (mode == 0 || mode == 1)
{
g_mode = mode;
}
else
{
printf("Invalid mode specified. Mode %d (US) used.\n", g_mode);
}
}
void get_info(void)
{
if (g_mode == 0)
{
printf("Enter distance traveled in kilometers: ");
scanf("%lf", &g_distance);
printf("Enter fuel consumed in liters: ");
scanf("%lf", &g_fuel);
}
else if (g_mode == 1)
{
printf("Enter distance traveled in miles: ");
scanf("%lf", &g_distance);
printf("Enter fuel consumed in gallons: ");
scanf("%lf", &g_fuel);
}
}
void show_info(void)
{
if (g_mode == 0)
{
double consumption = (g_fuel / g_distance) * 100;
printf("Fuel consumption is %.2f liters per 100 km.\n", consumption);
}
else if (g_mode == 1)
{
double consumption = g_distance / g_fuel;
printf("Fuel consumption is %.2f miles per gallon.\n", consumption);
}
}
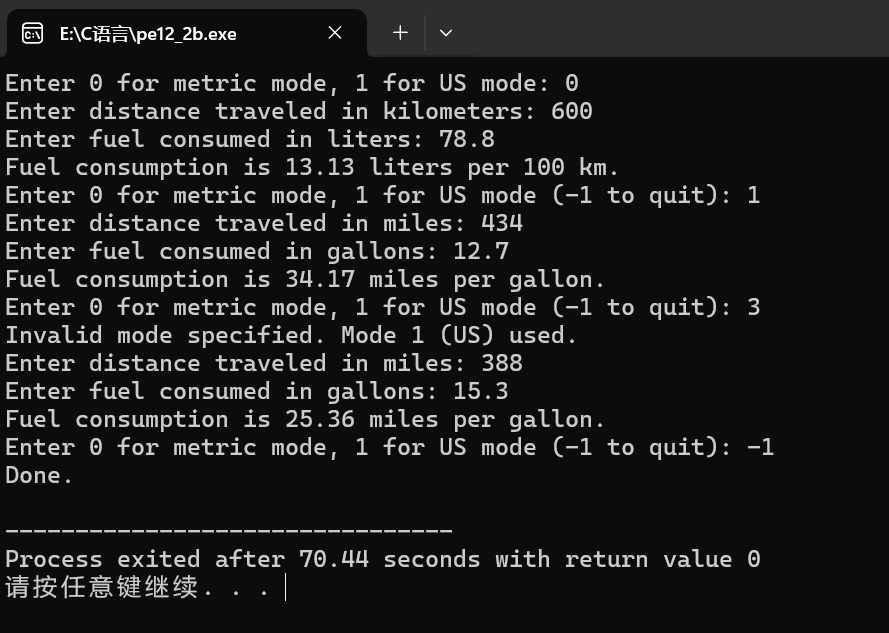
12.3:查了一下头文件怎么写,把全局变量改成自动变量
#include <stdio.h>
#include "pe12_2a.h"
int main(void)
{
int mode;
printf("Enter 0 for metric mode, 1 for US mode: ");
scanf("%d", &mode);
while (mode >= 0)
{
set_mode(mode);
double distance, fuel;
get_info(&distance, &fuel, mode);
show_info(distance, fuel, mode);
printf("Enter 0 for metric mode, 1 for US mode (-1 to quit): ");
scanf("%d", &mode);
}
printf("Done.\n");
return 0;
}
#ifndef PE12_2A_H
#define PE12_2A_H
void set_mode(int mode);
void get_info(double *distance, double *fuel, int mode);
void show_info(double distance, double fuel, int mode);
#endif
#include <stdio.h>
#include "pe12_2a.h"
// set_mode函数实现
void set_mode(int mode)
{
if (mode!= 0 && mode!= 1)
{
printf("Invalid mode specified. Mode 1 (US) used.\n");
mode = 1;
}
}
// get_info函数实现
void get_info(double *distance, double *fuel, int mode)
{
if (mode == 0)
{
printf("Enter distance traveled in kilometers: ");
scanf("%lf", distance);
printf("Enter fuel consumed in liters: ");
scanf("%lf", fuel);
}
else if (mode == 1)
{
printf("Enter distance traveled in miles: ");
scanf("%lf", distance);
printf("Enter fuel consumed in gallons: ");
scanf("%lf", fuel);
}
}
// show_info函数实现
void show_info(double distance, double fuel, int mode)
{
if (mode == 0)
{
double consumption = (fuel / distance) * 100;
printf("Fuel consumption is %.2f liters per 100 km.\n", consumption);
}
else if (mode == 1)
{
double consumption = distance / fuel;
printf("Fuel consumption is %.2f miles per gallon.\n", consumption);
}
}
12.8
//12.8有点难,重新看了一下动态分配部分的知识
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h> // 因为使用了free函数,需要包含此头文件
int* make_array(int elem, int val);
void show_array(const int ar[], int n);
int main(void)
{
int *pa;
int size;
int value;
printf("Enter the number of elements: ");
while (scanf("%d", &size) == 1 && size > 0)
{
printf("Enter the initialization value: ");
scanf("%d", &value);
pa = make_array(size, value);
if (pa)
{
show_array(pa, size);
free(pa);
}
printf("Enter the number of elements(<1 to quit): ");
}
printf("Done.\n");
return 0;
}
int* make_array(int elem, int val)
{
int *ptr = (int *)malloc(elem * sizeof(int));
if (ptr == NULL)
{
printf("Memory allocation failed.\n");
return NULL;
}
for (int i = 0; i < elem; i++)
{
ptr[i] = val;
}
return ptr;
}
// 显示数组内容,每行显示8个数
void show_array(const int ar[], int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
printf("%d ", ar[i]);
if ((i + 1) % 8 == 0)
{
printf("\n");
}
}
if (n % 8!= 0)
{
printf("\n");
}
}
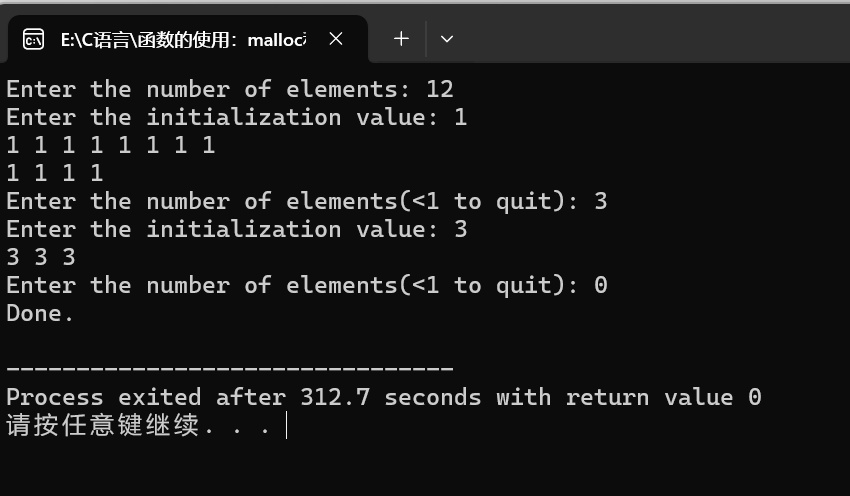
12.9
//12.9:指向指针的指针的动态分配,在网上查了好久才解决……
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
// 函数用于处理用户输入的单词
void handleWords() {
int numWords;
char tempWord[100]; // 这个数组用于临时存储输入的单词,可根据实际需求调整大小
// 获取要输入的单词数量
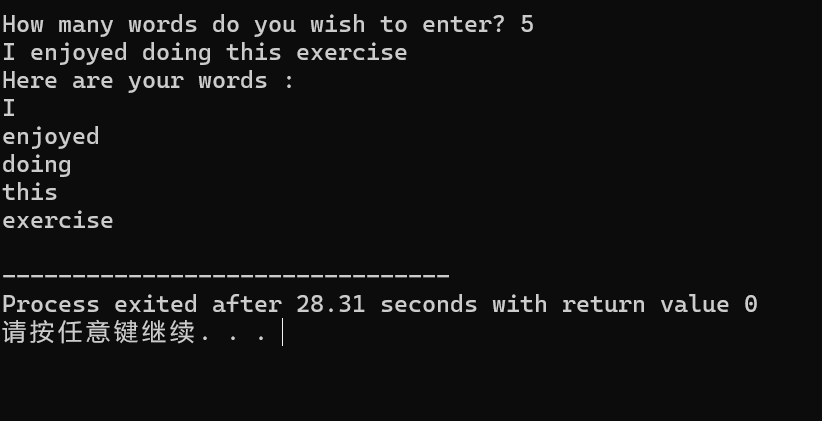
printf("How many words do you wish to enter? ");
scanf("%d", &numWords);
// 动态分配指针数组,存储指向每个单词的指针
char **wordArray = (char **)malloc(numWords * sizeof(char *));//这里是重难点
if (wordArray == NULL) {
printf("内存分配失败!\n");
return;
}
// 循环接收输入的每个单词
for (int i = 0; i < numWords; i++) {
// 读取一个单词到临时数组
scanf("%s", tempWord);
// 根据单词长度动态分配足够的空间来存储该单词
wordArray[i] = (char *)malloc((strlen(tempWord) + 1) * sizeof(char));
if (wordArray[i] == NULL) {
printf("Memory allocation failed.\n");
// 释放已分配的内存(如果之前已经分配了部分)
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
free(wordArray[j]);
}
free(wordArray);
return;
}
// 将单词从临时数组拷贝到动态分配的存储空间
strcpy(wordArray[i], tempWord);
}
// 显示输入的单词
printf("Here are your words :\n");
for (int i = 0; i < numWords; i++) {
printf("%s\n", wordArray[i]);
// 释放每个单词所占用的内存
free(wordArray[i]);
}
// 释放指针数组所占用的内存
free(wordArray);
}
int main() {
handleWords();
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号