Center-based 3D Object Detection and Tracking
Center-based 3D Object Detection and Tracking
Abstract
Three-dimensional objects are commonly represented as 3D boxes in a point-cloud. This representation mimics the well-studied image-based 2D bounding-box detection but comes with additional challenges. Objects in a 3D world do not follow any particular orientation, and box-based detectors have difficulties enumerating all orientations or fitting an axis-aligned bounding box to rotated objects. In this paper, we instead propose to represent, detect, and track 3D objects as points. Our framework, CenterPoint, first detects centers of objects using a keypoint detector and regresses to other attributes, including 3D size, 3D orientation, and velocity. In a second stage, it refines these estimates using additional point features on the object. In CenterPoint, 3D object tracking simplifies to greedy closest-point matching. The resulting detection and tracking algorithm is simple, efficient, and effective. CenterPoint achieved state-of-the-art performance on the nuScenes benchmark for both 3D detection and tracking, with 65.5 NDS and 63.8 AMOTA for a single model. On the Waymo Open Dataset, CenterPoint outperforms all previous single model method by a large margin and ranks first among all Lidar-only submissions. The code and pretrained models are available at https://github.com/tianweiy/CenterPoint.
Comments
- 目前SOTA的方法一般都是center-base anchor-free的
- apollo也更新了centerpoint
Q&A
1.动机 以及 center-base的优势
动机
- anchor-base有很多局限性,很多框和anchor不会贴合很好,借鉴2D的centerNet
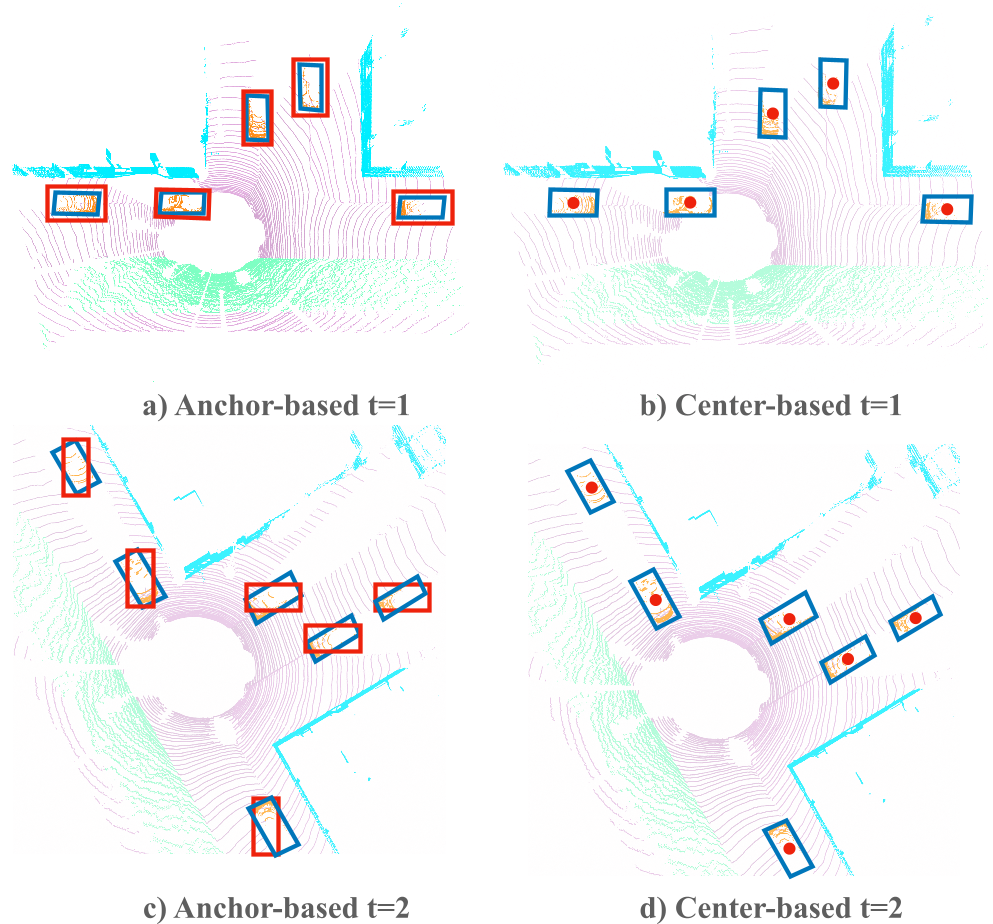
优势
yaw角偏离很多,长宽比很大,大小极端的case会表现更好
2.如何训练?怎样分配正负样本?
-
anchor-based的方法在分配正负样本的时候需要针对不同类别不同数据集,设置不同的IOU阈值
-
heat_map head
-
对于K类的任务,生成一张K通道的heat_map, 在每个object的位置取得局部最大值
-
真值:把标注 3D box 中心位置投影到BEV, 经过2D 高斯滤波 得到真值
-
2D-CenterNet 图像空间中几辆大车就可以把大部分image占据,而且object的中心点一般都很近,且objects之间大部分有IOU,3d-bev几乎很难会出现目标有overlap的情况
-
与2D中的centerNet相比,3D BEV map下的objects非常稀疏,大部分都是背景点,直接使用2D的centerNet中同样的监督方法,监督信号会非常稀疏
-
为了增加正样本的监督,增大了gt中心点的高斯高峰,通过增大2d-gaussian滤波的kernel_size:
-
-
w: 宽 l: 长 目标size越大 滤波半径越大,不如直接在bev-box的基础上做高斯滤波?(BSH-Det3D)[[BSH-Det3D: Improving 3D Object Detection with BEV Shape Heatmap]]
-
使用focal-loss
-
v1版本论文:
-
在每一类的target heatmap中 如果有overlap 取最大值
-
image.png
-
regression head
-
使用object中心点的feature, 4个单独的回归头预测box的不同属性, L1 loss
-
z
-
[l,w,h] 取对数
-
yaw: [sin, cos]
-
[[#red]] yaw损失为什么要取sin cos
-
损失函数?
-
训练第二阶段时
-
从第一阶段随机采样128个框,正负比例1:1
-
与gt iou大于0.55的作为正样本
-
2.二阶段的作用有多少?
-
在第一阶段中,仅仅使用目标中心点的feature做3Dbox 的回归,信息是不足够的
-
在自动驾驶中,lidar往往只能观测到物体的几条边,而不是中心
-
[[Fully Sparse 3D Object Detection]]
-
image.png
-
Two-Stage CenterPoint
-
第一阶段提供:3D box, backbone的输出bev feature map M
-
使用双线性插值从M得到 3D box前后左右4个面中心点以及3D中心处共5个点的feature,拼在一起后输入MLP,预测一个类别无关的置信度得分以及增强的3D box
-
置信度得分
-
真值:
-
-
代表第一阶段预测框和真值之间的IoU
-
score的损失函数 交叉熵:
-
-
infer时:
-
t-th 预测框 的得分构成:使用第一阶段得到的class得分和第二阶段的得分计算几何平均值作为最后的置信度分数:
-
-
box回归
-
在第一阶段的基础上预测一个refinement
-
L1损失
-
二阶段的增益
-
image.png
-
pointpillars提升不多
-
点数很少的nuScenes数据集以及size很小的物体提升不多,可能得原因是点数太少,限制了二阶段的改进
-
IoU-aware
-
image.png
-
得分不是变小了吗??
-
[[AFDetV2: Rethinking the Necessity of the Second Stage for Object Detection from Point Clouds]]
-
[[PillarNeXt: Rethinking Network Designs for 3D Object Detection in LiDAR Point Clouds]]
-
4.可以单独作为一个head使用吗?应用在pointpillars?
-
centerhead可以与大部分3D检测器兼容
-
简单anchor-based 换成 center-based可以带来性能提升
-
image.png
-
image.png
-
5.如何部署?latency怎样?
-
computation_graph.png





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· Manus的开源复刻OpenManus初探
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· C#/.NET/.NET Core技术前沿周刊 | 第 29 期(2025年3.1-3.9)
· 从HTTP原因短语缺失研究HTTP/2和HTTP/3的设计差异