C# 文件操作
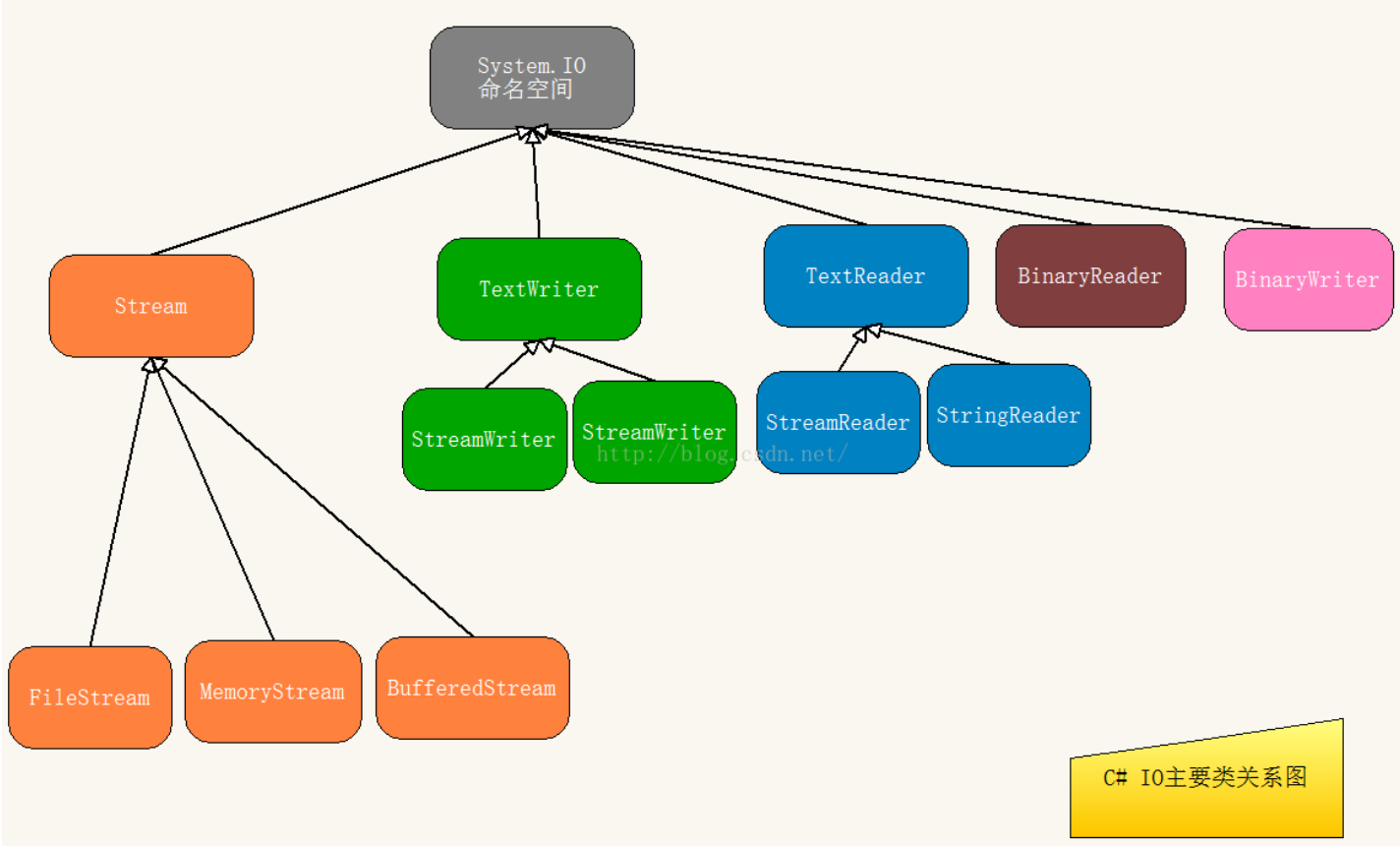
IO基础概念#
IO操作:文件/文件夹操作与读写。
文件夹:用来管理计算机文件的,每一个文件夹对应一块磁盘空间。它提供了指向对应空间的地址,它没有扩展名,也就不像文件的格式用扩展名来标识。
文件:一个具有符号的一组相关联元素的有序序列。文件可以包含范围非常广泛的内容。系统和用户都可以将具有一定独立功能的程序模块、一组数据或一组文字命名为一个文件,它具有永久存储。
流是一个字节序列,可用于对后备存储进行读取和写入操作,后备存储可以是多个存储媒介之一(例如,磁盘或内存)。
Stream 支持读取和写入字节。所有表示流的类都继承自Stream类。
流涉及三个基本操作:
(1)读取– 将数据从流传输到数据结构(如字节数组)中。
(2)写入– 将数据从数据源传输到流。
(3)查找– 对流中的当前位置进行查询和修改。
Path类#
Path类:对包含文件/目录的路径信息的 System.String实例执行操作。
string path = @"E:\Biao\MyProjects\IOTest\1.txt"; // 改变后缀名 string newPath = Path.ChangeExtension(path, "doc"); // 路径拼接 string path1 = @"E:\Biao\MyProjects"; string path2 = @"IOTest\1.txt"; string combinePath = Path.Combine(path1, path2);//path1 + path2; // 获取扩展名 string ext = Path.GetExtension(combinePath); // 获取文件名(带扩展名) string fileName = Path.GetFileName(combinePath); // 获取文件名(不带扩展名) string fileNameNoExtention = Path.GetFileNameWithoutExtension(combinePath); // 获取完整路径 string fullPath = Path.GetFullPath(combinePath); // 是否有扩展名 bool isHasExtension = Path.HasExtension(combinePath);
目录操作 Directory/DirectoryInfo#
Directory:用于通过目录和子目录进行创建、移动、删除、枚举的静态方法。
Directorylnfo: 用于创建、移动、删除、枚举目录和子目录的实例方法。
Directory 操作#
string path = @"E:\Biao\MyProjects\IOTest\mu_1"; string path2 = @"E:\Biao\MyProjects\IOTest\mu_2"; //创建目录、判断目录是否存在 if (!Directory.Exists(path)) { Directory.CreateDirectory(path); } // 删除目录 第二个参数为true的话:可以删除path的子目录;如果为false的话,path必须为空目录才能删除,否则会抛异常 Directory.Delete(path, true); // 移动目录(包括子目录)注意要目标目录要加 目录/文件名 Directory.Move(path, path2 + @"\mu_1"); // 获取子目录、文件 string[] sonDirectories = Directory.GetDirectories(path); string[] sonFiles = Directory.GetFiles(path);
DirectoryInfo 操作#
/// <summary> /// 递归遍历 某个目录下的所有子目录和文件 /// </summary> /// <param name="path"></param> /// <param name="result"></param> private void GetAllDirectoriesAndFiles(string path, List<string> result) { // 创建实例对象 DirectoryInfo directoryInfo = new DirectoryInfo(path); // 获取对象的所有目录和文件 DirectoryInfo[] directories = directoryInfo.GetDirectories(); FileInfo[] files = directoryInfo.GetFiles(); // 把所有文件添加到result这个链表中 result.AddRange(files.Select(f => f.FullName)); // 依次遍历子目录 foreach(DirectoryInfo directory in directories) { // 将该子目录添加到result这个链表中 result.Add(directory.FullName); // 让子目录递归调用此方法(递归重复) GetAllDirectoriesAndFiles(directory.FullName, result); } }
文件操作 File/FileInfo#
File:提供用于创建、复制、删除、移动和打开文件的静态方法,并协助创建FileStream对象。
FileInfo:提供用于创建、复制、删除、移动和打开文件的实例方法,并协助创建FileStream对象。
FileMode 打开文件的方式 Create CreateNew Append Open OpenOrCreate
FileAccess 文件访问权限 Read Write ReadWrite
FileMode 创建、删除、复制、移动、追加文本#
string path = @"E:\Biao\MyProjects\IOTest\1.txt"; string path2 = @"E:\Biao\MyProjects\IOTest\2.txt"; /// 以下将以2种方式实现(File/FileInfo) /// 创建文件 if (!File.Exists(path)) { File.Create(path); //File.Create(path, 1024);//缓冲区大小 //StreamWriter sw= File.CreateText(path); } FileInfo fi = new FileInfo(path); fi.Create(); //StreamWriter sw = fi.CreateText(); /// 删除文件 File.Delete(path); FileInfo fi = new FileInfo(path); fi.Delete(); /// 复制文件 源文件path内容不能为空 File.Copy(path, path2); //File.Copy(path, path2, true);// 遇到同名文件,是否覆盖 FileInfo fi = new FileInfo(path); fi.CopyTo(path2); //fi.CopyTo(path2, true); /// 移动文件 File.Move(path, path2); //File.Move(path, path2,true); FileInfo fi = new FileInfo(path); fi.MoveTo(path2); //fi.MoveTo(path2,true); /// 追加文本 //StreamWriter sw = File.AppendText(path); File.AppendAllText(path, "你好"); //List<string> list = new List<string>(); //list.Add("追加第1行"); //list.Add("追加第2行"); //list.Add("追加第3行"); //File.AppendAllLines(path, list); FileInfo fi = new FileInfo(path); StreamWriter sw = fi.AppendText();
FileAccess 打开、读取、写入#
string path = @"E:\Biao\MyProjects\IOTest\1.txt"; //文件打开、读写 /// 文件打开 File.Open(path, FileMode.Open); //File.Open(path, FileMode.Create); //File.Open(path, FileMode.Create,FileAccess.ReadWrite); //File.OpenRead(path);// 只读 //File.OpenWrite(path);// 只写 //File.OpenText(path);// 打开文本文件 FileInfo fi= new FileInfo(path); fi.Open(FileMode.Open); //fi.Open(FileMode.CreateNew, FileAccess.Read); //fi.OpenWrite(); //fi.OpenRead(); //fi.OpenText(); /// 文件读取 File.ReadAllLines(path); //File.ReadAllText(path); //File.ReadAllBytes(path);//二进制文件 //File.ReadAllText(path);//文本文件 /// 文件写入 string[] strs = new string[10]; File.WriteAllLines(path, strs); //string str = "11111111111"; //File.WriteAllText(path, str); //byte[] bytes=new byte[10]; //File.WriteAllBytes(path,bytes);
流#
Stream介绍#
Stream:提供字节序列的一般视图。这是一个抽象类。它是所有流的抽象基类
提供了以字节的形式从流中读取内容
【字符流】StreamReader和StreamWriter类帮我们实现在流上读写字符流的功能
常用的Stream的子类有:【字节流】
1)MemoryStream 存储在内存中的字节流
2)FileStream 存储在文件系统的字节流
3)BuferedStream 为其他流提供缓冲的流
StreamReader 读取【字符流】#
StreamReader派生于TextReader,以下关于TextReader介绍。

string path = @"E:\Biao\MyProjects\IOTest\1.txt"; /// StreamReader读取 TextReader reader = new StreamReader(path); //StreamReader reader = new StreamReader(path); // 方式1:一行一行读 string s= reader.ReadLine(); while (s != null) { Console.WriteLine(s); s = reader.ReadLine(); } // 方式2:从头到尾 //string s = reader.ReadToEnd(); //Console.WriteLine(s); // 方式3:读取下一个字符,不是读取次字符 reader.Read();// 读完之后,更改到下一个字符位置 reader.Peek();// 读完之后,不更改状态 reader.Close();// 关闭
StreamWriter 写入【字符流】#
StreamWriter派生于TextWriter,以下关于TextWriter介绍。

string path = @"E:\Biao\MyProjects\IOTest\1.txt"; /// StreamWriter写入 TextWriter writer = new StreamWriter(path,true);//追加的方式写入 //TextWriter writer = new StreamWriter(path); writer.Write(writer.NewLine);//新行 writer.WriteLine("追加第一句话!"); writer.Write("追加第二句话!"); writer.WriteLine(33333); writer.Flush();//如果不加这句,writer写入的内容将在Close()之后写进文件;加上这句,将在执行这句话后,直接写入了文件。 writer.WriteLine("追加第4句话"); writer.Close(); writer.Dispose();//释放
FileStream 【字节流】#
FileStream介绍#
FileStream对文件系统中的文件进行读取、写入、打开和关闭,使用Read、Write、CopyTo和 Flush方法来执行同步操作,或使用ReadAsync、WriteAsync、CopyToAsync和l FlushAsync方法执行异步操作。
使用异步方法来执行占用大量资源的文件操作,而不会阻止主线程。
构造函数:
FileStream(String,FileMode): FileStream(String,FileMode,FileAccess) FileStream(String, FileMode, FileAccess, FileShare) FileStream(String, FileMode, FileAccess,FileShare, Int32)
第一个参数是文件路径;第二个参数是文件模式,表示以何种方式打开或创建文件;
第三个是文件的访问方式;第四个:文件的共享方式;第五个:缓冲区大小
FileStream使用#
同步
string path = @"E:\Biao\MyProjects\IOTest\1.txt"; string path2 = @"E:\Biao\MyProjects\IOTest\2.txt"; byte[] data=new byte[1024]; using (FileStream fr=new FileStream(path, FileMode.OpenOrCreate,FileAccess.Read)) { using(FileStream fw=new FileStream(path2, FileMode.OpenOrCreate, FileAccess.Write)) { int count = 0; do { count=fr.Read(data, 0, data.Length); fw.Write(data, 0, count); }while(count!=0); } }
异步【对比同步】
private async void button6_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { string path = @"E:\Biao\MyProjects\IOTest\1.txt"; string path2 = @"E:\Biao\MyProjects\IOTest\2.txt"; // 异步复制 await FileStreamCopyFileAsync(path, path2); } private async Task FileStreamCopyFileAsync(string sourcePath,string targetPath) { byte[] data = new byte[1024]; using (FileStream fr = new FileStream(sourcePath, FileMode.OpenOrCreate, FileAccess.Read)) { using (FileStream fw = new FileStream(targetPath, FileMode.OpenOrCreate, FileAccess.Write)) { int count = 0; do { count = await fr.ReadAsync(data, 0, data.Length); fw.Write(data, 0, count); } while (count != 0); } } }
MemoryStream 内存流【字节流】#
MemoryStream介绍#
MemoryStream 创建一个流,其后备存储为内存。
内存流 数据以无符号字节数组的形式保存在内存中,系统可以直接访问这些封装的数据而不必读取磁盘文件。更加贴近底层数据,读取的效率更高(读取速度更快,和文件流的主要区别),内存流可以降低系统对临时缓冲区和临时文件的需要。
因此我们编程中常常用内存流作为中转,与其他流进行数据交换。(如利用MemoryStream操作文件,然后传给FileStream中)
内存流到文件流的转换:将数据写入内存流,再转给文件流,再写入文件
MemoryStream使用#
private void button7_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { //中转应用 string path = @"E:\Biao\MyProjects\IOTest\1.txt"; string path2 = @"E:\Biao\MyProjects\IOTest\2.txt"; byte[] data = new byte[1024]; // 开启一个内存流ms MemoryStream ms= new MemoryStream(); // 将fr从文件读取的缓存流写入到ms的内存流中 using(FileStream fr=new FileStream(path,FileMode.OpenOrCreate, FileAccess.Read)) { int count = 0; do { count = fr.Read(data, 0, data.Length); ms.Write(data, 0, count); }while (count != 0); } // 将ms中的内存流写入到fw的缓存流中 using (FileStream fw = new FileStream(path2, FileMode.OpenOrCreate, FileAccess.Write)) { ms.WriteTo(fw); } // ms关闭、释放 ms.Close(); ms.Dispose(); }
BufferedStream 缓冲流 [字节流]#
BufferedStream介绍#
缓冲流,给另一个流添加一个缓冲区,以进行读写操作。
BufferedStream比StreamReader和StreamWriter的效率更高,特别是对于大文件,对于txt文件StreamReader和StreamWriter来讲可以以一行一行的方式进行操作,但是对于其他类型的文件这种方式就显得无能为力了,
此时使用BufferedStream可以方便的实现,同样对于可以有一行一行进行操作的文件类型,使用BufferedStream也有更高的效率。
缓冲区是内存中用于缓存数据的字节块,缓冲数据能够减少对操作系统的调用次数,缓冲数据主要存储在缓冲区中。
缓冲区提高读写性能。
缓冲区可用于读取或写入,但不能同时使用这两种方法。
BufferedStream 用于在不需要缓冲区时防止缓冲区降低输入和输出速度。
BufferedStream使用#
private void button8_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { string path = @"E:\Biao\MyProjects\IOTest\1.txt"; string path2 = @"E:\Biao\MyProjects\IOTest\2.txt"; byte[] data = new byte[1024]; FileStream fr = new FileStream(path, FileMode.OpenOrCreate, FileAccess.Read); FileStream fw = new FileStream(path2, FileMode.OpenOrCreate, FileAccess.Write); using(BufferedStream br = new BufferedStream(fr, 1024)) { using(BufferedStream bw = new BufferedStream(fw, 1024)) { int count = 0; do { count = fr.Read(data, 0, data.Length); bw.Write(data, 0, count); } while (count != 0); } } }
BinaryReader与BinaryWriter 二进制文件的读写#
BinaryReader与BinaryWriter介绍#
BinaryReader与BinaryWriter使用#
private void button9_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { string path = @"E:\Biao\MyProjects\IOTest\1.txt"; string path2 = @"E:\Biao\MyProjects\IOTest\2.txt"; FileStream fr = new FileStream(path, FileMode.OpenOrCreate, FileAccess.Read); BinaryReader br = new BinaryReader(fr); FileStream fw = new FileStream(path2, FileMode.OpenOrCreate, FileAccess.Write); BinaryWriter bw = new BinaryWriter(fw); byte[] data = new byte[1024 * 1024]; int count = 0; do { count = br.Read(data, 0, data.Length); bw.Write(data, 0, count); } while (count != 0); br.Close(); bw.Close(); }





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 开源Multi-agent AI智能体框架aevatar.ai,欢迎大家贡献代码
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY