go实例之排序
1、默认排序
使用sort包进行排序。排序是就地排序,因此它会更改给定的切片,并且不返回新的切片。
1 package main 2 3 import "fmt" 4 import "sort" 5 6 func main() { 7 8 // Sort methods are specific to the builtin type; 9 // here's an example for strings. Note that sorting is 10 // in-place, so it changes the given slice and doesn't 11 // return a new one. 12 strs := []string{"c", "a", "b"} 13 sort.Strings(strs) 14 fmt.Println("Strings:", strs) 15 16 // An example of sorting `int`s. 17 ints := []int{7, 2, 4} 18 sort.Ints(ints) 19 fmt.Println("Ints: ", ints) 20 21 // We can also use `sort` to check if a slice is 22 // already in sorted order. 23 s := sort.IntsAreSorted(ints) 24 fmt.Println("Sorted: ", s) 25 }
执行上面代码,将得到以下输出结果
1 Strings: [a b c] 2 Ints: [2 4 7] 3 Sorted: true
从上述代码可知,排序不同类型切片,调用不同接口,排序时直接对参数进行修改,排序接口不对排序后切片进行返回。
2、自定义排序
自定义排序需要我们声明一个相应类型,并实现sort.Interface-Len,Less,Swap在这个类型上,Less接口是正真的排序方法,Swap用于交换两个值,Len用于求出切片大小。如下示例代码,首先将原始 fruits 切片转换为ByLength来实现自定义排序,然后对该类型切片使用sort.Sort()方法。
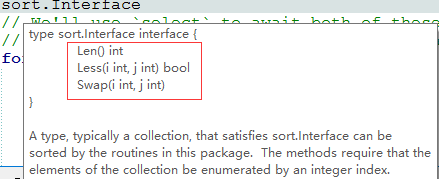
图1 sort.Interface定义
其实自定义排序就是对接口的使用。针对ByLength结构重写了sort.Interface接口的方法。如图1所示,是在LiteIDE中sort.Interface的提示
1 package main 2 3 import "sort" 4 import "fmt" 5 6 // In order to sort by a custom function in Go, we need a 7 // corresponding type. Here we've created a `ByLength` 8 // type that is just an alias for the builtin `[]string` 9 // type. 10 type ByLength []string 11 12 // We implement `sort.Interface` - `Len`, `Less`, and 13 // `Swap` - on our type so we can use the `sort` package's 14 // generic `Sort` function. `Len` and `Swap` 15 // will usually be similar across types and `Less` will 16 // hold the actual custom sorting logic. In our case we 17 // want to sort in order of increasing string length, so 18 // we use `len(s[i])` and `len(s[j])` here. 19 func (s ByLength) Len() int { 20 return len(s) 21 } 22 func (s ByLength) Swap(i, j int) { 23 s[i], s[j] = s[j], s[i] 24 } 25 func (s ByLength) Less(i, j int) bool { 26 return len(s[i]) < len(s[j]) 27 } 28 29 // With all of this in place, we can now implement our 30 // custom sort by casting the original `fruits` slice to 31 // `ByLength`, and then use `sort.Sort` on that typed 32 // slice. 33 func main() { 34 fruits := []string{"peach", "banana", "kiwi"} 35 sort.Sort(ByLength(fruits)) 36 fmt.Println(fruits) 37 }
执行上面代码,将得到以下输出结果
1 [kiwi peach banana]


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号