Spring Security 随记
基本功能(认证+授权)
https://blog.csdn.net/Lammonpeter/article/details/79611439
https://www.bilibili.com/video/av40943281
核心过滤器链
https://blog.csdn.net/dushiwodecuo/article/details/78913113

l流程 :SecurityContext装配<——>认证登录< ——>异常<——>鉴权<——>Mvc(dispatchServlet)
图中为过滤器链流程中的一些核心过滤器,请求线程chain.doFilter()方法向下调用过滤器。整个过程是同一个线程的方法栈,后进先出。图中请求线是进栈,响应线是出栈。
第一个橙色的过滤器是请求进入时根据SessionID检查Session(本地/分布式redis等)中是否已存在SecurityContext,若存在则放入SecurityContextHolder中作为线程变量。响应返回退出时,他是最后一道通过,会清除SecurityContextHolder,将SecurityContext放到Session中。保证不同请求线程能根据SessionID从Session中取得对应用户的SecurityContext。
其中绿色为认证过滤器。第一个绿色为不同认证功能对应的不同过滤器(根据不同的登录方式选择不同的过滤器),最后一个绿色是所有请求都会经过的匿名过滤器。
匿名过滤器最后检查SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication()==null,若是真则当前线程在前面的认证过滤器没有从持久层或是sesson中得到用户信息,匿名过滤器会统一为当前线程添加一个匿名Authentication到SecurityContextHolder。
最后一个FilterSecurityInterceptor,是所有请求都会经过的最后一个鉴权过滤器,他是鉴权的核心实现。通过它就会访问到controller,不通过会抛出异常给蓝色的异常过滤器处理。
因为链上的都是过滤器,所以Security在dispatchServlet之前执行。既在拦截器+AOP之前。
SecurityContextHolder
通过SecurityContextHolder取得当前线程对应用户的信息。
方法一:SecurityContextHolder
Authentication authentication = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
User principal =
(org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User) authentication.getPrincipal();
return principal.getUsername();方法二:Spring自动注入
@RequestMapping("/url")
public String echo2(Authentication authentication) {
}
@RequestMapping("/url2")
public String echo(@AuthenticationPrincipal UserDetails user) {
}用户是通过用户名密码的方式登陆的,所以Authentication是UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken类型
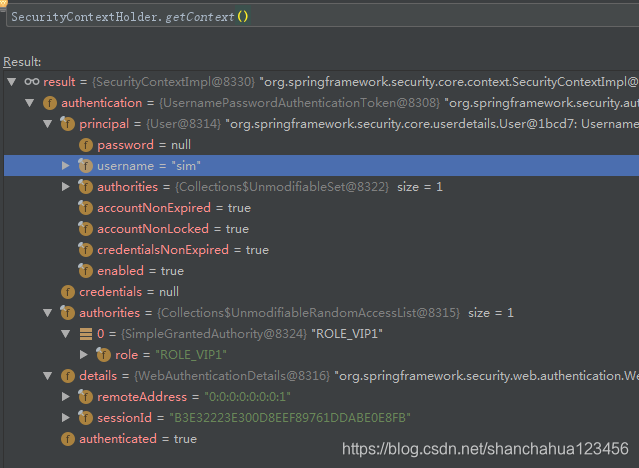
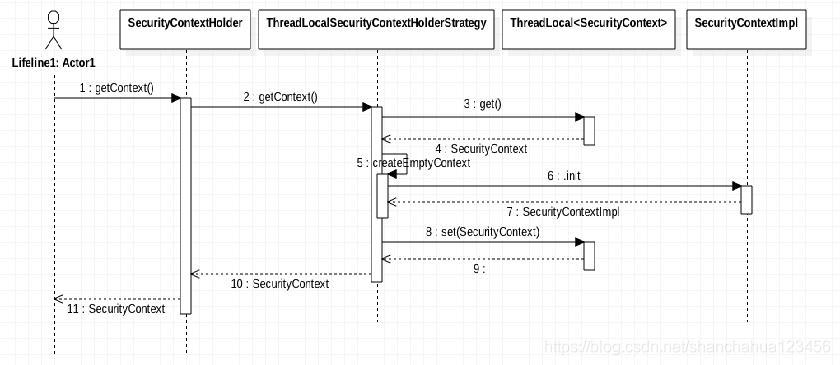
认证流程
验证登录信息,创建用户Authentication,放入SecurityContextHolder,最终将SecurityContext存入Session中。
之后请求直接从Session中取出SecurityContext。
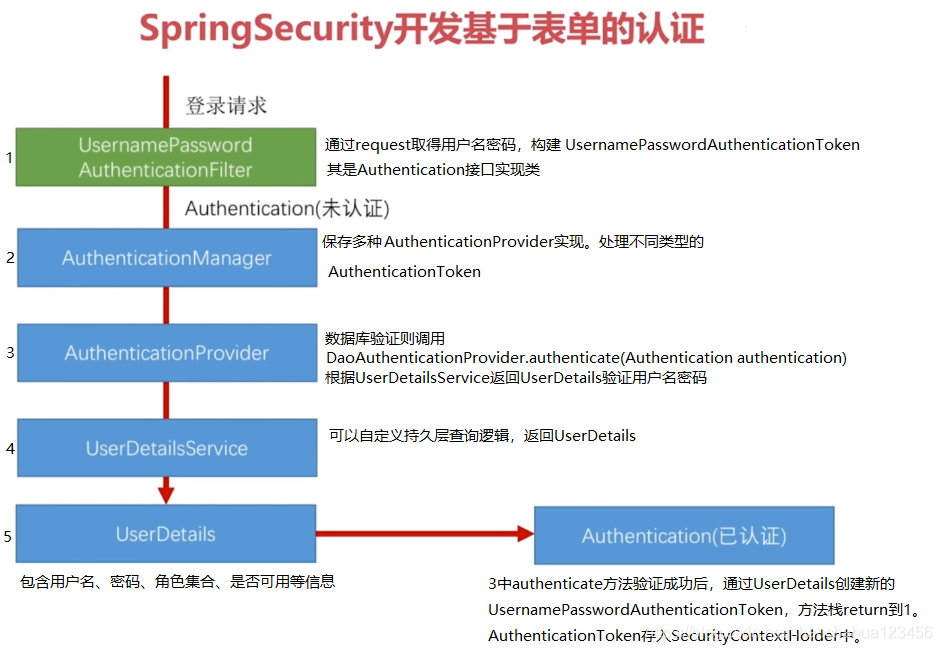
FilterSecurityInterceptor鉴权过滤器
用户权限信息+URL权限信息+决策器实现 鉴权工作
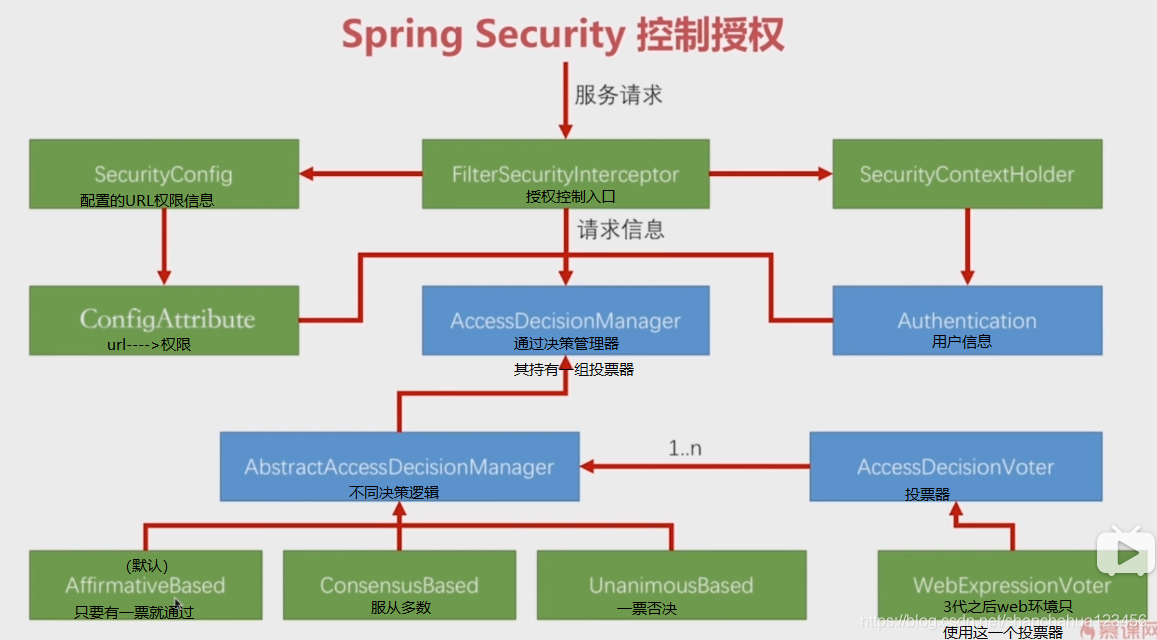
FilterSecurityInterceptor中核心验证方法
public void invoke(FilterInvocation fi) throws IOException, ServletException {
if ((fi.getRequest() != null)
&& (fi.getRequest().getAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED) != null)
&& observeOncePerRequest) {
//通过Request中的属性,判断是否已经经过此过滤器,是则放行
fi.getChain().doFilter(fi.getRequest(), fi.getResponse());
}
else {
//首次进入 在Request添加属性
if (fi.getRequest() != null && observeOncePerRequest) {
fi.getRequest().setAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED, Boolean.TRUE);
}
//beforeInvocation鉴权 若鉴权失败 抛异常
InterceptorStatusToken token = super.beforeInvocation(fi);
try {
fi.getChain().doFilter(fi.getRequest(), fi.getResponse());
}
finally {
super.finallyInvocation(token);
}
super.afterInvocation(token, null);
}
}beforeInvocation方法是鉴权的核心(URL权限缓存+决策器+用户信息)
其通过securityMetadataSource.getAttributes()读取url对应的权限,将(用户信息+ request+url权限)传入 accessDecisionManager.decide(authenticated, object, attributes)方法进行决策。
protected InterceptorStatusToken beforeInvocation(Object object) {
Assert.notNull(object, "Object was null");
final boolean debug = logger.isDebugEnabled();
if (!getSecureObjectClass().isAssignableFrom(object.getClass())) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Security invocation attempted for object "
+ object.getClass().getName()
+ " but AbstractSecurityInterceptor only configured to support secure objects of type: "
+ getSecureObjectClass());
}
//SecurityMetadataSource取得URL对应权限
Collection<ConfigAttribute> attributes = this.obtainSecurityMetadataSource()
.getAttributes(object);
if (attributes == null || attributes.isEmpty()) {
if (rejectPublicInvocations) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Secure object invocation "
+ object
+ " was denied as public invocations are not allowed via this interceptor. "
+ "This indicates a configuration error because the "
+ "rejectPublicInvocations property is set to 'true'");
}
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Public object - authentication not attempted");
}
publishEvent(new PublicInvocationEvent(object));
return null; // no further work post-invocation
}
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Secure object: " + object + "; Attributes: " + attributes);
}
if (SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication() == null) {
credentialsNotFound(messages.getMessage(
"AbstractSecurityInterceptor.authenticationNotFound",
"An Authentication object was not found in the SecurityContext"),
object, attributes);
}
Authentication authenticated = authenticateIfRequired();
// Attempt authorization
try {
//accessDecisionManager决策器通过(用户信息+ request+url权限)鉴权
this.accessDecisionManager.decide(authenticated, object, attributes);
}
catch (AccessDeniedException accessDeniedException) {
publishEvent(new AuthorizationFailureEvent(object, attributes, authenticated,
accessDeniedException));
throw accessDeniedException;
}
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Authorization successful");
}
if (publishAuthorizationSuccess) {
publishEvent(new AuthorizedEvent(object, attributes, authenticated));
}
// Attempt to run as a different user
Authentication runAs = this.runAsManager.buildRunAs(authenticated, object,
attributes);
if (runAs == null) {
if (debug) {
logger.debug("RunAsManager did not change Authentication object");
}
// no further work post-invocation
return new InterceptorStatusToken(SecurityContextHolder.getContext(), false,
attributes, object);
}
else {
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Switching to RunAs Authentication: " + runAs);
}
SecurityContext origCtx = SecurityContextHolder.getContext();
SecurityContextHolder.setContext(SecurityContextHolder.createEmptyContext());
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(runAs);
// need to revert to token.Authenticated post-invocation
return new InterceptorStatusToken(origCtx, true, attributes, object);
}
}Spring Security 动态加载URL权限
自定义FilterSecurityInterceptor(鉴权过滤器):继承AbstractSecurityInterceptor,使用自定义的securityMetadataSource+accessDecisionManager。调用super.beforeInvocation进行鉴权。
自定义securityMetadataSource(URL权限缓存):实现FilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource接口,
自定义数据结构保存URL权限SecurityConfig,覆盖实现getAttributes()读取url对应的权限,为决策器提供URL权限。
自定义accessDecisionManager(决策器):实现AccessDecisionManager接口,实现decide(authenticated, object, attributes)方法通过(用户信息+ request+url权限)进行匹配决策。
https://blog.csdn.net/shanchahua123456/article/details/88949064
简单用例
SpringSecurity动态修改用户权限
每个用户都有自己的Authentication,其保存在SecurityContextHolder中。Authentication是通过SpringSecurity的UserDetial实现填充信息。
@GetMapping("/vip/test")
@Secured("ROLE_VIP") // 需要ROLE_VIP权限可访问
public String vipPath() {
return "仅 ROLE_VIP 可看";
}
@GetMapping("/vip")
public boolean updateToVIP() {
// 得到当前的认证信息
Authentication auth = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
// 生成当前的所有授权
List<GrantedAuthority> updatedAuthorities = new ArrayList<>(auth.getAuthorities());
// 添加 ROLE_VIP 授权
updatedAuthorities.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("ROLE_VIP"));
// 生成新的认证信息
Authentication newAuth = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(auth.getPrincipal(), auth.getCredentials(), updatedAuthorities);
// 重置认证信息
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(newAuth);
return true;
}假设当前你的权限只有 ROLE_USER。那么按照上面的代码:
1、直接访问 /vip/test 路径将会得到403的Response;
2、访问 /vip 获取 ROLE_VIP 授权,再访问 /vip/test 即可得到正确的Response。
转自http://www.spring4all.com/article/155
OncePerRequestFilter 与 GenericFilterBean
OncePerRequestFilter: https://blog.csdn.net/f641385712/article/details/87793736
自定义Security过滤器
HttpSessionRequestCache
配置细化
授权表达式放在antMatchers(URL)之后
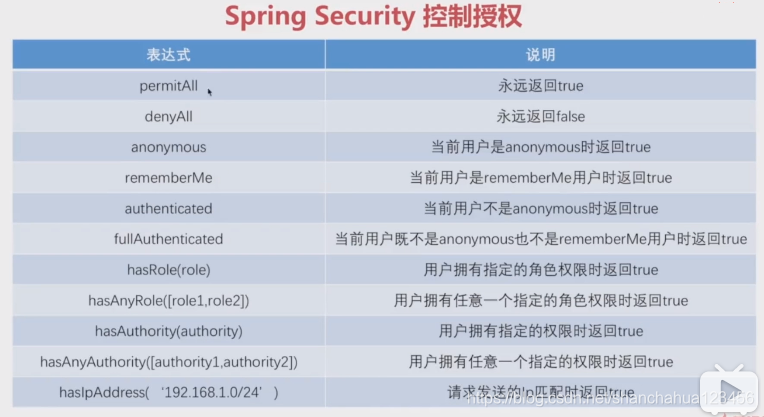
1 对GET请求,URL="/user/{id}"权限拦截
authorizeRequests().antMatchers(HttpMethod.GET,"/user/*").hasRole("ADMIN")2 通过hasRole方法底层源码可以看到最终拼接的权限表达式是"hasRole('ROLE_ADMIN')"。所以用户权限对应的是ROLE_ADMIN。
private static String hasRole(String role) {
Assert.notNull(role, "role cannot be null");
if (role.startsWith("ROLE_")) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("role should not start with 'ROLE_' since it is automatically inserted. Got '" + role + "'");
} else {
return "hasRole('ROLE_" + role + "')";
}
}3 hasAuthority()与hasRole()不同,其实完全匹配,hasRole是自动加ROLE。
比如:
hasAuthority("read") 用户需要"read"权限
hasRole("read") 用户需要"ROLE_read"权限
4 符合配置
authorizeRequests().antMatchers("/user/*").access("hasRole('ADMIN) and hasAuthority('read') ") spring session redis+security 相同用户单个session的解决方案
https://www.e-learn.cn/index.php/content/redis/730910
在springsecurity配置中,注册spring session redis 的sessionregistry。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号