自顶向下学习RTOS第1讲-RTOS任务切换
1 RTOS任务切换
任务切换: 就是从任务A切换到任务B,涉及以下几个问题:
- 选择切换到哪个任务?(which) ----> 调度策略问题
- 什么时候调度? (when) ----> 被动调度(如时间片)还是主动调度
- 调度时候要做什么? (how)----> 现场的保留与恢复
本篇主要关注现场的保留与恢复。
现场 = PC指针(包括寄存器组) + 独立栈
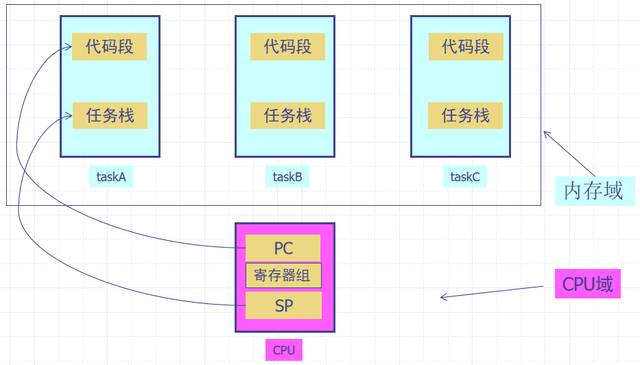
如下图所示,是RTOS多任务切换示意图。图中是内存中有3个任务块:taskA,taskB,taskC 以及CPU寄存器组。
PC指针指向哪个代码段,哪个任务就开始执行。
如:当PC指针指向taskA时,则taskA运行,当PC指针指向taskB时taskB任务开始运行。
但是为了保证task切换出去又能切换回来,则需要保留当前运行环境。
当前运行环境保留在SP指向的任务栈中。
所以:任务的切换指的是CPU指针的切换,需要考虑上下文的保留与恢复问题,上下文保留在任务栈中。
2 ARM Cotrex-M3系列任务切换
ARM Cotrex-M3平台上,任务切换都是基于触发PendSV异常进入中断,然后在中断处理函数中实现任务切换。这部分许多文章都提及到了。详细情况可参考《UCOS-II在CORTEXT-M3(STM32)上的任务切换示意》一文。
使用PendSV异常的优点:
- 设置PendSV异常,通过进入中断自动保存一部分寄存器,可以加快上下文切换速度;
- 将PendSV中断优先级置为最低,可以优先执行优先级较高的中断处理。
但是,从学习的角度看,可以绕过PendSV异常,直接蛮干的切换任务。
如下一个150行左右的代码,构造了5个任务组成循环链表结构,通过主动释放CPU,依次轮询调度。
(裁剪了许多东西,如任务只保留ip与sp,保留现场只保留ip与sp,其中ip保存到堆栈里,sp保留到全局变量里,这样做是不完备的,最好保存整个寄存器组)。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
//================ debug uart config =====================//
#define ITM_PORT8(n) (*(volatile unsigned char *)(0xe0000000 + 4*(n)))
#define ITM_PORT16(n) (*(volatile unsigned short *)(0xe0000000 + 4*(n)))
#define ITM_PORT32(n) (*(volatile unsigned long *)(0xe0000000 + 4*(n)))
#define DEMCR (*(volatile unsigned long *)(0xE000EDFC))
#define TRCENA 0X01000000
int fputc(int ch, FILE *f)
{
if(DEMCR & TRCENA) {
while(ITM_PORT32(0) == 0);
ITM_PORT8(0) = ch;
}
return ch;
}
//========================================================//
#define STACK_SIZE 1024
#define MAX_TASK_NUM 5
struct Thread {
unsigned long ip;
unsigned int *sp;
};
typedef struct PCB {
struct Thread thread;
int pid;
volatile long state; /* -1 idle, 0 runnable */
unsigned int stack[STACK_SIZE];
struct PCB *next;
} tPCB;
tPCB task[MAX_TASK_NUM];
tPCB *current_task = NULL;
tPCB *next_task = NULL;
void tTaskRunFirst(void);
void tTaskSwitch(void);
void tTask_schedule(void);
void my_process(void)
{
int i = 0;
while (1) {
i++;
if (i % 100 == 0) {
printf("this is process %d - \r\n", current_task->pid);
tTask_schedule();
printf("this is process %d + \r\n", current_task->pid);
}
}
}
void StackInit (tPCB * task, void (*entry)(void), unsigned int ** stack)
{
(*stack)--;
**stack = (unsigned long)entry; // the entry
}
void tTaskInit(int task_num)
{
int i = 0;
task[i].pid = i;
task[i].state = 0;
task[i].thread.ip = (unsigned long)my_process;
task[i].thread.sp = &task[i].stack[STACK_SIZE - 1];
task[i].next = &task[i];
StackInit(&task[i], my_process, &(task[i].thread.sp));
for (i = 1; i < task_num; i++) {
task[i].pid = i;
task[i].state = 0;
task[i].thread.ip = (unsigned long)my_process;
task[i].thread.sp = &task[i].stack[STACK_SIZE - 1];
task[i].next = task[i - 1].next;
task[i - 1].next = &task[i];
StackInit(&task[i], my_process, &(task[i].thread.sp));
}
}
int main(void)
{
printf("Init tasks\r\n");
tTaskInit(MAX_TASK_NUM);
/* run the first task */
current_task = &task[0];
tTaskRunFirst();
}
void tTask_schedule(void)
{
if (current_task == NULL ||
current_task->next == NULL) {
return;
}
printf("enter task schedule ->\r\n");
next_task = current_task->next;
if (next_task->state == 0) {
/* switch to next process */
tTaskSwitch();
}
}
__asm void tTaskRunFirst(void)
{
IMPORT current_task
/* R0 = current_task->thread.ip */
LDR R0, =current_task
LDR R0, [R0]
LDR R0, [R0, #4]
/* POP */
LDMIA R0!,{R14};
/* refresh current_task->thread.ip */
LDR R1, =current_task
LDR R1, [R1]
STR R0, [R1, #4]
BX R14
}
__asm void tTaskSwitch(void)
{
IMPORT current_task
IMPORT next_task
/* R0 = current_task->thread.ip */
LDR R0, =current_task
LDR R0, [R0]
LDR R0, [R0, #4]
/* PUSH */
STMDB R0!, {R14};
/* refresh current_task->thread.ip */
LDR R1, =current_task
LDR R1, [R1]
STR R0, [R1, #4]
/* current_task = next_task; */
LDR R0, =current_task
LDR R1, =next_task
LDR R1, [R1]
STR R1, [R0]
/* R0 = next_task->thread.ip */
LDR R0, =next_task
LDR R0, [R0]
LDR R0, [R0, #4]
/* POP */
LDMIA R0!,{R14};
/* refresh next_task->thread.ip */
LDR R1, =next_task
LDR R1, [R1]
STR R0, [R1, #4]
BX R14
}
运行环境:MDK5 Sim环境
运行结果:
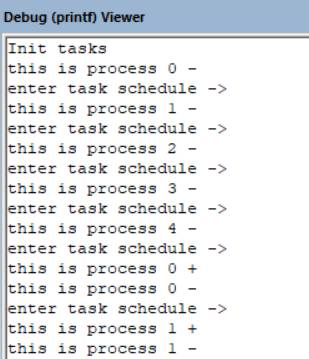
上述代码能正常运行,表示我们对任务切换的理解方大体不差(这么做当然还有其它问题,比如怎么写成时间片轮询的模式?需要考虑更多问题)。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号