Day058--django--app
1. 完整的登录示例
form表单使用的注意事项:
1. action="" method="post" action 提交的地址 method 请求的方式
2. input标签要有name属性
3. 有一个input的类型是sumbit 或者 button按钮
注释掉settings.py中的MIDDLEWARE中的'django.middleware.csrf.CsrfViewMiddleware'
就可以提交post请求, 否则出现403拒绝访问
GET和POST的区别:
1. GET 获取一个页面
login/?user=alex&pwd=alexdsb
在Django中获取数据
request.GET {}
request.GET['user']
request.GET.get('user')
2. POST 提交数据
数据不可见 请求体中
在Django中获取数据
request.POST {}
request.POST['user']
request.POST.get('user')
form表单使用的注意事项:
1. action="" method="post" action 提交的地址 method 请求的方式
2. input标签要有name属性
3. 有一个input的类型是sumbit 或者 button按钮
注释掉settings.py中的MIDDLEWARE中的'django.middleware.csrf.CsrfViewMiddleware'
就可以提交post请求, 否则出现403拒绝访问
GET和POST的区别:
1. GET 获取一个页面
login/?user=alex&pwd=alexdsb
在Django中获取数据
request.GET {}
request.GET['user']
request.GET.get('user')
2. POST 提交数据
数据不可见 请求体中
在Django中获取数据
request.POST {}
request.POST['user']
request.POST.get('user')
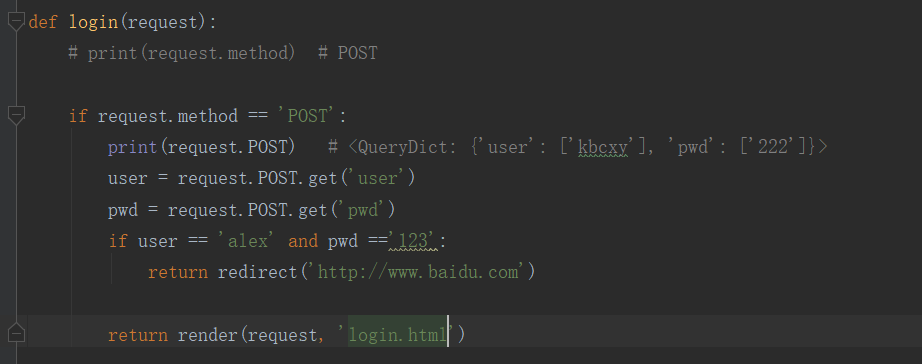
HttpResponse
render
redirect
重定向:
redirect('http://www.baidu.com' )
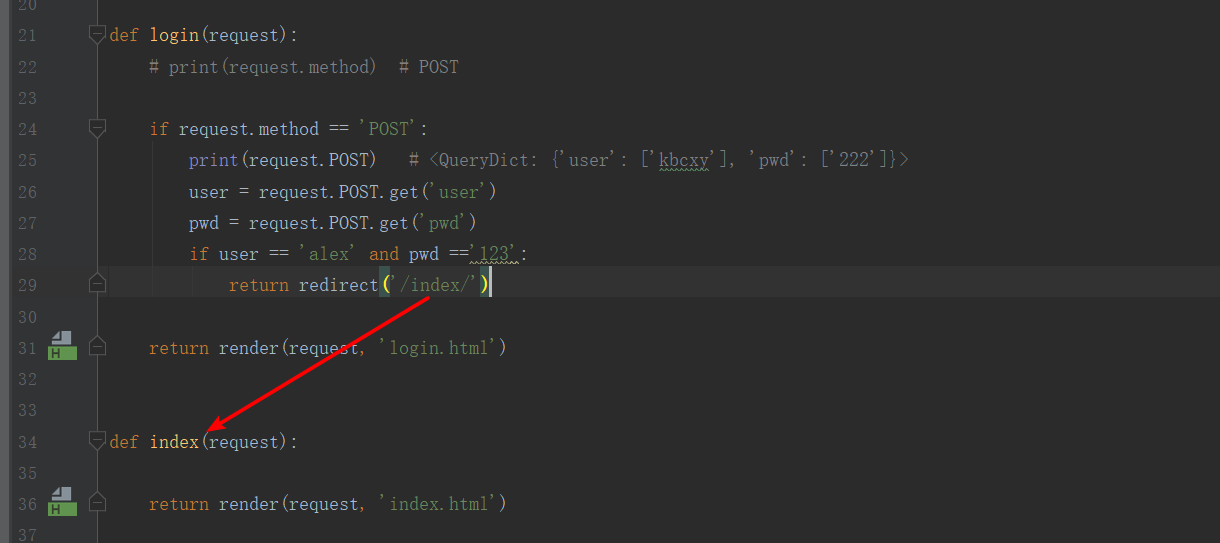
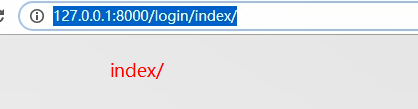
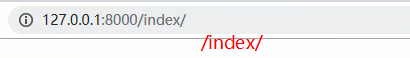
如果/index/ 的前面没有加/ ,则url叠加, /代表根 返回location的响应头

2. APP
项目 老男孩
APP python学院 linux学院
创建APP
1. 命令行:
python manage.py startapp app名称
2. pycharm
tools run manage.py task
startapp app名称

注册app
INSTALLED_APPS 列表中添加
'app01',
'app01.apps.App01Config' # 推荐写法
把函数都写在app中的views中
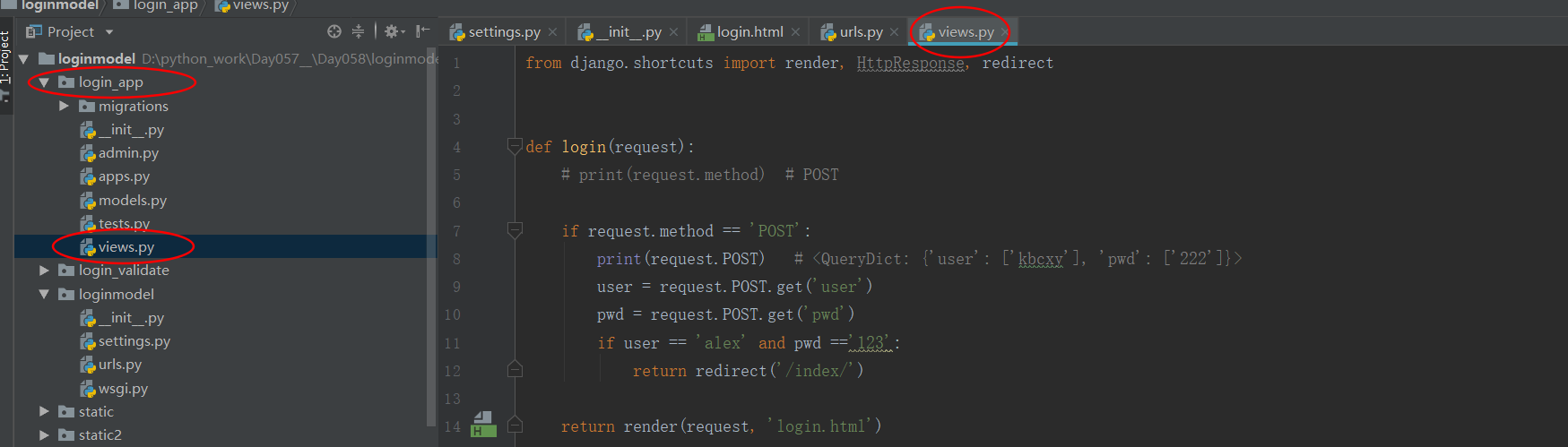
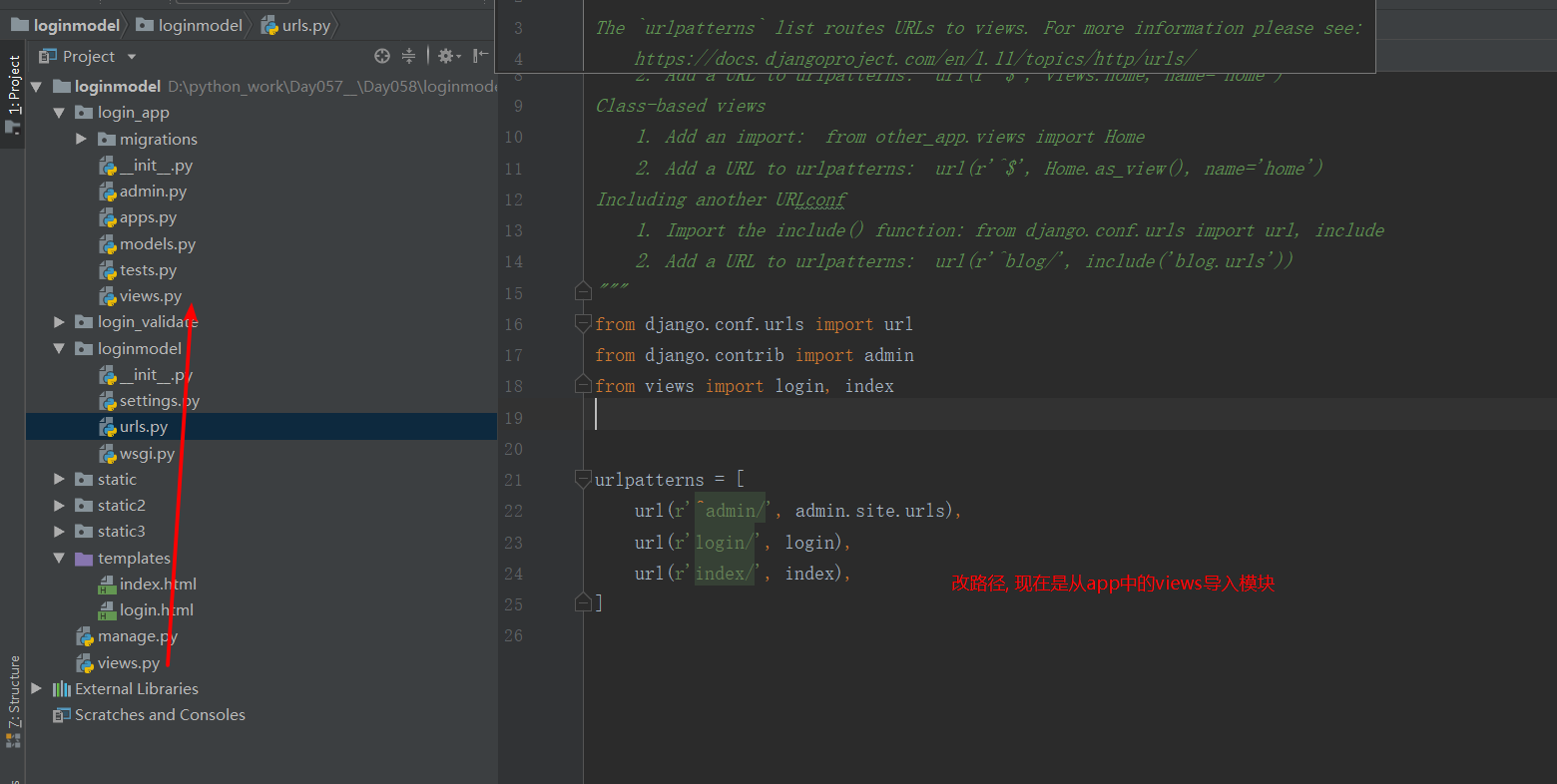

删除app
''' You need to remove or check the following: 1. Remove the app from INSTALLED_APPS. 2. Remove any database tables for the models in that app (see app_name_model_name in your database). 3. Check for any imports in other apps (it could be that they're importing code from that app). 4. Check templates if they are using any template tags of that app (which would produce errors if that app is no longer there). 5. Check your settings file to see if you're not using any code from that app (such as a context processor in your_app/context_processors.py, if it has such as file). 6. Check if any static content of the app is used in other apps. 7. Remove the app directory entirely. When you've been following proper coding principles (i.e., each Django app is a self-contained part of the web application) then most situations above won't occur.
But when other apps do use some parts of that app, you need to check that first as it may require refactoring before deleting the app.
This answer refers to https://stackoverflow.com/questions/11382734/how-to-delete-an-app-from-a-django-project. '''
3. ORM介绍和使用 Object Relational Mapping 对象关系映射
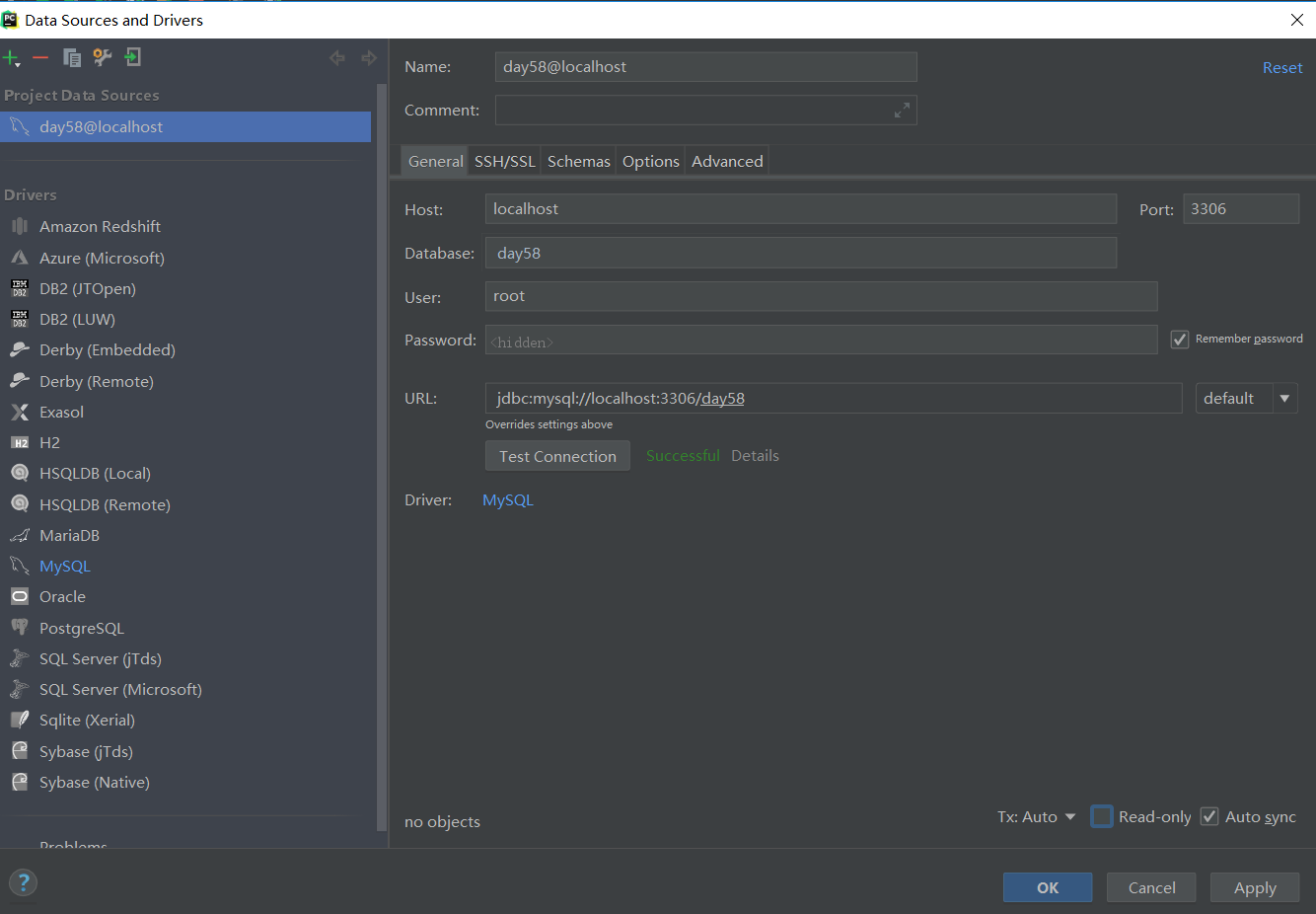
1. 使用mysql数据的步骤:
1. 创建mysql数据库
2. 在settings.py 中配置
DATABASES = {
'default': {
'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.mysql',
'NAME': 'day58',
'HOST': '127.0.0.1',
'PORT': 3306,
'USER': 'root',
'PASSWORD': '',
}
}
3. 告诉Django使用pymysql模块连接mysql数据库
在与settings.py同级目录下的__init__.py中写代码:
import pymysql
pymysql.install_as_MySQLdb()
4. 在models.py中写类(models.Model):
class User(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=32)
pwd = models.CharField(max_length=32)
}
3. 告诉Django使用pymysql模块连接mysql数据库
在与settings.py同级目录下的__init__.py中写代码:
import pymysql
pymysql.install_as_MySQLdb()
4. 在models.py中写类(models.Model):
class User(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=32)
pwd = models.CharField(max_length=32)
# def __str__(self):
# return self.name
5. 执行数据量迁移的命令行:
python manage.py makemigrations # 把models.py的变更记录记录下来
python manage.py migrate # 把变更记录的操作同步到数据库中
5. 执行数据量迁移的命令行:
python manage.py makemigrations # 把models.py的变更记录记录下来
python manage.py migrate # 把变更记录的操作同步到数据库中
如果tools-run manage.py task 直接输入 makemigrations -> migrate

2. ORM的操作:
1. all 获取所有数据
models.User.objects.all() ——》 对象列表
2. get 获取某一条数据(没有或者是多个的时候报错)
models.User.objects.get(name='alex') ——》 对象
3. filter 获取满足条件的所有的对象
models.User.objects.filter(name='alex',pwd='1') ——》 对象列表
4. obj.name name字段的值
obj.pwd pwd字段的值
obj.id obj.pk

2. ORM的操作:
1. all 获取所有数据
models.User.objects.all() ——》 对象列表
2. get 获取某一条数据(没有或者是多个的时候报错)
models.User.objects.get(name='alex') ——》 对象
3. filter 获取满足条件的所有的对象
models.User.objects.filter(name='alex',pwd='1') ——》 对象列表
4. obj.name name字段的值
obj.pwd pwd字段的值
obj.id obj.pk
` 固定前缀
$ 固定后缀



