C++的四种cast——dynamic_cast
先来看这一段代码:
#include <iostream> using namespace std; class Base{ public: virtual void print(){ cout << "Base print" << endl; } void work(){ cout << "Base work" << endl; } }; class Derive : public Base{ public: virtual void print(){ cout << "Derive print" << endl; } void work(){ cout << "Derive work" << endl; } }; int main() { Base * children = new Derive(); children->work(); children->print(); return 0; }
这段代码的输出结果为:
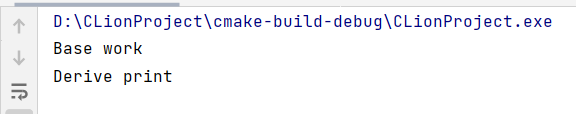
分析结果:print()是虚函数,在运行时的类型来决定运行结果;而work()函数不是虚函数,只是类的普通成员函数,在编译期间决定,所以调用的Base::work()函数。
那如果我们需要调用Derive的work函数呢,就需要使用dynamic_cast进行转换。
Derive * pDerive = dynamic_cast<Derive *>(pBase);
若转型成功,则 dynamic_cast 返回 新类型 类型的值。若转型失败且 新类型 是指针类型,则它返回该类型的空指针。若转型失败且 新类型 是引用类型,则它抛出与类型 std::bad_cast 的处理块匹配的异常。
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/hp_cpp/article/details/104095700






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· Manus的开源复刻OpenManus初探
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· C#/.NET/.NET Core技术前沿周刊 | 第 29 期(2025年3.1-3.9)
· 从HTTP原因短语缺失研究HTTP/2和HTTP/3的设计差异