快速排序,选择排序,冒泡排序
三种排序算法是在数组排序中用到比较多的,下面来具体说明各种排序方法以及区别
快速排序法
使用快速排序方法对a[n]排序
从a[n]中选择一个元素作为基准,一般选a[0],设定low指向a[0](队首),high指向a[n-1](队尾),
先从队尾开始向前扫描,若a[high]>a[0],则high++,否则将a[high]赋值给a[low],即a[low]=a[high]
然后从队首开始向前扫描,若a[low]<a[0],则low++,否则a[high]=a[low]
这样,会将所有小于基准数a[0]的元素放到a[0]左边,把大于a[0]的元素都放到a[0]右边
再使用递归分别对左边、右边的子数组进行排序,最终完成排序
1 //快速排序算法 2 static void quicksort(int arr[], int low, int high){ 3 if(low < high){ 4 int temp = arr[low];//temp是作为比较的基数 5 while(low < high){ 6 // 当队尾的元素大于等于基准数据时,向前挪动high指针 7 while(low < high && arr[high] >= temp){ 8 high--; 9 } 10 //此时是arr[high] < temp,将arr[high]赋值给arr[low] 11 arr[low] = arr[high]; 12 13 // 当队首的元素大于等于基准数据时,向后挪动low指针 14 while(low < high && arr[low] <= temp){ 15 low++; 16 } 17 //此时是arr[low] > temp, 将arr[low]赋值给arr[high] 18 arr[high] = arr[low]; 19 } 20 //当一轮循环过后,low = high时,此时的low或high就是temp的正确索引位置 21 //此时low位置的值并不是tmp,所以需要将temp赋值给arr[low] 22 arr[low] = temp; 23 int index = low;//返回temp的索引位置 24 25 // 递归调用,按照上述方法流程继续对index位置两端的子数组进行排序 26 quicksort(arr, 0, index-1); 27 quicksort(arr, index+1, high); 28 } 29 } 30 31 //冒泡排序,小到大 32 @Test 33 public void bubbleSort(){ 34 Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); 35 int temp, arr[]; 36 while(sc.hasNext()){//可循环进行测试 37 //输入数组长度和数组,比如:输入5回车后,再输入 1 3 4 2 6 38 int n = sc.nextInt(); 39 arr = new int[n]; 40 for(int i =0;i<n;i++){ 41 arr[i] = sc.nextInt(); 42 } 43 //数组中相临两数比较,前面的大于后者就交换位置 44 //冒泡排序:每一轮将依次出现一个最大数(最右边),次大数... 45 for(int i=0;i<n-1;i++){ 46 for(int j=0;j<n-1-i;j++){ 47 if(arr[j] > arr[j+1]){ 48 temp = arr[j]; 49 arr[j] = arr[j+1]; 50 arr[j+1] = temp; 51 } 52 } 53 } 54 //排序后 55 for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ 56 System.out.print(arr[i]+" "); 57 } 58 } 59 } 60 61 //选择排序,小到大 62 @Test 63 public void selectSort(){ 64 Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); 65 int temp, arr[]; 66 while(sc.hasNext()){//可循环进行测试 67 int n = sc.nextInt(); 68 arr = new int[n]; 69 for(int i =0;i<n;i++){ 70 arr[i] = sc.nextInt(); 71 } 72 //数组中每个数依次与它后面的数进行比较,若前者大于后者,交换二者位置 73 for(int i=0;i<n-1;i++){ 74 for(int j=i+1;j<n;j++){ 75 if(arr[i]>arr[j]){ 76 temp = arr[i]; 77 arr[i] = arr[j]; 78 arr[j] = temp; 79 } 80 } 81 } 82 //排序后 83 for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ 84 System.out.print(arr[i]+" "); 85 } 86 } 87 }
另外,冒泡排序和选择排序相似,时间复杂度也相同。
下面是各种排序算法的复杂度比较:
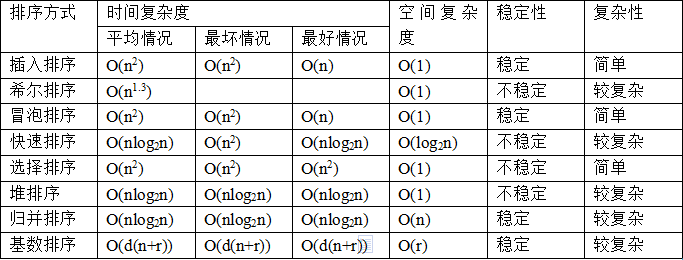
以上就是三种排序法的介绍,如有不足指出!
快速排序可参考:https://blog.csdn.net/nrsc272420199/article/details/82587933


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号