Hibernate 示例
目录结构
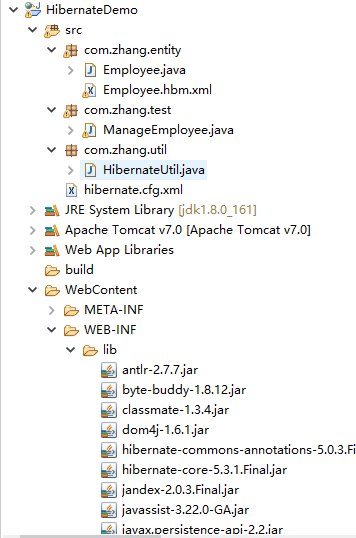
1.编写数据库
create table EMPLOYEE ( id INT NOT NULL auto_increment, first_name VARCHAR(20) default NULL, last_name VARCHAR(20) default NULL, salary INT default NULL, PRIMARY KEY (id) );
2.配置数据库文件---hibernate.cfg.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration SYSTEM "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd"> <hibernate-configuration> <session-factory> <property name="hibernate.dialect"> org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect </property> <property name="hibernate.connection.driver_class"> com.mysql.jdbc.Driver </property> <!-- Assume test is the database name --> <property name="hibernate.connection.url"> jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test </property> <property name="hibernate.connection.username"> root </property> <property name="hibernate.connection.password"> </property> <!-- List of XML mapping files --> <mapping resource="com/zhang/entity/Employee.hbm.xml" /> </session-factory> </hibernate-configuration>
3.创建持久化类---Employee.java
package com.zhang.entity; public class Employee{ private int id; private String firstName; private String lastName; private int salary; public Employee() {} public Employee(String fname, String lname, int salary) { this.firstName = fname; this.lastName = lname; this.salary = salary; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId( int id ) { this.id = id; } public String getFirstName() { return firstName; } public void setFirstName( String first_name ) { this.firstName = first_name; } public String getLastName() { return lastName; } public void setLastName( String last_name ) { this.lastName = last_name; } public int getSalary() { return salary; } public void setSalary( int salary ) { this.salary = salary; } }
4.映射文件---Employee.hbm.xml(将已经定义的类或类组与数据库中的表对应起来)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD//EN" "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <hibernate-mapping> <class name="com.zhang.entity.Employee" table="EMPLOYEE"> <meta attribute="class-description"> This class contains the employee detail. </meta> <id name="id" type="int" column="id"> <generator class="native"/> </id> <property name="firstName" column="first_name" type="string"/> <property name="lastName" column="last_name" type="string"/> <property name="salary" column="salary" type="int"/> </class> </hibernate-mapping>
5.工具类---HibernateUtil.java(解析配置文件)
一些固定而且经常使用的步骤我们期望做成一个工具类,以后再需要重复步骤时咱们仅需要引用此工具类就可以,从而避免了一直创建重复代码。比如加载数据库的驱动等,这里Hibernate中我们每个主程序都需要加载hibernate.cfg.xml文件、创建SessionFactory对象、创建Session对象、关闭session。这些都是固定化的步骤,因此我们将它们写在工具类HibernateUtil中,以后咱们直接引用此文件创建各对象即可,大大减少了代码量,提高了代码复用性。
package com.zhang.util; import org.hibernate.Session; import org.hibernate.SessionFactory; import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistryBuilder; import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration; import org.hibernate.service.ServiceRegistry; public final class HibernateUtil { private HibernateUtil(){ } private static SessionFactory sessionFactory; static{ Configuration cfg = new Configuration(); cfg.configure(); ServiceRegistry sr = new StandardServiceRegistryBuilder().applySettings(cfg.getProperties()).build(); sessionFactory = cfg.buildSessionFactory(sr); } public static SessionFactory getSeesionFactory(){ return sessionFactory; } public static Session getSession(){ return sessionFactory.openSession(); } }
6.测试类---ManageEmployee.java(与数据库连接)
Session 用于获取与数据库的物理连接。 Session 对象是轻量级的,并且设计为在每次需要与数据库进行交互时被实例化。持久态对象被保存,并通过 Session 对象检索找回。
Session session = factory.openSession(); Transaction tx = null; try { tx = session.beginTransaction(); // do some work ... tx.commit(); } catch (Exception e) { if (tx!=null) tx.rollback(); e.printStackTrace(); }finally { session.close(); }
package com.zhang.test; import java.util.List; import java.util.Date; import java.util.Iterator; import org.hibernate.HibernateException; import org.hibernate.Session; import org.hibernate.Transaction; import org.hibernate.SessionFactory; import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration; import com.zhang.entity.Employee; public class ManageEmployee { private static SessionFactory factory; public static void main(String[] args) { try{ factory = new Configuration().configure().buildSessionFactory(); }catch (Throwable ex) { System.err.println("Failed to create sessionFactory object." + ex); throw new ExceptionInInitializerError(ex); } ManageEmployee ME = new ManageEmployee(); /* Add few employee records in database */ Integer empID1 = ME.addEmployee("Zara", "Ali", 1000); Integer empID2 = ME.addEmployee("Daisy", "Das", 5000); Integer empID3 = ME.addEmployee("John", "Paul", 10000); /* List down all the employees */ ME.listEmployees(); /* Update employee's records */ ME.updateEmployee(empID1, 5000); /* Delete an employee from the database */ ME.deleteEmployee(empID2); /* List down new list of the employees */ ME.listEmployees(); } /* Method to CREATE an employee in the database */ public Integer addEmployee(String fname, String lname, int salary){ Session session = factory.openSession(); Transaction tx = null; Integer employeeID = null; try{ tx = session.beginTransaction(); Employee employee = new Employee(fname, lname, salary); employeeID = (Integer) session.save(employee); tx.commit(); }catch (HibernateException e) { if (tx!=null) tx.rollback(); e.printStackTrace(); }finally { session.close(); } return employeeID; } /* Method to READ all the employees */ public void listEmployees( ){ Session session = factory.openSession(); Transaction tx = null; try{ tx = session.beginTransaction(); List employees = session.createQuery("FROM Employee").list(); for (Iterator iterator = employees.iterator(); iterator.hasNext();){ Employee employee = (Employee) iterator.next(); System.out.print("First Name: " + employee.getFirstName()); System.out.print(" Last Name: " + employee.getLastName()); System.out.println(" Salary: " + employee.getSalary()); } tx.commit(); }catch (HibernateException e) { if (tx!=null) tx.rollback(); e.printStackTrace(); }finally { session.close(); } } /* Method to UPDATE salary for an employee */ public void updateEmployee(Integer EmployeeID, int salary ){ Session session = factory.openSession(); Transaction tx = null; try{ tx = session.beginTransaction(); Employee employee = (Employee)session.get(Employee.class, EmployeeID); employee.setSalary( salary ); session.update(employee); tx.commit(); }catch (HibernateException e) { if (tx!=null) tx.rollback(); e.printStackTrace(); }finally { session.close(); } } /* Method to DELETE an employee from the records */ public void deleteEmployee(Integer EmployeeID){ Session session = factory.openSession(); Transaction tx = null; try{ tx = session.beginTransaction(); Employee employee = (Employee)session.get(Employee.class, EmployeeID); session.delete(employee); tx.commit(); }catch (HibernateException e) { if (tx!=null) tx.rollback(); e.printStackTrace(); }finally { session.close(); } } }
Hibernate 教程




【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】凌霞软件回馈社区,博客园 & 1Panel & Halo 联合会员上线
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】博客园社区专享云产品让利特惠,阿里云新客6.5折上折
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步