Shell编程二
告警系统需求分析


1.(虽然之前我们学习了zabbix,但有时候也不能满足我们的需求,比如比较冷门的监控项目需要写自定义脚本,或者服务器网络有问题,没有办法将客户端的数据发送到服务端。)
程序架构:
bin下是主程序文件
conf下是配置文件
shares下是各个监控脚本
mail下是邮件引擎
log下是日志
告警系统主脚本
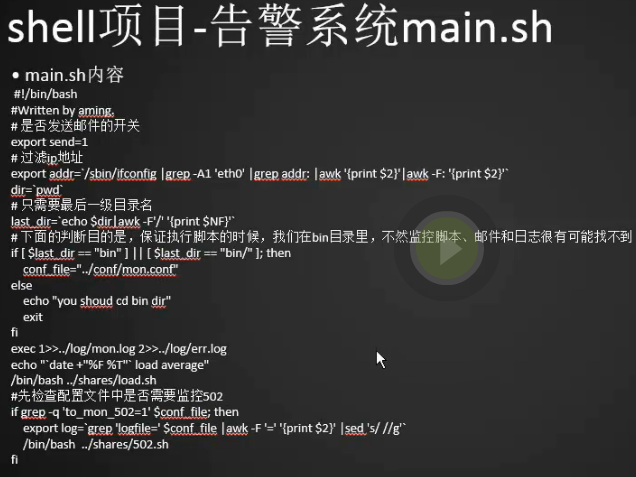
主脚本
1.创建相应的目录
1 2 3 4 5 | [root@centos-02 ~]# cd /usr/local/sbin/[root@centos-02 sbin]# mkdir mon[root@centos-02 sbin]# cd mon/[root@centos-02 mon]# mkdir bin conf shares log mail[root@centos-02 mon]# |
2.编辑告警系统的主脚本
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 | [root@centos-02 mon]# cd bin/[root@centos-02 bin]# vim main.sh#!/bin/bash#Written by SYJ.# 是否发送邮件的开关<br># export 使子脚本都能用send变量(用于将shell变量输出为环境变量,或者将shell函数输出为环境变量)export send=1# 过滤ip地址export addr=`/sbin/ifconfig |grep -A1 "ens33: "|awk '/inet/ {print $2}'`dir=`pwd`# 只需要最后一级目录名last_dir=`echo $dir|awk -F'/' '{print $NF}'` (NF 表示的是浏览记录的域的个数 $NF表示的最后一个Field(列),即输出最后一个字段的内容 )# 下面的判断目的是,保证执行脚本的时候,我们在bin目录里,不然监控脚本、邮件和日志很有可能找不到if [ $last_dir == "bin" ] || [ $last_dir == "bin/" ]; then conf_file="../conf/mon.conf"else echo "you shoud cd bin dir" exitfiexec 1>>../log/mon.log 2>>../log/err.logecho "`date +"%F %T"` load average"/bin/bash ../shares/load.sh#先检查配置文件中是否需要监控502if grep -q 'to_mon_502=1' $conf_file; then export log=`grep 'logfile=' $conf_file |awk -F '=' '{print $2}' |sed 's/ //g'` (查找主配置中的log路径) /bin/bash ../shares/502.shfi |
告警系统配置文件
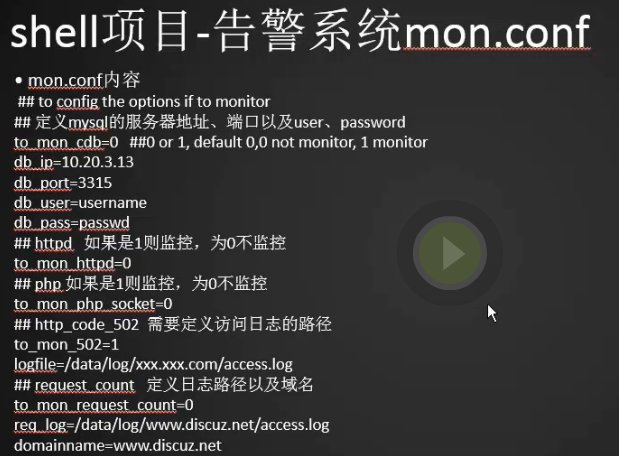
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 | [root@bogon bin]# cd ../conf/[root@bogon conf]# vim mon.conf[root@bogon conf]# ## to config the options if to monitor## 定义mysql的服务器地址、端口以及user、passwordto_mon_cdb=0 ##0 or 1, default 0,0 not monitor, 1 monitordb_ip=10.20.3.13db_port=3315db_user=usernamedb_pass=passwd## httpd 如果是1则监控,为0不监控to_mon_httpd=0 ## php 如果是1则监控,为0不监控to_mon_php_socket=0## http_code_502 需要定义访问日志的路径to_mon_502=1logfile=/data/log/xxx.xxx.com/access.log## request_count 定义日志路径以及域名to_mon_request_count=0req_log=/data/log/www.discuz.net/access.logdomainname=www.discuz.net |
告警系统监控项目

1.Shell项目-子脚本,监控系统平均负载
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | [root@bogon conf]# cd ../[root@bogon mon]# cd shares/[root@bogon shares]# pwd/usr/local/sbin/mon/shares[root@bogon shares]# vim load.sh[root@bogon shares]# #! /bin/bash##Writen by aming##load=`uptime |awk -F 'average:' '{print $2}'|cut -d',' -f1|sed 's/ //g' |cut -d. -f1`if [ $load -gt 10 ] && [ $send -eq "1" ] (如果负载大于10的时候并且可以发邮件)then echo "$addr `date +%T` load is $load" >../log/load.tmp /bin/bash ../mail/mail.sh aming_test@163.com "$addr\_load:$load" `cat ../log/load.tmp`fiecho "`date +%T` load is $load" |
2.测试负载
1 2 3 | [root@bogon shares]# uptime |awk -F 'average:' '{print $2}'|cut -d',' -f1|sed 's/ //g' |cut -d. -f10[root@bogon shares]# |
3.监控nginx报错502

1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | [root@bogon shares]# vim 502.sh[root@bogon shares]##! /bin/bashd=`date -d "-1 min" +%H:%M`c_502=`grep :$d: $log |grep ' 502 '|wc -l` (找出一分钟以前的所有日志)if [ $c_502 -gt 10 ] && [ $send == 1 ]; then echo "$addr $d 502 count is $c_502">../log/502.tmp /bin/bash ../mail/mail.sh $addr\_502 $c_502 ../log/502.tmpfiecho "`date +%T` 502 $c_502" |
监控磁盘使用率

1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 | [root@bogon shares]# vim disk.sh[root@bogon shares]# #! /bin/bashrm -f ../log/disk.tmpLANG=enfor r in `df -h |awk -F '[ %]+' '{print $5}'|grep -v Use` (以空格或者%分割)do if [ $r -gt 90 ] && [ $send -eq "1" ]then echo "$addr `date +%T` disk useage is $r" >>../log/disk.tmpfiif [ -f ../log/disk.tmp ]then df -h >> ../log/disk.tmp /bin/bash ../mail/mail.sh $addr\_disk $r ../log/disk.tmp echo "`date +%T` disk useage is nook"else echo "`date +%T` disk useage is ok" |
awk处理文档的时候我们可以选择多个分割符,$3打印第三段
1 2 3 4 5 | [root@centos-02 ~]# echo "12:aa#33:44#55" |awk -F '[:#]' '{print $3}'33[root@centos-02 ~]# echo "12:aa#33:44#55" |awk -F '[:#]' '{print NF}'5[root@centos-02 ~]# |
告警系统邮件引擎
1.建立邮件服务器文件
#####脚本使用说明######
#1. 首先定义好脚本中的邮箱账号和密码
#2. 脚本执行命令为:python mail.py 目标邮箱 "邮件主题" "邮件内容"1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 | [root@centos-02 shares]# pwd/usr/local/sbin/mon/shares[root@centos-02 shares]# cp /usr/lib/zabbix/alertscripts/mail.py ../mail/mail.py[root@centos-02 shares]# cat /usr/lib/zabbix/alertscripts/mail.py #!/usr/bin/env python#-*- coding: UTF-8 -*-import os,sysreload(sys)sys.setdefaultencoding('utf8')import getoptimport smtplibfrom email.MIMEText import MIMETextfrom email.MIMEMultipart import MIMEMultipartfrom subprocess import *def sendqqmail(username,password,mailfrom,mailto,subject,content): gserver = 'smtp.163.com' gport = 25 try: msg = MIMEText(unicode(content).encode('utf-8')) msg['from'] = mailfrom msg['to'] = mailto msg['Reply-To'] = mailfrom msg['Subject'] = subject smtp = smtplib.SMTP(gserver, gport) smtp.set_debuglevel(0) smtp.ehlo() smtp.login(username,password) smtp.sendmail(mailfrom, mailto, msg.as_string()) smtp.close() except Exception,err: print "Send mail failed. Error: %s" % errdef main(): to=sys.argv[1] subject=sys.argv[2] content=sys.argv[3] sendqqmail('sunyujun_de@163.com', 'sunyujun163','sunyujun_de@163.com',to,subject,content)if __name__ == "__main__": main()[root@centos-02 shares]# |
2.建立mail.sh文件
##在mail目录下创建脚本mail.sh ,当系统服务异常的时候就会调用mail.sh
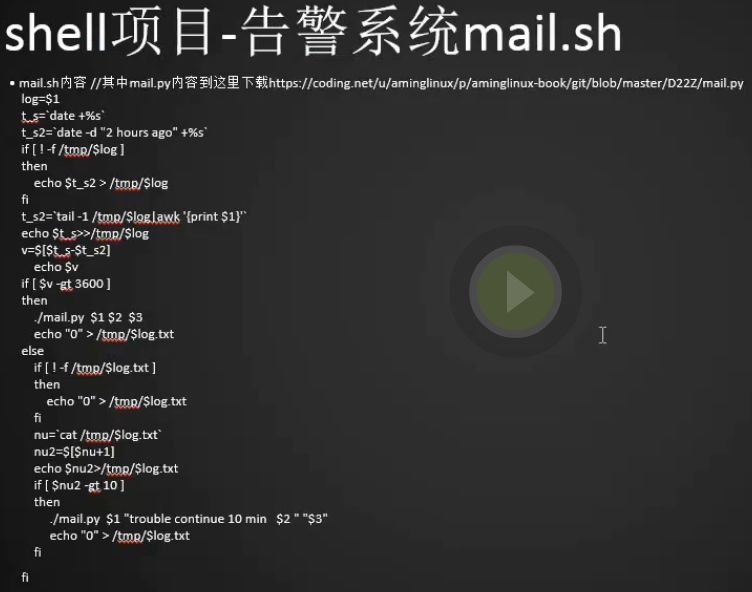
#增加如下内容:(核心功能记时3600秒,记数10次)1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 | [root@centos-02 shares]# cd ../mail/[root@centos-02 mail]# vim mail.sh[root@centos-02 mail]# log=$1t_s=`date +%s`t_s2=`date -d "2 hours ago" +%s`if [ ! -f /tmp/$log ]then echo $t_s2 > /tmp/$logfit_s2=`tail -1 /tmp/$log|awk '{print $1}'`echo $t_s>>/tmp/$logv=$[$t_s-$t_s2]echo $vif [ $v -gt 3600 ]then ./mail.py $1 $2 $3 echo "0" > /tmp/$log.txtelse if [ ! -f /tmp/$log.txt ] then echo "0" > /tmp/$log.txt fi nu=`cat /tmp/$log.txt` nu2=$[$nu+1] echo $nu2>/tmp/$log.txt if [ $nu2 -gt 10 ] then ./mail.py $1 "trouble continue 10 min $2" "$3" echo "0" > /tmp/$log.txt fifi |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 | #本脚本用于做告警收敛#这个在main.sh主函数中定义了$loglog=$1t_s=date +%s#时间戳1t_s2=date -d "2 hours ago" +%s#时间戳2(两个小时之前的时间)#定义该时间戳的目的是保证第一次执行该脚本时v大于一小时#保证第一次执行的时候能报警#因为只有发生故障的时候才会执行该脚本,所以第一次执行必须要报警if [ ! -f /tmp/$log ]thenecho $t_s2 > /tmp/$logfi#创建记录时间戳的日志文件t_s2=tail -1 /tmp/$log|awk '{print $1}'echo $t_s>>/tmp/$logv=$[$t_s-$t_s2]#两个时间戳的间隔时间echo $v#计时器:if [ $v -gt 3600 ]then#如果时间间隔大于1小时,则启动报警系统./mail.py $1 $2 $3echo "0" > /tmp/$log.txt#$log.txt为计数器文件:elseif [ ! -f /tmp/$log.txt ]thenecho "0" > /tmp/$log.txtfi#查看计数器文件中的数字nu=cat /tmp/$log.txtnu2=$[$nu+1]echo $nu2>/tmp/$log.txt#重置$log.txt数值if [ $nu2 -gt 10 ]then#告警收敛:该故障持续十分钟,开始报警./mail.py $1 "trouble continue 10 min $2" "$3"echo "0" > /tmp/$log.txt#告警结束后重新开始计数fifi |
最终的目录结构
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | [root@localhost ~]# tree /usr/local/sbin/mon/usr/local/sbin/mon├── bin│ └── main.sh├── conf│ └── mon.conf├── log├── mail│ ├── mail.py│ └── mail.sh└── shares ├── 502.sh ├── disk.sh └── load.sh |
编写cron计划
1 2 3 | # 每分钟执行一次,这样告警时间间隔收敛至10分钟,这里必须进入到/usr/local/sbin/mon/bin目录下[root@localhost ~]# crontab -e* * * * * cd /usr/local/sbin/mon/bin; bash main.sh |
分发系统介绍(上线脚本)

1.场景:
业务越来越大,网站app,后端,编程语言是php,所以就需要配置lamp或者lnmp,最好还需要把代码上传到服务器上;但是因为业务增加,代码增加,多台机器,就会非常麻烦;这是只需要一个分发系统,就可以把每次更新的代码发布到需要更新的服务器上
expect:实现传输文件、远程执行命令、无需密码,它可以让一些需要交互的任务自动化地完成。相当于模拟了用户和命令行的交互操作。
一个具体的场景:远程登陆服务器,并执行命令
登录时输入密码需要交互,bash脚本无法完成,可以使用expect来完成。
expect脚本远程登录
1.安装expect
1 | [root@bogon shares]# yum install -y expect |
2.写experct的脚本,自动远程登录,并执行命令
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | [root@bogon ~]# vim 1.expect[root@bogon ~]# #! /usr/bin/expectset host " 10.21.95.58" //定义变量 host 被分发机器的IPset passwd "root" //定义变量 密码 被分发机器的密码spawn ssh root@$host //通过 shell 调用变量 host 远程登录被分发机器expect { //这里有两种情况,如果是第一次登录需要选择yes/no,第二次执行的话就走password了"yes/no" { send "yes\r"; exp_continue} //是否要建立连接"password:" { send "$passwd\r" } //输入被分发机器的密码}interact //停留在远程机器,不退出(expect eof停留几秒钟退出) |
3.首次用ssh登录远程机器会让用户选择yes or no,所以配置文件中会有这项配置,第二次登录就不会了,如果还想让出现需要清除known_hosts里面的内容
1 2 3 4 5 6 | [root@bogon ~]# ssh 10.21.95.58The authenticity of host '10.21.95.58 (10.21.95.58)' can't be established.ECDSA key fingerprint is 18:59:d2:46:49:14:c3:70:66:09:7f:70:85:49:d8:c3.Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? noHost key verification failed.[root@bogon ~]# |
1 | [root@bogon ~]# vim /root/.ssh/known_hosts |
4.给文件添加执行的权限并执行
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | [root@bogon ~]# chmod a+x 1.expect [root@bogon ~]# ./1.expect spawn ssh root@10.21.95.58The authenticity of host '10.21.95.58 (10.21.95.58)' can't be established.ECDSA key fingerprint is 18:59:d2:46:49:14:c3:70:66:09:7f:70:85:49:d8:c3.Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yesWarning: Permanently added '10.21.95.58' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts.root@10.21.95.58's password: Last login: Wed Mar 21 10:06:52 2018 from 10.21.95.237[root@sunyujun02 ~]# |
1 2 3 4 | [root@sunyujun02 ~]# exit登出Connection to 10.21.95.58 closed.[root@bogon ~]# |
5.自动远程登录后,执行命令并退出
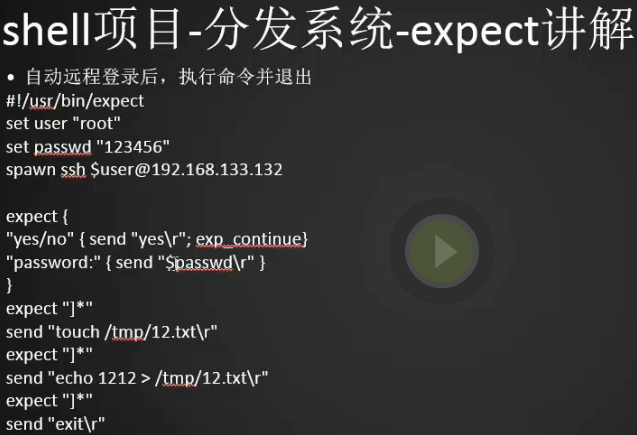
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | [root@bogon ~]# vim 2.expect[root@bogon ~]# #!/usr/bin/expectset user "root"set passwd "root"spawn ssh $user@10.21.95.58expect {"yes/no" { send "yes\r"; exp_continue}"password:" { send "$passwd\r" }}expect "]*" //当遇到提示符为 ]* 也就是登录后的[root@bogon ~]#send "touch /tmp/12.txt\r" // 则创建该文件 expect "]*" send "echo 1212 > /tmp/12.txt\r" //然后在文件中输入文本信息 expect "]*" send "exit\r" //退出 |
6.执行2.expect
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | [root@bogon ~]# vim 2.expect[root@bogon ~]# chmod a+x 2.expect [root@bogon ~]# ./2.expect spawn ssh root@10.21.95.58root@10.21.95.58's password: Last login: Wed Mar 21 10:28:25 2018 from 10.21.95.122[root@sunyujun02 ~]# touch /tmp/12.txtecho 1212 > /tmp/12.txt[root@sunyujun02 ~]# echo 1212 > /tmp/12.txt[root@sunyujun02 ~]# [root@bogon ~]# [root@bogon ~]# |
7.登录到02服务器查看是否建立文件和写操作成功
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | [root@bogon ~]# ./1.expect spawn ssh root@10.21.95.58root@10.21.95.58's password: Last login: Wed Mar 21 11:06:31 2018 from 10.21.95.122[root@sunyujun02 ~]# ls -l /tmp/12.txt -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 5 3月 21 11:06 /tmp/12.txt[root@sunyujun02 ~]# cat /tmp/12.txt 1212[root@sunyujun02 ~]# |
1 2 3 | [root@sunyujun02 ~]# logoutConnection to 10.21.95.58 closed.[root@bogon ~]# |
expect脚本传递参数
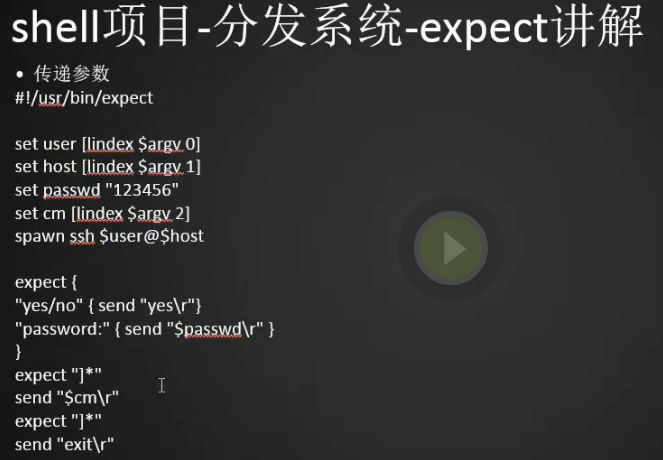
1. expect是可以传递参数的,就像shell我们有$1 $2
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | #!/usr/bin/expectset user [lindex $argv 0] # 第一个参数set host [lindex $argv 1] # 第二个参数 set passwd "root"set cm [lindex $argv 2] #第三个参数,我就是我们要执行的命令spawn ssh $user@$hostexpect {"yes/no" { send "yes\r"}"password:" { send "$passwd\r" }}expect "]*"send "$cm\r"expect "]*"send "exit\r" |
2.给脚本权限并执行ls
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | [root@localhost ~]# chmod a+x 3.expect [root@localhost ~]# ./3.expect root 10.21.95.58 lsspawn ssh root@10.21.95.58root@10.21.95.58's password: Last login: Fri Mar 23 11:00:55 2018 from 10.21.95.122[root@sunyujun02 ~]# ls1.txt do linux 公共 图片 音乐anaconda-ks.cfg done lnmp-install.log 模板 文档 桌面a.txt echo rsyncd 视频 下载[root@sunyujun02 ~]# [root@localhost ~]# |
3.执行多条命令
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | [root@sunyujun02 ~]# [root@localhost ~]# ./3.expect root 10.21.95.58 "ls;w;vmstat 1"spawn ssh root@10.21.95.58root@10.21.95.58's password: Last login: Fri Mar 23 11:05:34 2018 from 10.21.95.122[root@sunyujun02 ~]# ls;w;vmstat 11.txt do linux 公共 图片 音乐anaconda-ks.cfg done lnmp-install.log 模板 文档 桌面a.txt echo rsyncd 视频 下载w: 66 column window is too narrowprocs -----------memory---------- ---swap-- -----io---- -system-- ------cpu----- r b swpd free buff cache si so bi bo in cs us sy id wa st 3 0 197536 267956 40 263476 0 1 49 3 45 76 0 0 99 0 0 0 0 197536 267972 40 263484 0 0 0 0 79 158 0 0 100 0 0 0 0 197536 267940 40 263484 0 0 0 0 58 105 0 0 100 0 0 0 0 197536 267940 40 263484 0 0 0 0 78 134 1 0 99 0 0^C[root@localhost ~]# |
expect脚本同步文件

1.将远程58服务器上/tmp/12.txt文件同步到当前服务器122下的tmp目录下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | #!/usr/bin/expectset passwd "root"spawn rsync -av root@10.21.95.58:/tmp/12.txt /tmp/expect {"yes/no" { send "yes\r"}"password:" { send "$passwd\r" }}expect eof |
2.在58服务器上建立12.txt文件
1 2 3 4 5 | [root@sunyujun02 ~]# touch /tmp/12.txt[root@sunyujun02 ~]# echo 12 > /tmp/12.txt [root@sunyujun02 ~]# cat /tmp/12.txt 12[root@sunyujun02 ~]# |
3.给执行权限并执行脚本,12.txt文件同步成功
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | [root@localhost ~]# chmod a+x 4.expect [root@localhost ~]# ./4.expect spawn rsync -av root@10.21.95.58:/tmp/12.txt /tmp/root@10.21.95.58's password: receiving incremental file list12.txtsent 30 bytes received 82 bytes 224.00 bytes/sectotal size is 3 speedup is 0.03[root@localhost ~]# cat /tmp/12.txt 12[root@localhost ~]# |
4.我们将脚本中的expect eof注释掉看看有什么差异,发现还没有来得及传输呢就直接退出了,所以需要加上,尤其是在传输文件的时候一定要加上
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | [root@localhost ~]# vim 4.expect #!/usr/bin/expectset passwd "root"spawn rsync -av root@10.21.95.58:/tmp/12.txt /tmp/expect {"yes/no" { send "yes\r"}"password:" { send "$passwd\r" }}#expect eof[root@localhost ~]# ./4.expect spawn rsync -av root@10.21.95.58:/tmp/12.txt /tmp/root@10.21.95.58's password: [root@localhost ~]# |
expect脚本指定host和要同步的文件
1.我们执行下面的命令会有默认10秒超时停止的情况,那么怎么在脚本中设置超时时间呢
1 | [root@localhost ~]# ./3.expect root 10.21.95.58 "vmstat 1" |
2.设置脚本超时时间单位秒,如果设置永不超时可以写-1,这样vmstat命令就可以一直执行了
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | #!/usr/bin/expectset user [lindex $argv 0]set host [lindex $argv 1]set passwd "root"set cm [lindex $argv 2]spawn ssh $user@$hostexpect {"yes/no" { send "yes\r"}"password:" { send "$passwd\r" }}expect "]*"send "$cm\r"set timeout 3expect "]*"send "exit\r" |
3.将本地122服务器 /tmp/12.txt文件同步到58服务器的/tmp/12.txt
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | [root@localhost ~]# vim 5.expect#!/usr/bin/expectset passwd "root"set host [lindex $argv 0]set file [lindex $argv 1]spawn rsync -av $file root@$host:$fileexpect {"yes/no" { send "yes\r"}"password:" { send "$passwd\r" }}expect eof[root@localhost ~]# chmod a+x 5.expect [root@localhost ~]# ./5.expect 10.21.95.122 "/tmp/12.txt"spawn rsync -av /tmp/12.txt root@10.21.95.122:/tmp/12.txtroot@10.21.95.122's password: sending incremental file listsent 31 bytes received 12 bytes 28.67 bytes/sectotal size is 3 speedup is 0.07[root@localhost ~]# |
构建文件分发系统
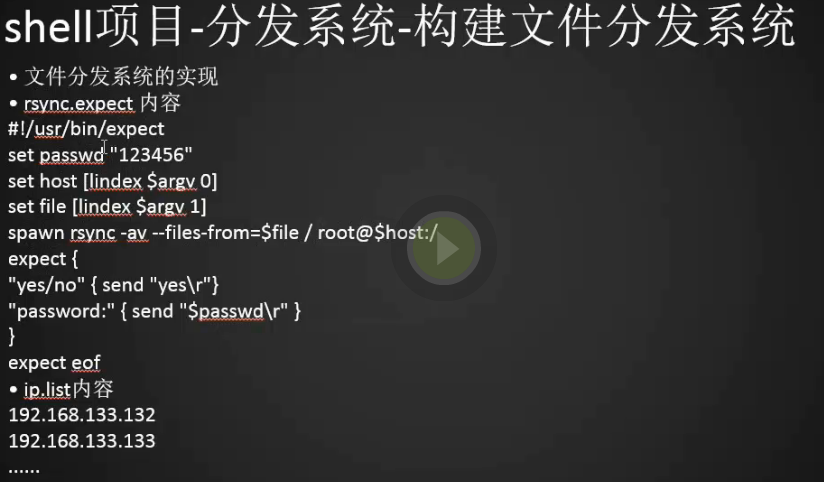
1.核心命令,执行这个命令就可以将文件列表里面的数据(需要将文件路径写到文件列表里面list.txt,里面的文件路径必须是绝对路径)同步到远程服务器
1 | rsync -av --files-from=list.txt / root@host:/ |
2.创建rsync.expect文件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | [root@centos-02 ~]# vim rsync.expect [root@centos-02 ~]##!/usr/bin/expectset passwd "root"set host [lindex $argv 0]set file [lindex $argv 1] (指的是文件列表file.list)spawn rsync -avR --files-from=$file / root@$host:/ (R是当目标服务器没有当前文件目录时会自动创建)expect {"yes/no" { send "yes\r"}"password:" { send "$passwd\r" }}expect eof |
3.创建file.list文件,并写上两个同步文件的路径,文件里面的内容为文件名
1 2 3 4 5 | [root@centos-02 ~]# vim /tmp/file.list [root@centos-02 ~]# cat /tmp/file.list /tmp/123.txt/tmp/456.txt[root@centos-02 ~]# |
4.可能同步到不止一台服务器,所以需要创建ip列表文件,前提是这两台机器的密码是一样的,如果不一样脚本中需要分别指定机器的密码(这样有一个问题,expect文件一旦暴露,密码将泄露,最好搞成秘钥认证登录,就不用输入密码这步脚本了),
1 2 3 4 5 | [root@centos-02 ~]# vim /tmp/ip.list [root@centos-02 ~]# cat /tmp/ip.list 127.0.0.1192.168.133.66[root@centos-02 ~]# |
5.创建rsync.sh,作用就是遍历一下ip地址
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | [root@centos-02 ~]# vim rsync.sh [root@centos-02 ~]# cat rsync.sh #!/bin/bashfor ip in `cat /tmp/ip.list`do ./rsync.expect $ip /tmp/file.listdone[root@centos-02 ~]# chmod a+x ./rsync.expect[root@centos-02 ~]# |
6.执行shell脚本(一定用保证两边都安装了rsync包)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 | [root@centos-02 ~]# sh -x rsync.sh ++ cat /tmp/ip.list+ for ip in '`cat /tmp/ip.list`'+ ./rsync.expect 192.168.133.66 /tmp/file.listspawn rsync -avR --files-from=/tmp/file.list / root@192.168.133.66:/root@192.168.133.66's password: building file list ... donetmp/tmp/123.txttmp/456.txtsent 165 bytes received 53 bytes 145.33 bytes/sectotal size is 8 speedup is 0.04+ for ip in '`cat /tmp/ip.list`'+ ./rsync.expect 127.0.0.1 /tmp/file.listspawn rsync -avR --files-from=/tmp/file.list / root@127.0.0.1:/root@127.0.0.1's password: building file list ... donesent 68 bytes received 12 bytes 53.33 bytes/sectotal size is 8 speedup is 0.10[root@centos-02 ~]# |
7.查看远程服务器上是否同步了文件
1 2 3 4 5 6 | [root@centos-03 /]# ls -l /tmp/总用量 8-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 4 3月 23 23:36 123.txt-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 4 3月 23 23:37 456.txtdrwx------ 3 root root 17 3月 23 23:24 systemd-private-7b6b3a19f79e438685bb4af38b25fb33-vmtoolsd.service-722O8i[root@centos-03 /]# |
批量远程执行命令

1.定义expect脚本
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | [root@centos-02 ~]# vim exec.expect[root@centos-02 ~]# cat exec.expect #!/usr/bin/expectset host [lindex $argv 0]set passwd "root"set cm [lindex $argv 1]spawn ssh root@$hostexpect {"yes/no" { send "yes\r"}"password:" { send "$passwd\r" }}expect "]*"send "$cm\r"expect "]*"send "exit\r"[root@centos-02 ~]# |

2.定义shell脚本
1 2 3 4 5 6 | [root@centos-02 ~]# cat exec.sh #!/bin/bashfor ip in `cat /tmp/ip.list`do ./exec.expect $ip "hostname"done |
3.给权限并执行shell
1 2 | [root@centos-02 ~]# chmod a+x exec.expect [root@centos-02 ~]# |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | [root@centos-02 ~]# sh exec.shspawn ssh root@192.168.133.66root@192.168.133.66's password: Last login: Sat Mar 24 01:45:07 2018 from 192.168.133.88[root@centos-03 ~]# spawn ssh root@127.0.0.1root@127.0.0.1's password: Last login: Sat Mar 24 01:45:08 2018 from localhost[root@centos-02 ~]# hostnamecentos-02[root@centos-02 ~]# [root@centos-02 ~]# |





【推荐】还在用 ECharts 开发大屏?试试这款永久免费的开源 BI 工具!
【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步