UNIX环境高级编程11.6线程同步
// threads/mutex1.c 11-5
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <apue.h>
struct foo {
int f_count;
pthread_mutex_t f_lock;
int f_id;
/* ... more stuff here ... */
};
struct foo* foo_alloc(int id) /* allocate the object */
{
foo* fp;
if ((fp = (foo*)malloc(sizeof(foo))) != NULL)
{
fp->f_count = 1;
fp->f_id = id;
if (pthread_mutex_init(&fp->f_lock, NULL) != 0)
{
free(fp);
return(NULL);
}
/* ... continue initialization ... */
}
return(fp);
}
void foo_hold(foo *fp) /* add a reference to the object */
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&fp->f_lock);
fp->f_count++;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&fp->f_lock);
}
void foo_rele(foo* fp) /* release a reference to the object */
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&fp->f_lock);
if (--fp->f_count == 0)
{ /* last reference */
pthread_mutex_unlock(&fp->f_lock);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&fp->f_lock);
free(fp);
}
else
{
pthread_mutex_unlock(&fp->f_lock);
}
}
void* thr_fn(void* arg)
{
printf("new thread: %lx\n", pthread_self());
for (int i = 0; i < 90000000; i++)
{
foo_hold(static_cast<foo*>(arg));
}
return((void *)8888);
}
int main()
{
pthread_t ntid;
int err;
void* ret;
foo* pf = foo_alloc(1);
err = pthread_create(&ntid, NULL, thr_fn, static_cast<void*>(pf));
if (0 != err)
{
err_quit("can't create thread: %s\n", strerror(err));
}
printf("main thread: %lx\n", pthread_self());
for (int i = 0; i < 90000000; i++)
{
foo_hold(static_cast<foo*>(pf));
}
err = pthread_join(ntid, &ret);
if (err != 0)
{
err_quit("can't join with thread 1: %s\n", strerror(err));
}
printf("new thread exit code %d\n", (int)(long)ret);
printf("pf->fcount = %d\n", pf->f_count);
return 0;
}
关于互斥量,就先看到这里,一些逻辑的东西,等有时间再仔细看,或者说,目前先没有必要看,先读一下,其它的线程同步的知识。
// threads/rwlock.c 11-8
#include <stdlib.h>
// #include <stdio.h>
// #include <string.h>
// #include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include "apue.h"
struct job {
job(pthread_t threadid): j_id(threadid)
{
memset((char*)this + sizeof(pthread_t), 0,
sizeof(job) - sizeof(pthread_t));
}
pthread_t j_id; /* tells which thread handles this job */
struct job *j_next;
struct job *j_prev;
/* ... more stuff here ... */
bool finished;
};
struct queue {
struct job *q_head;
struct job *q_tail;
pthread_rwlock_t q_lock;
};
/*
* Initialize a queue.
*/
int queue_init(struct queue *qp)
{
int err;
qp->q_head = NULL;
qp->q_tail = NULL;
err = pthread_rwlock_init(&qp->q_lock, NULL);
if (err != 0)
return(err);
/* ... continue initialization ... */
return(0);
}
/*
* Insert a job at the head of the queue.
*/
void job_insert(struct queue *qp, struct job *jp)
{
pthread_rwlock_wrlock(&qp->q_lock);
jp->j_next = qp->q_head;
jp->j_prev = NULL;
if (qp->q_head != NULL)
qp->q_head->j_prev = jp;
else
qp->q_tail = jp; /* list was empty */
qp->q_head = jp;
pthread_rwlock_unlock(&qp->q_lock);
}
/*
* Append a job on the tail of the queue.
*/
void job_append(struct queue *qp, struct job *jp)
{
// write lock
pthread_rwlock_wrlock(&qp->q_lock);
printf("%ld %s write lock\n", pthread_self(), __FUNCTION__);
fflush(stdout);
jp->j_next = NULL;
jp->j_prev = qp->q_tail;
if (qp->q_tail != NULL)
{
qp->q_tail->j_next = jp;
}
else
{
qp->q_head = jp; /* list was empty */
}
qp->q_tail = jp;
pthread_rwlock_unlock(&qp->q_lock);
printf("%ld %s unlock\n", pthread_self(), __FUNCTION__);
fflush(stdout);
}
/*
* Remove the given job from a queue.
*/
void job_remove(struct queue *qp, struct job *jp)
{
// write lock
pthread_rwlock_wrlock(&qp->q_lock);
printf("%ld %s write lock\n", pthread_self(), __FUNCTION__);
fflush(stdout);
if (jp == qp->q_head)
{
qp->q_head = jp->j_next;
if (qp->q_tail == jp)
{
qp->q_tail = NULL;
}
else
{
jp->j_next->j_prev = jp->j_prev;
}
} else if (jp == qp->q_tail)
{
qp->q_tail = jp->j_prev;
jp->j_prev->j_next = jp->j_next;
}
else
{
jp->j_prev->j_next = jp->j_next;
jp->j_next->j_prev = jp->j_prev;
}
pthread_rwlock_unlock(&qp->q_lock);
printf("%ld %s unlock\n", pthread_self(), __FUNCTION__);
fflush(stdout);
}
/*
* Find a job for the given thread ID.
*/
job* job_find(struct queue *qp, pthread_t id)
{
struct job *jp;
// read lock
if (pthread_rwlock_rdlock(&qp->q_lock) != 0)
{
return(NULL);
}
printf("%ld %s read lock\n", pthread_self(), __FUNCTION__);
fflush(stdout);
for (jp = qp->q_head; jp != NULL; jp = jp->j_next)
{
if (pthread_equal(jp->j_id, id))
{
break;
}
}
pthread_rwlock_unlock(&qp->q_lock);
printf("%ld %s unlock\n", pthread_self(), __FUNCTION__);
fflush(stdout);
return(jp);
}
void DoSomeWork(job* pJob)
{
pthread_t threadid = pthread_self();
printf("%ld DoSomeWork threadid \n", threadid);
fflush(stdout);
pJob->finished = true;
usleep(10);
}
void* thr_fn(void* arg)
{
pthread_t threadid = pthread_self();
printf("%ld thread start threadid \n", threadid);
fflush(stdout);
int job_done = 0;
job* pJob;
for ( ; ; )
{
printf("%ld begin job finding \n", threadid);
fflush(stdout);
pJob = job_find(static_cast<queue*>(arg), threadid);
if (NULL != pJob)
{
printf("%ld job found \n", threadid);
fflush(stdout);
DoSomeWork(pJob);
printf("%ld %d job done \n", threadid, job_done + 1);
fflush(stdout);
job_remove(static_cast<queue*>(arg), pJob);
if (50000 == ++job_done)
{
break; // thread has do 5 job, thread return;
}
}
}
printf("%ld I have finised %d job , returning threadid \n", threadid, job_done);
fflush(stdout);
return((void *)0);
}
int main()
{
pthread_t threadid0;
pthread_t threadid1;
void* ret;
int err;
queue queue0;
queue_init(&queue0);
err = pthread_create(&threadid0, NULL, thr_fn, static_cast<void*>(&queue0));
if (0 != err)
err_quit("can't create thread: %s\n", strerror(err));
err = pthread_create(&threadid1, NULL, thr_fn, static_cast<void*>(&queue0));
if (0 != err)
err_quit("can't create thread: %s\n", strerror(err));
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++)
{
job* pJob;
if (0 == i % 2)
{
pJob = new job(threadid0);
}
else
{
pJob = new job(threadid1);
}
usleep(100);
job_append(&queue0, pJob);
}
printf("begin pthread_join thread0 \n");
err = pthread_join(threadid0, &ret);
if (err != 0)
err_quit("can't join with thread 0: %s\n", strerror(err));
printf("thread 0 exit code %d\n", (int)(long)ret);
printf("begin pthread_join thread1 \n");
err = pthread_join(threadid1, &ret);
if (err != 0)
err_quit("can't join with thread 1: %s\n", strerror(err));
printf("thread 1 exit code %d\n", (int)(long)ret);
printf("main thread exiting\n");
return 0;
}
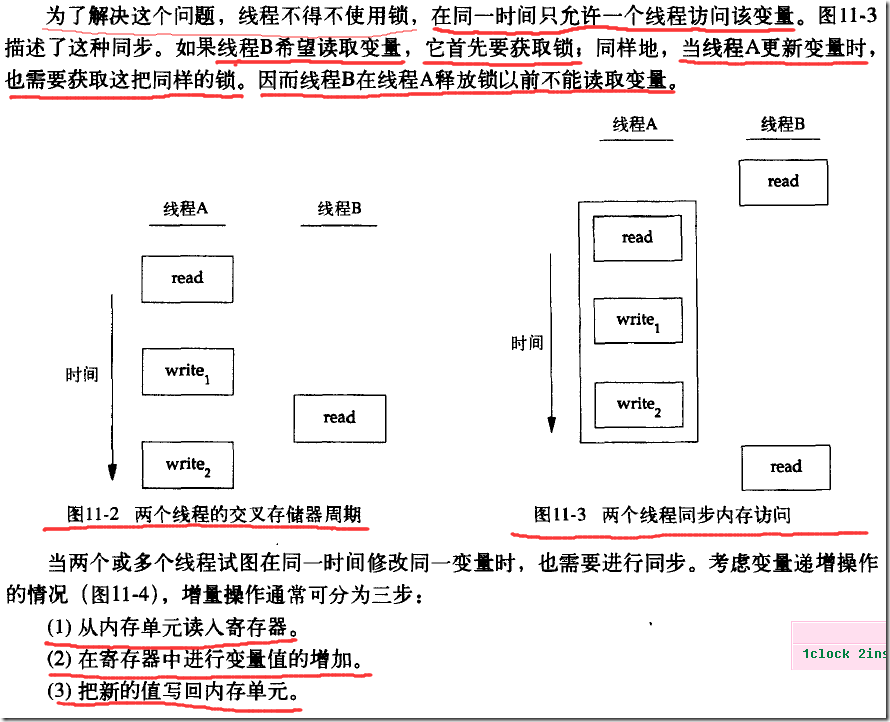
将10万个job加入一个工作队列中,每个job加入工作队列时,指定由哪个线程来完成,一共有两个线程,线程工作时,从队列中找到第一个由自已线程来处理的工作,然后完成它,然后把工作从队列中删除,查找时使用的是读锁定,删除时使用的是写锁定,这个锁是用来维护队列的。
每一个工作由主线程来插入到队列中,一个线程向队列中插入10万工作jobs,插入也是使用写锁定。这个例子中还有一个问题,在线程中我曾经使用sleep函数,发现只是sleep(1),在线程中也会一直睡,sleep(1)这行语句就一直执行不返回,不知道是什么原因,我将sleep改为usleep问题解决。

![EW)_KRL%`4G[S$$B@K][%_R EW)_KRL%`4G[S$$B@K][%_R](http://images0.cnblogs.com/blog/405501/201502/071756038446198.png)
![Z{}_[ZY$I%`A[L]2@D%1HUO Z{}_[ZY$I%`A[L]2@D%1HUO](http://images0.cnblogs.com/blog/405501/201502/071756073607571.png)
![KD7_KQY4`_}[G[EE2])8W@2 KD7_KQY4`_}[G[EE2])8W@2](http://images0.cnblogs.com/blog/405501/201502/071756087971045.png)




![RUL]2EF~}{F7NHWD64A$9HJ RUL]2EF~}{F7NHWD64A$9HJ](http://images0.cnblogs.com/blog/405501/201502/091530140425993.png)

![LFE8NFATM$9%05]}XMPYT)I LFE8NFATM$9%05]}XMPYT)I](http://images0.cnblogs.com/blog/405501/201502/091530217769929.png)












