强化学习基础:基本概念和动态规划
问题描述
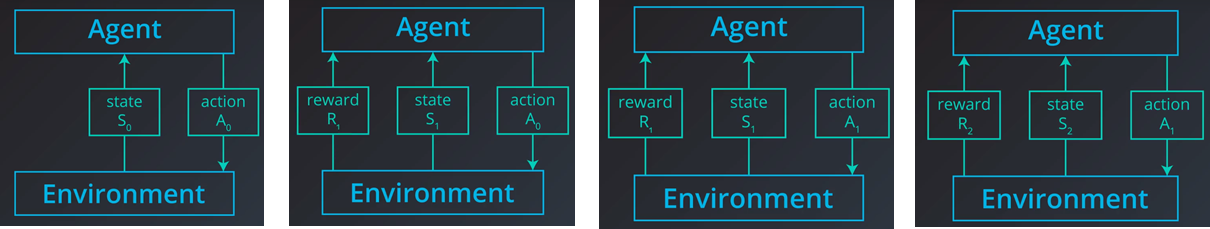
目标:最大化期望累加奖励(expected cumulative reward)
- Episodic Task: 在某个时间步结束,$S_0,A_0,R_1,S_1,A_1,R_2,S_2,\cdots,A_{T-1},R_T,S_T(i.e., terminal\text{ }states)$
- Continuing Task: 没有明确的结束信号,$S_0,A_0,R_1,S_1,A_1,R_2,S_2,\cdots$
- The discounted return(cumulative reward) at time step t: $G_{t}=R_{t+1}+\gamma R_{t+2}+\gamma^{2} R_{t+3}+\ldots,\text{ }0\leq\gamma\leq{1}$
马尔可夫决策过程MDP
- $\mathcal{S}$: the set of all (nonterminal) states; $\mathcal{S}^+$: S+{terminal states} (only for episodic task)
- $\mathcal{A}$: the set of possible actions; $\mathcal{A}(s)$: the set of possible actions available in state $s\in\mathcal{S}$
- $\mathcal{R}$: the set of rewards; $\gamma$: discount rate, $0\leq\gamma\leq{1}$
- the one-step dynamics: $p\left(s^{\prime}, r | s, a\right) = \mathbb{P}\left(S_{t+1}=s^{\prime}, R_{t+1}=r | S_{t}=s, A_{t}=a\right)\text{ for each possible }s^{\prime}, r, s, \text { and } a$
问题求解
- Deterministic Policy $\pi$:a mapping $\mathcal{S} \rightarrow \mathcal{A}$; Stochastic Policy $\pi$: a mapping $\mathcal{S} \times \mathcal{A} \rightarrow[0,1], \text{ i.e., }\pi(a | s)=\mathbb{P}\left(A_{t}=a | S_{t}=s\right)$
- State-Value Function以及Action-Value Function
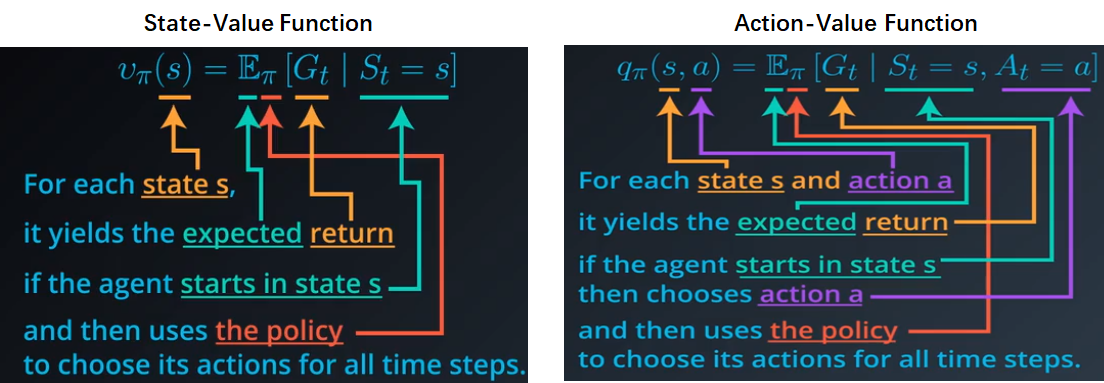
-
Bellman Equation: $v_{\pi}(s)=\mathbb{E}_{\pi}\left[R_{t+1}+\gamma v_{\pi}\left(S_{t+1}\right) | S_{t}=s\right]$
- Policy $\pi^{\prime}\geq\pi \text{ } \Longleftrightarrow \text{ } v_{\pi^{\prime}}(s) \geq v_{\pi}(s)$ for all $s \in \mathcal{S}$; Optimal policy(may not be unique) $\pi_*\geq\pi \text{ for all possible }\pi$
- All optimal policies have the same state-value function $v_*$ and the same action-value function $q_*$
- $\pi_{*}(s)=\arg \max _{a \in \mathcal{A}(s)} q_{*}(s, a)$
求解方法:Dynamic Programming
假设条件:智能体(Agent)事先知道马尔科夫决策过程(MDP)的信息,不需要从与环境(Environment)的交互中逐渐学习
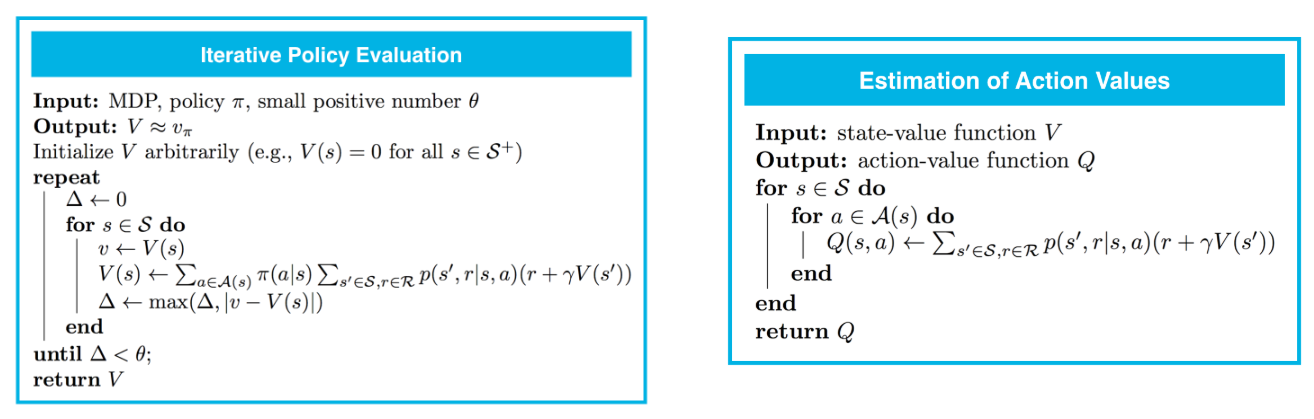
方法1:Policy Iteration
- 问题一(左图):estimate the state-value function $v_{\pi}$ corresponding to a policy $\pi$
- 问题二(右图):obtain the action-value function $q_{\pi}$ from the state-value function $v_{\pi}$
- 问题三(左图):take an estimate of the state-value function $v_{\pi}$ corresponding to a policy $\pi$, returns a new policy $\pi^{\prime}\geq\pi$
- 问题四(右图):solve an MDP in the dynamic programming setting

方法2:Truncated Policy Iteration
In this approach, the evaluation step is stopped after a fixed number of sweeps through the state space
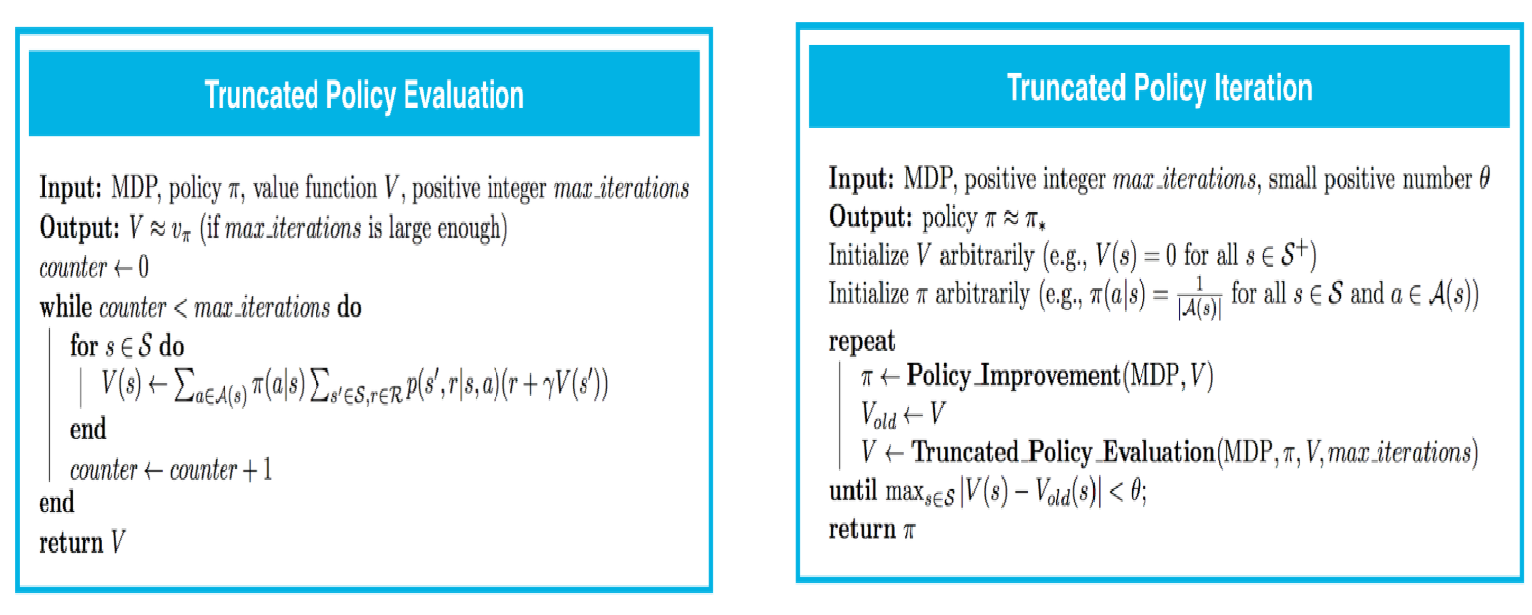
方法3:Value Iteration
In this approach, each sweep over the state space simultaneously performs policy evaluation and policy improvement



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号