数据结构与算法之PHP实现链表类(单链表/双链表/循环链表)
链表是由一组节点组成的集合。每个节点都使用一个对象的引用指向它的后继。指向另一个节点的引用叫做链。
链表分为单链表、双链表、循环链表。
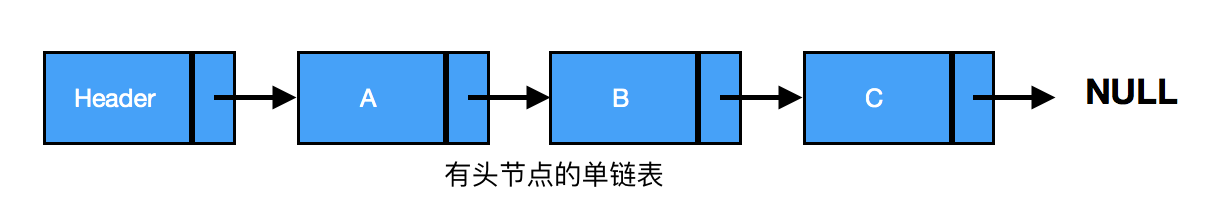
一、单链表
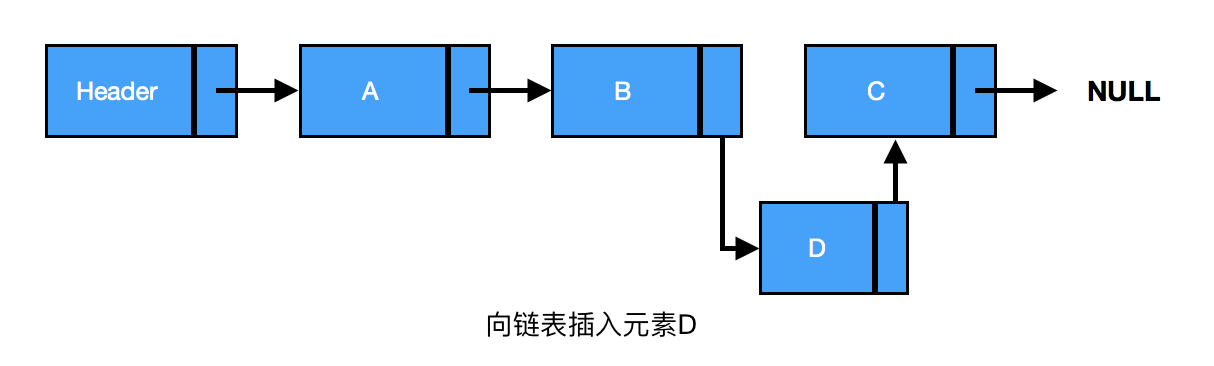
插入:链表中插入一个节点的效率很高。向链表中插入一个节点,需要修改它前面的节点(前驱),使其指向新加入的节点,而新加入的节点则指向原来前驱指向的节点(见下图)。
由上图可知,B、C之间插入D,三者之间的关系为
current为插入节点的前驱节点
new->next = current->next // 新节点D指向B的后继节点C
current->next = new // B节点指向新节点D
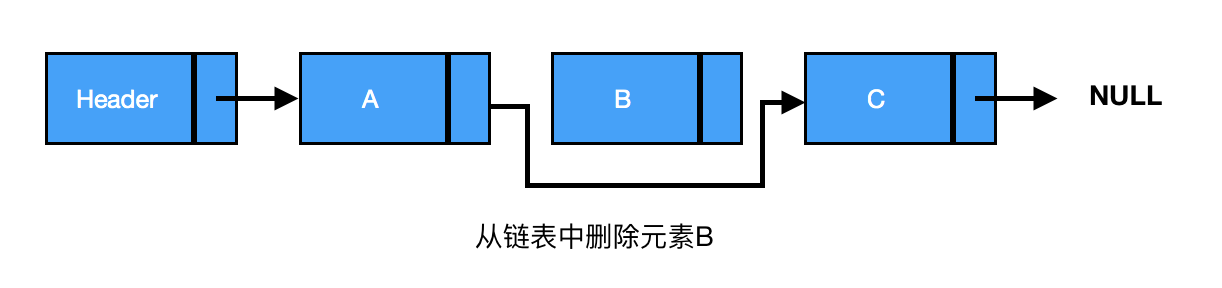
删除:从链表中删除一个元素,将待删除元素的前驱节点指向待删除元素的后继节点,同时将待删除元素指向 null,元素就删除成功了(见下图)。
由上图可知,A、C之间删除B,三者之间的关系为
current为要删除节点的前驱节点
current->next = current->next->next // A节点指向C节点
具体代码如下:
<?php // 节点类 class Node { public $data; // 节点数据 public $next; // 下一节点 public function __construct($data) { $this->data = $data; $this->next = NULL; } } // 单链表类 class SingleLinkedList { private $header; // 头节点 function __construct($data) { $this->header = new Node($data); } // 查找节点 public function find($item) { $current = $this->header; while ($current->data != $item) { $current = $current->next; } return $current; } // (在节点后)插入新节点 public function insert($item, $new) { $newNode = new Node($new); $current = $this->find($item); $newNode->next = $current->next; $current->next = $newNode; return true; } // 更新节点 public function update($old, $new) { $current = $this->header; if ($current->next == null) { echo "链表为空!"; return; } while ($current->next != null) { if ($current->data == $old) { break; } $current = $current->next; } return $current->data = $new; } // 查找待删除节点的前一个节点 public function findPrevious($item) { $current = $this->header; while ($current->next != null && $current->next->data != $item) { $current = $current->next; } return $current; } // 从链表中删除一个节点 public function delete($item) { $previous = $this->findPrevious($item); if ($previous->next != null) { $previous->next = $previous->next->next; } } // findPrevious和delete的整合 public function remove($item) { $current = $this->header; while ($current->next != null && $current->next->data != $item) { $current = $current->next; } if ($current->next != null) { $current->next = $current->next->next; } } // 清空链表 public function clear() { $this->header = null; } // 显示链表中的元素 public function display() { $current = $this->header; if ($current->next == null) { echo "链表为空!"; return; } while ($current->next != null) { echo $current->next->data . "  "; $current = $current->next; } } } $linkedList = new SingleLinkedList('header'); $linkedList->insert('header', 'China'); $linkedList->insert('China', 'USA'); $linkedList->insert('USA','England'); $linkedList->insert('England','Australia'); echo '链表为:'; $linkedList->display(); echo "</br>"; echo '-----删除节点USA-----'; echo "</br>"; $linkedList->delete('USA'); echo '链表为:'; $linkedList->display(); echo "</br>"; echo '-----更新节点England为Japan-----'; echo "</br>"; $linkedList->update('England', 'Japan'); echo '链表为:'; $linkedList->display(); //echo "</br>"; //echo "-----清空链表-----"; //echo "</br>"; //$linkedList->clear(); //$linkedList->display(); // 输出: 链表为:China USA England Australia -----删除节点USA----- 链表为:China England Australia -----更新节点England为Japan----- 链表为:China Japan Australia
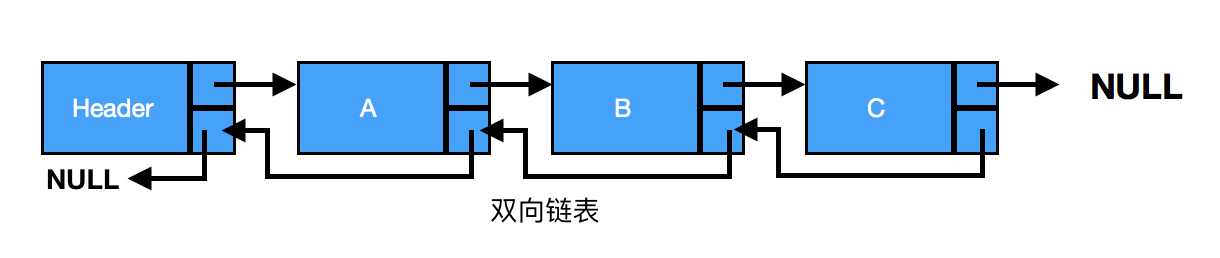
二、双链表
单链表从链表的头节点遍历到尾节点很简单,但从后向前遍历就没那么简单了。它的每个数据结点中都有两个指针,分别指向直接后继和直接前驱。
所以,从双向链表中的任意一个结点开始,都可以很方便地访问它的前驱结点和后继结点。
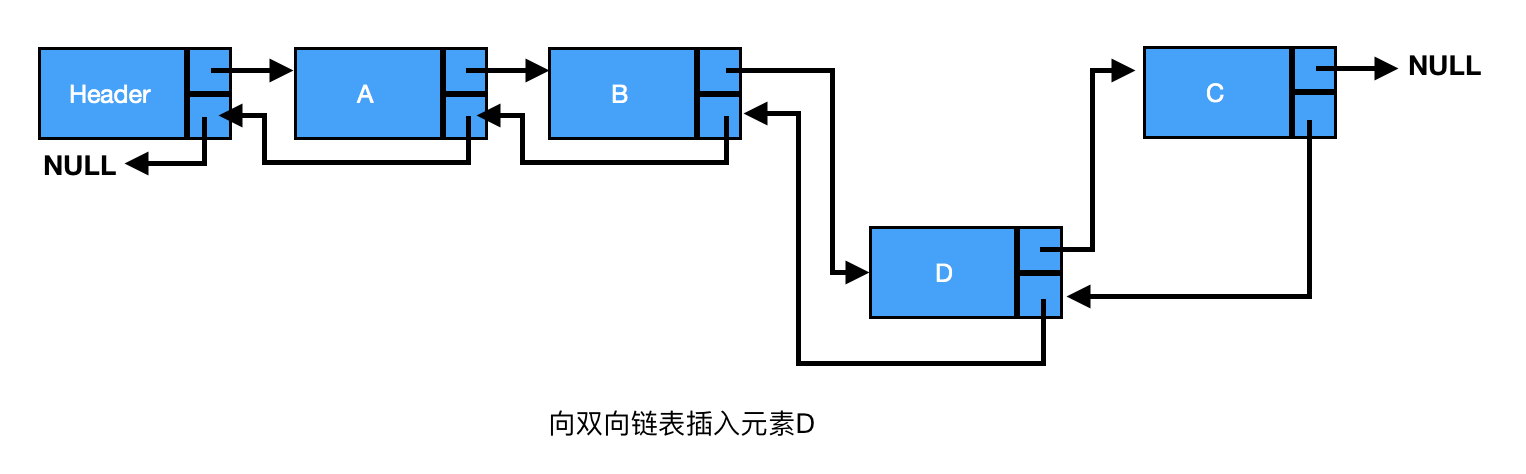
插入:插入一个节点时,需要指出该节点正确的前驱和后继。
修改待插入节点的前驱节点的next属性,使其指向新加入的节点,而新插入的节点的next属性则指向原来前驱指向的节点,同时将原来前驱指向的节点的previous属性指向新节点,而新加入节点的previous属性指向它前驱节点(见下图)。
由上图可知,B、C之间插入D,三者之间的关系为
current为插入节点的前驱节点
new->next = current->next // 新节点D的next属性指向B的后继节点C
current->next->previous = new // B的后继节点C的previous属性指向新节点D(原先是C的previous属性指向B)
current->next = new // B的next属性指向新节点D
new->previous = current // B的previous属性指向节点B
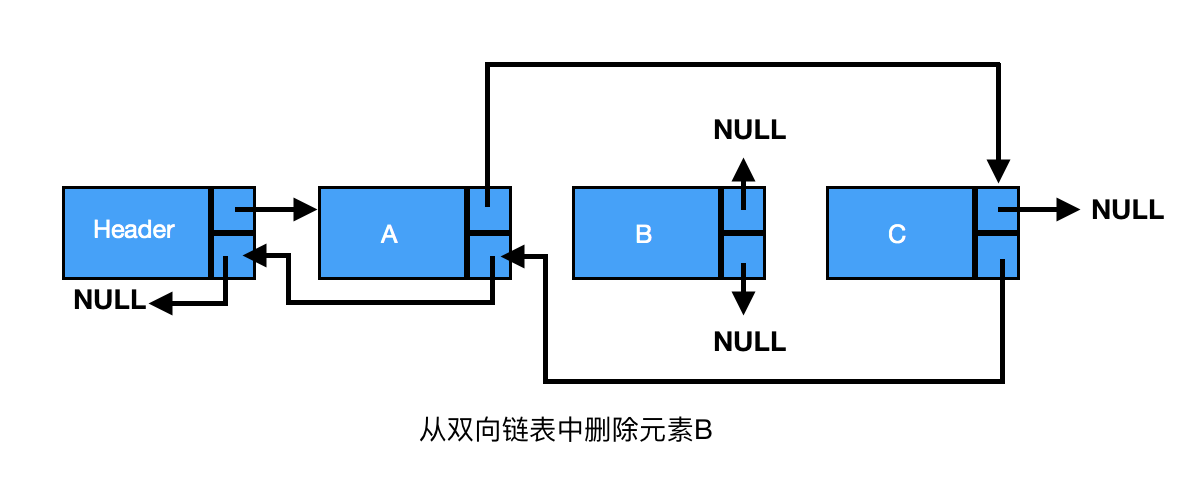
删除:双向链表的删除操作比单向链表的效率更高,因为不需要再查找前驱节点了。
首先需要在链表中找出存储待删除数据的节点,然后设置该节点前驱的 next 属性,使其指向待删除节点的后继;设置该节点后继的 previous 属性,使其指向待删除节点的前驱。
由上图可知,B、C之间删除D,三者之间的关系为
current为要删除的节点
current->previous->next = current->next // B的前驱节点A的next属性指向B的后继节点C
current->next->previous = current->previous // B的后继节点C的previous属性指向B的前驱节点A
current->previous = null // B的previous属性指向null
current->next = null // B的next属性指向null
具体代码如下:
<?php // 节点类 class Node { public $data; // 节点数据 public $previous = NULL; // 前驱 public $next = NULL; // 后继 public function __construct($data) { $this->data = $data; $this->previous = NULL; $this->next = NULL; } } // 双链表类 class DoubleLinkedList { private $header; // 头节点 function __construct($data) { $this->header = new Node($data); } // 查找节点 public function find($item) { $current = $this->header; while ($current->data != $item) { $current = $current->next; } return $current; } // 查找链表最后一个节点 public function findLast() { $current = $this->header; while ($current->next != null) { $current = $current->next; } return $current; } //(在节点后)插入新节点 public function insert($item, $new) { $newNode = new Node($new); $current = $this->find($item); $newNode->next = $current->next; $newNode->previous = $current; $current->next = $newNode; return true; } // 从链表中删除一个节点 public function delete($item) { $current = $this->find($item); if ($current->next != null) { $current->previous->next = $current->next; $current->next->previous = $current->previous; $current->next = null; $current->previous = null; return true; } } // 显示链表中的元素 public function display() { $current = $this->header; if ($current->next == null) { echo "链表为空!"; return; } while ($current->next != null) { echo $current->next->data . "  "; $current = $current->next; } } // 反序显示双向链表中的元素 public function dispReverse() { $current = $this->findLast(); while ($current->previous != null) { echo $current->data . "  "; $current = $current->previous; } } } // 测试 $linkedList = new DoubleLinkedList('header'); $linkedList->insert('header', 'China'); $linkedList->insert('China', 'USA'); $linkedList->insert('USA','England'); $linkedList->insert('England','Australia'); echo '链表为:'; $linkedList->display(); echo "</br>"; echo '-----删除节点USA-----'; echo "</br>"; $linkedList->delete('USA'); echo '链表为:'; $linkedList->display(); // 输出: 链表为:China USA England Australia -----删除节点USA----- 链表为:China England Australia
三、循环链表
循环链表和单向链表相似,节点类型都是一样的。唯一的区别是,在创建循环链表时,让其头节点的 next 属性指向它本身,即:head.next = head,这种行为会传导至链表中的每个节点,使得每个节点的 next 属性都指向链表的头节点。换句话说,链表的尾节点指向头节点,形成了一个循环链表。
在循环链表中,涉及遍历的操作,其终止条件是判断它们是否等于头结点,而不是像单链表那样判别p或p->next是否为空。
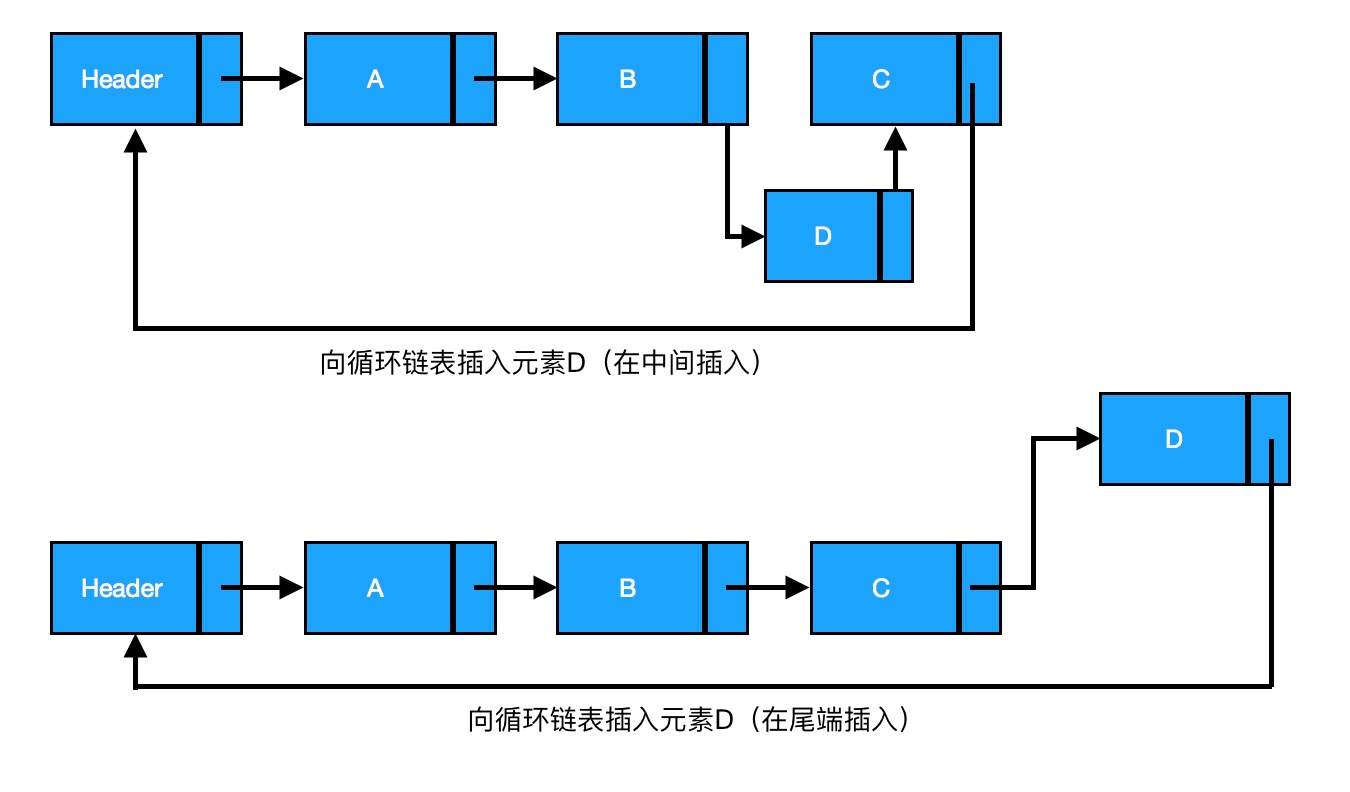
插入:如果不是在链表尾端插入,则与单链表相似,将待插入节点的前驱节点指向新加入的节点,而新加入的节点指向原来前驱指向的节点;如果是在尾端插入,则待插入节点的前驱节点指向新加入的节点,而新加入的节点指向头节点(见下图)。
由上图可知,插入节点D,B、C、D三者之间的关系为
current为插入节点的前驱节点
// 中间
new->next = current->next // 新节点D指向B的后继节点C
current->next = new // B节点指向新节点D
// 尾端
current->next = new // C节点指向新节点D
new->next = header // 新节点D指向头节点Header
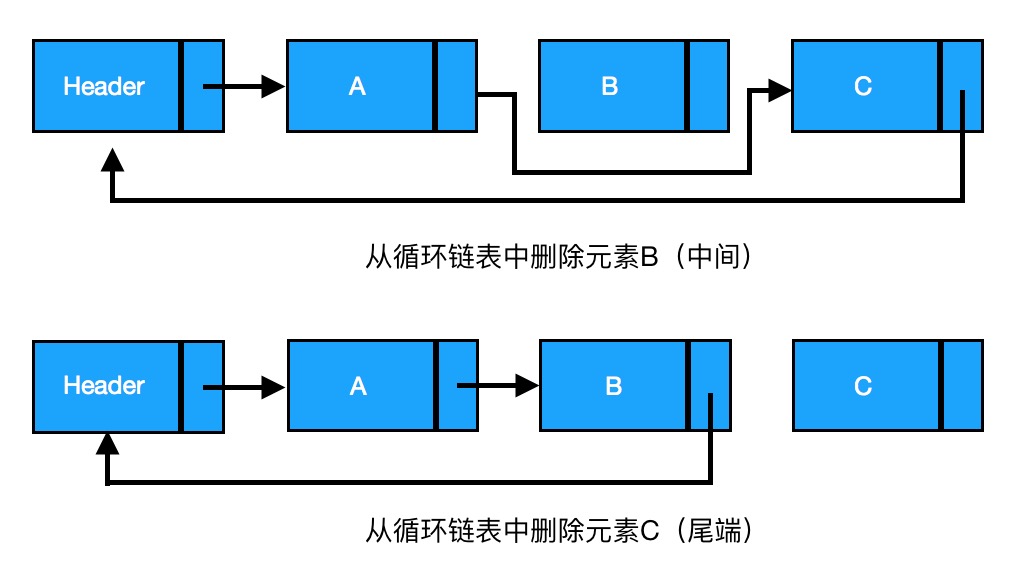
删除:如果删除的是中间元素,则与单链表操作相同,将待删除节点的前驱节点指向待删除节点的后继节点;如果删除的是尾端元素,则将待删除节点的前驱节点指向头节点。
由上图可知,删除节点时,B、C、D三者之间的关系为
current为要删除节点的前驱节点
// 中间
current->next = current->next->next // A节点指向C节点
// 尾端
current->next = header // B节点指向头节点Header
具体代码如下:
<?php // 节点类 class Node { public $data; // 节点数据 public $previous; public $next; // 下一节点 public function __construct($data) { $this->data = $data; $this->next = NULL; } } // 循环链表类 class CircularLinkedList { private $header; // 头节点 function __construct($data) { $this->header = new Node($data); $this->header->next = $this->header; } // 查找节点 public function find($item) { $current = $this->header; while ($current->data != $item) { $current = $current->next; } return $current; } // 插入新节点 public function insert($item, $new) { $newNode = new Node($new); $current = $this->find($item); if ($current->next != $this->header) { // 链表中间 $current->next = $newNode; $newNode->next = $current->next; } else { // 链表尾端 $current->next = $newNode; $newNode->next = $this->header; } return true; } // 删除节点 public function delete($item) { $current = $this->header; while ($current->next != null && $current->next->data != $item) { $current = $current->next; } if ($current->next != $this->header) { // 链表中间 $current->next = $current->next->next; } else { // 链表尾端 $current->next = $this->header; } } // 显示链表中的元素 public function display() { $current = $this->header; while ($current->next != $this->header) { echo $current->next->data . "  "; $current = $current->next; } } } // 测试 $linkedList = new CircularLinkedList('header'); $linkedList->insert('header', 'China'); $linkedList->insert('China', 'USA'); $linkedList->insert('USA', 'England'); $linkedList->insert('England', 'Australia'); echo '链表为:'; $linkedList->display(); echo "</br>"; echo '-----删除节点USA-----'; echo "</br>"; $linkedList->delete('USA'); echo '链表为:'; $linkedList->display(); // 输出: 链表为:China USA England Australia -----删除节点USA----- 链表为:China England Australia
注:循环链表还可以分为单循环链表和双循环链表,这里只实现了单循环链表。





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:基于图像分类模型对图像进行分类
· go语言实现终端里的倒计时
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· 25岁的心里话
· ollama系列01:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 按钮权限的设计及实现