源码分析--LinkedList(JDK1.8)
LinkedList与ArrayList一样都是List接口的实现类,底层用双向链表实现。
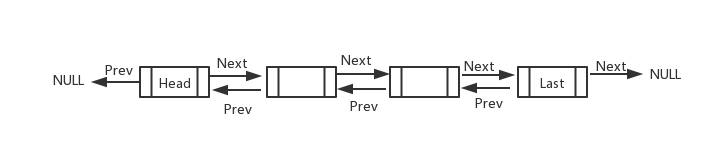
LinkedList本身用一个内部类实现链表元素。
private static class Node<E> { E item; Node<E> next; Node<E> prev; Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) { this.item = element; this.next = next; this.prev = prev; } }
E item就是当前元素。next为下一个节点,prev为上一个节点。
主要方法分析:
1.add()
public boolean add(E e) { linkLast(e); return true; } /** * Links e as last element. */ void linkLast(E e) { final Node<E> l = last; final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null); last = newNode; if (l == null) first = newNode; else l.next = newNode; size++; modCount++; }
插入元素后,新建newNode节点,将newNode置为last,再进行指针移动。所以插入效率比ArrayList的数组复制高很多。
2、get()
public E get(int index) { checkElementIndex(index); return node(index).item; } /** * Returns the (non-null) Node at the specified element index. */ Node<E> node(int index) { // assert isElementIndex(index); if (index < (size >> 1)) { Node<E> x = first; for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) x = x.next; return x; } else { Node<E> x = last; for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--) x = x.prev; return x; } }
- index合理性判断
- 利用双向链表特性,将index与size/2进行比较
- 小于就从头开始遍历
- 大于就从尾开始遍历
这种遍历方式在index越靠近size/2时,效率越低,需要遍历的元素越多。远远不如ArrayList那种直接用index在数组中的get方式。
3、区别与ArrayList,LinkedList还实现了push()和pop()方法。分别用以将元素推入链表第一个和取出并删除第一个元素。代码简单不再赘述。



