Java中包装类型
什么是拆箱和装箱
自动装箱和拆箱是 Java 编译器在基本类型和它们对应的包装类之间进行的自动转换。
自动装箱
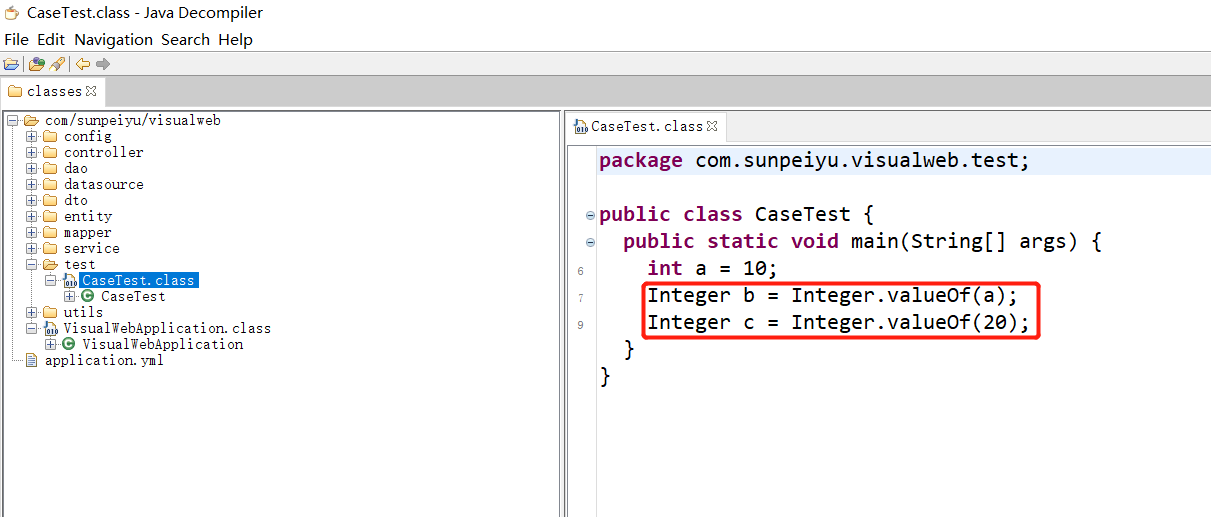
int类型变量转换为Integer类型变量,还是直接赋值Integer类型的变量,都使用了自动装箱,调用Integer.valueof();方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10;
Integer b = a;
Integer c = 20;
}
Java编译后:
自动拆箱
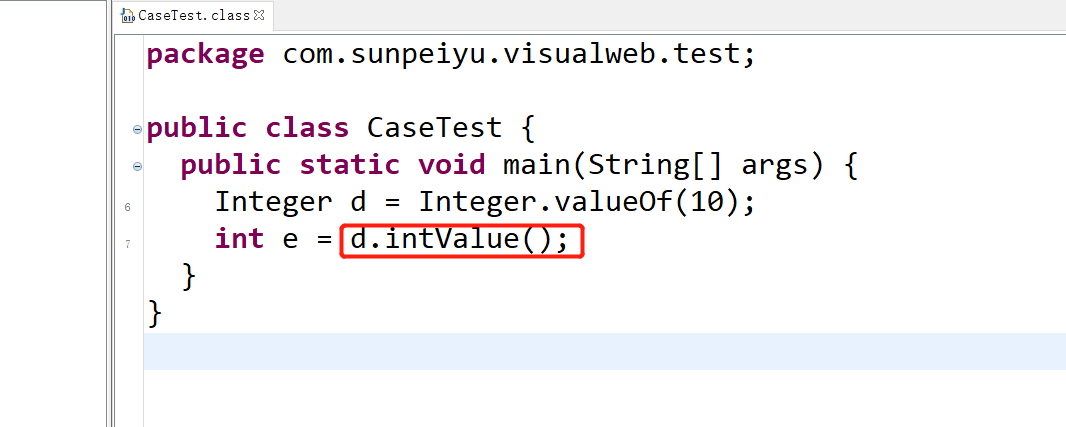
Integer类型变量转换为int类型变量,使用了自动拆箱,调用Integer.intValue();方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer d = 10;
int e = d;
}
Java编译后:
Integer缓存
Integer定义了一个静态内部类IntegerCache作为缓存
源码
private static class IntegerCache {
//常量最小值-128
static final int low = -128;
//常量最大值
static final int high;
//Integer缓存数组
static final Integer cache[];
static {
//初始化h变量为127
int h = 127;
String integerCacheHighPropValue =
sun.misc.VM.getSavedProperty("java.lang.Integer.IntegerCache.high");
if (integerCacheHighPropValue != null) {
int i = parseInt(integerCacheHighPropValue);
//说明i最小可以取到127,规定了i的下限,所以i>=127
i = Math.max(i, 127);
//由于i>=127并且Integer.MAX_VALUE - (-low)>128,因此可以得到h>=127
h = Math.min(i, Integer.MAX_VALUE - (-low));
}
high = h;
//初始化Integer缓存数组
cache = new Integer[(high - low) + 1];
//数组中的初始值是-128
int j = low;
//循环为数组赋值,数组0位是-128,最大是127(临界值)
for(int k = 0; k < cache.length; k++)
cache[k] = new Integer(j++);
}
private IntegerCache() {}
}
/**
* 返回一个表示指定的 int 值的 Integer 实例。
* 如果不需要新的 Integer 实例,则通常应优先使用该方法,而不是构造方法 Integer(int)
* 因为该方法有可能通过缓存经常请求的值而显著提高空间和时间性能
*/
public static Integer valueOf(int i) {
assert IntegerCache.high >= 127;
//当-128<=i<=127时,直接从缓存数组中取出值
if (i >= IntegerCache.low && i <= IntegerCache.high)
return IntegerCache.cache[i + (-IntegerCache.low)];
//否则返回新的Integer对象
return new Integer(i);
}
测试Integer缓存
public static void main(String[] args) {
//标准的装箱过程
Integer i =new Integer(100);
Integer i1 =100;
Integer i2 =100;
Integer i3 =128;
Integer i4 =128;
System.out.println("i==i1 :"+(i==i1));
System.out.println("i1==i2 :"+(i1==i2));
System.out.println("i3==i4 :"+(i3==i4));
}
结果:
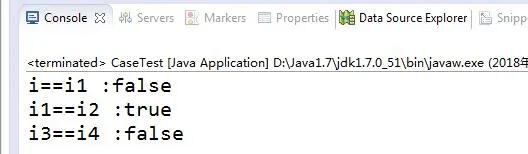
说明:
- i == i1 :
由于i本身是new Integer的方式在堆中单独开辟空间,i1是 -128<=i1<=127,所以i1是从缓存中取出数据的。而缓存的地址和new Integer单独开辟空间对应的地址不同,返回false。 - i1 == i2 :
i1是 -128<=i1<=127,所以i1是从缓存中取出数据的。i2是-128<=i2<=127,所以i2也是从缓存中取出数据的。所以i1和i2对应的是同一个缓存地址,返回true。 - i3 == i4 :
i3>127并且i4>127,所以i3和i4分别是new Integer这种单独开辟空间,地址不同,返回false。


