4.4 最短路径
一.最短路径的简介
1.目标:给定一个边赋权有向图,找出从s到t的最短路径。
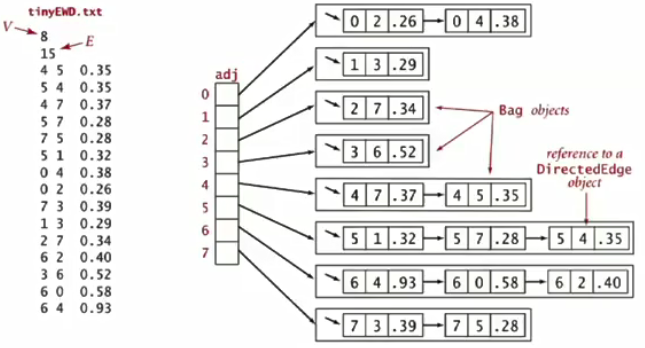
2.加权有向边的实现以及加权有向图(bag构成的数组,每一个bag中存从该点指出的边)的实现:

package com.cx.graph; public class DirectedEdge { private final int v,w; private final double weight; public DirectedEdge(int v,int w,double weight) { //有向边的起点,终点和权重 this.v=v; this.w=w; this.weight=weight; } public int from() { return v; } public int to() { return w; } public double weight() { return weight; } }

package com.cx.graph; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.Bag; public class EdgeWeightedDigraph { private final int V; private final Bag<DirectedEdge>[] adj; public EdgeWeightedDigraph(int V) { this.V=V; adj=(Bag<DirectedEdge>[])new Bag[V]; for(int v=0;v<V;v++) { adj[v]=new Bag<DirectedEdge>(); } } //添加一条有向边 public void addEdge(DirectedEdge e) { int v=e.from(); adj[v].add(e); } public Iterable<DirectedEdge> adj(int v){ return adj[v]; } }
3.最短路径的数据结构
(1)edgeTo[v]指的是树中连接v和它的父节点的边(也就是从s到v的最短路径上的最后一条边),用于得到最短路径的具体内容
(2)distTo[v]指的是从s到v的已知最短路径的长度。
代码实现:

private void relax(DirectedEdge e) { int v=e.from(),w=e.to(); //边的松弛 if(distTo[w]>distTo[v]+e.weight()) { //更新distTo和edgeTo distTo[w]=distTo[v]+e.weight(); edgeTo[w]=e; } }
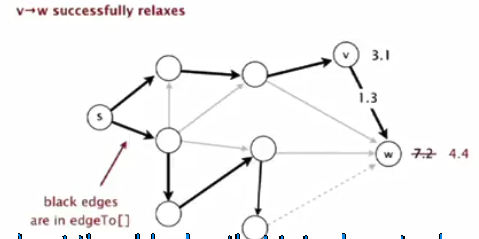
4.边的松弛e=v->w
(1)distTo[v]是已知的s到v的最短路径的长度(上面粗黑线)
(2)distTo[w]是已知的s到w的最短路径的长度(下面的粗黑线)
(3)edgeTo[w]是已知的s到w的最短路径的最后一条边
(4)如果e=v->w提供了到w的更短的路,这条路通过v,那么更新distTo[w]和edgeTo[w]
代码实现:

private double distTo(int v) { return distTo[v]; } public boolean hasPathTo(int v) { return distTo[v]<Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY; } public Iterable<DirectedEdge> pathTo(int v){ if(!hasPathTo(v)) return null; Stack<DirectedEdge> path=new Stack<DirectedEdge>(); for(DirectedEdge e=edgeTo[v];e!=null;e=edgeTo[e.from()]) path.push(e); return path; }
5.最优性条件
令G是一幅加权有向图,那么distTo[]是从s出发的最短路径的长度当且仅当:
(1)对于每一个顶点v,distTo[v]是从s到v的某一条路径的长度
(2)对于每一条边e=v->w,distTo[w]<=distTo[v]+e.weight()
6.通用的最短路径算法:初始化distTo[s]=0,其他的点distTo[]=∞。重复松弛边,直到满足最优性条件。
7.该算法没有指定边的放松顺序。下面有三种有效的实现:
(1)Dijkstra 算法(无负数权重)
(2)拓扑排序算法(无有向环)
(3)Bellman-Ford算法(无负权重环)
二.Dijkstra算法(算法前提:无负数权重)
1.思想:(边的放松顺序为当时距离s的距离从小到大的顺序)
(1)将从s出发的点的距离从小到大的考虑。(这个点满足以前不在树中,并且具有最小的distTo[]的值)
Consider vertices in increasing order of distance from s(non-tree vertex with the lowest distTo[] value)
(2)将这个点加入到树,并且将其他从这个点出发的边进行边的松弛操作。
Add vertex to tree and relax all edges pointing from that vertex
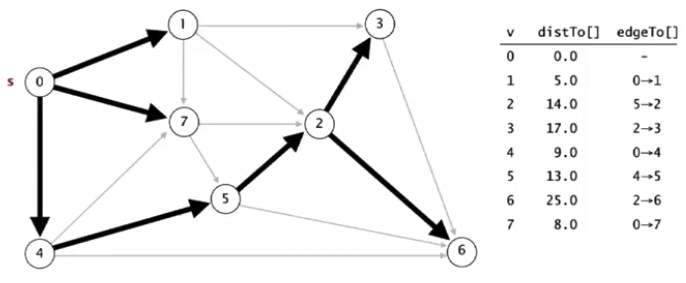
2.举例说明:初始化distTo[s]=0,其他的点distTo[]=∞
(1)从0开始考虑,对0-1,0-7,0-4三条边进行松弛操作,更新这三个点的distTo[]和edgeTo[]。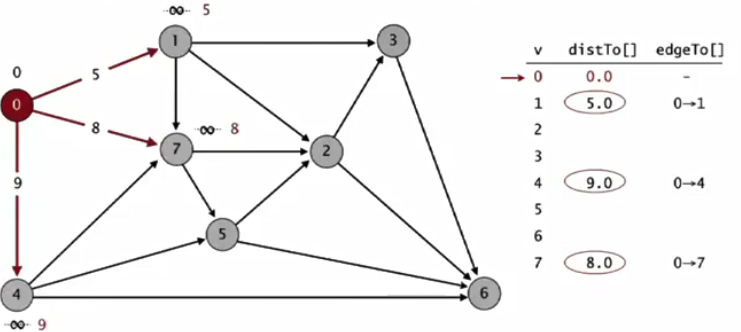
(2)考虑最小distTo[]且不在树中的点1,对1-7,1-2,1-3三条边进行松弛操作,5+4>8,不更新点7,更新2和3
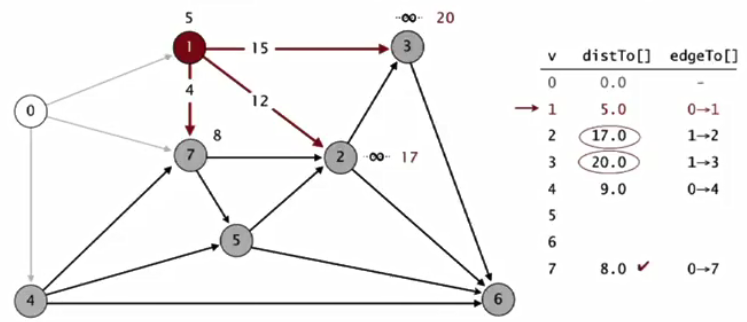
(3)考虑最小distTo[]且不在树中的点7,对7-2,7-5进行松弛操作,8+7<17,更新点2,更新点5
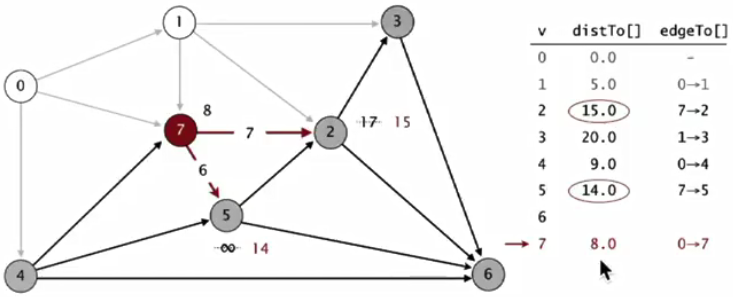
(4)考虑最小distTo[]且不在树中的点4,对4-7,4-5,4-6进行松弛操作,9+5>8,9+4<14,更新点5和6,不更新点7
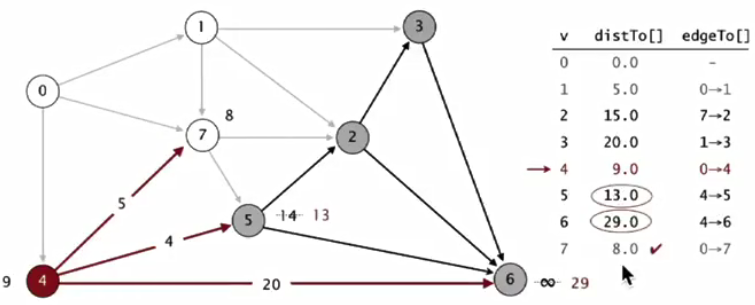
(5)考虑最小distTo[]且不在树中的点5,对5-2,5-6进行松弛操作,13+1<15,13+13<26,更新点2和6
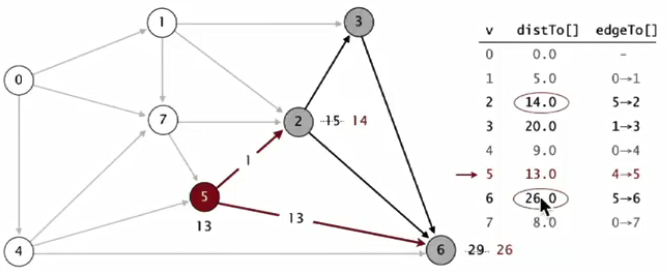
(6)如此重复上述过程,得到最终结果(s到其他点的最短路径)
3.代码实现:

package com.cx.graph; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.IndexMinPQ; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.Stack; public class DijkstraSP { //从s到v的最短路径上的最后一条边 private DirectedEdge[] edgeTo; //从s到v的已知最短路径的长度 private double[] distTo; private IndexMinPQ<Double> pq; public DijkstraSP(EdgeWeightedDigraph G,int s) { edgeTo=new DirectedEdge[G.V()]; distTo=new double[G.V()]; pq=new IndexMinPQ<Double>(G.V()); //初始化distTo[s]=0,其他的为无穷大 for(int v=0;v<G.V();v++) distTo[v]=Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY; distTo[s]=0.0; //将起点放入队列 pq.insert(s, 0.0); while(!pq.isEmpty()) { //根据到s的距离进行边的松弛 int v=pq.delMin(); for(DirectedEdge e:G.adj(v)) relax(e); } } private void relax(DirectedEdge e) { int v=e.from(),w=e.to(); //边的松弛 if(distTo[w]>distTo[v]+e.weight()) { //更新distTo和edgeTo distTo[w]=distTo[v]+e.weight(); edgeTo[w]=e; //还需要更新优先级队列 if(pq.contains(w)) pq.decreaseKey(w, distTo(w)); else pq.insert(w, distTo(w)); } } private double distTo(int v) { return distTo[v]; } public boolean hasPathTo(int v) { return distTo[v]<Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY; } public Iterable<DirectedEdge> pathTo(int v){ if(!hasPathTo(v)) return null; Stack<DirectedEdge> path=new Stack<DirectedEdge>(); for(DirectedEdge e=edgeTo[v];e!=null;e=edgeTo[e.from()]) path.push(e); return path; } }

/****************************************************************************** * Compilation: javac IndexMinPQ.java * Execution: java IndexMinPQ * Dependencies: StdOut.java * * Minimum-oriented indexed PQ implementation using a binary heap. * ******************************************************************************/ package edu.princeton.cs.algs4; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.NoSuchElementException; /** * The {@code IndexMinPQ} class represents an indexed priority queue of generic keys. * It supports the usual <em>insert</em> and <em>delete-the-minimum</em> * operations, along with <em>delete</em> and <em>change-the-key</em> * methods. In order to let the client refer to keys on the priority queue, * an integer between {@code 0} and {@code maxN - 1} * is associated with each key鈥攖he client uses this integer to specify * which key to delete or change. * It also supports methods for peeking at the minimum key, * testing if the priority queue is empty, and iterating through * the keys. * <p> * This implementation uses a binary heap along with an array to associate * keys with integers in the given range. * The <em>insert</em>, <em>delete-the-minimum</em>, <em>delete</em>, * <em>change-key</em>, <em>decrease-key</em>, and <em>increase-key</em> * operations take logarithmic time. * The <em>is-empty</em>, <em>size</em>, <em>min-index</em>, <em>min-key</em>, * and <em>key-of</em> operations take constant time. * Construction takes time proportional to the specified capacity. * <p> * For additional documentation, see <a href="http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/24pq">Section 2.4</a> of * <i>Algorithms, 4th Edition</i> by Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne. * * @author Robert Sedgewick * @author Kevin Wayne * * @param <Key> the generic type of key on this priority queue */ public class IndexMinPQ<Key extends Comparable<Key>> implements Iterable<Integer> { private int maxN; // maximum number of elements on PQ private int n; // number of elements on PQ private int[] pq; // binary heap using 1-based indexing private int[] qp; // inverse of pq - qp[pq[i]] = pq[qp[i]] = i private Key[] keys; // keys[i] = priority of i /** * Initializes an empty indexed priority queue with indices between {@code 0} * and {@code maxN - 1}. * @param maxN the keys on this priority queue are index from {@code 0} * {@code maxN - 1} * @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code maxN < 0} */ public IndexMinPQ(int maxN) { if (maxN < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException(); this.maxN = maxN; n = 0; keys = (Key[]) new Comparable[maxN + 1]; // make this of length maxN?? pq = new int[maxN + 1]; qp = new int[maxN + 1]; // make this of length maxN?? for (int i = 0; i <= maxN; i++) qp[i] = -1; } /** * Returns true if this priority queue is empty. * * @return {@code true} if this priority queue is empty; * {@code false} otherwise */ public boolean isEmpty() { return n == 0; } /** * Is {@code i} an index on this priority queue? * * @param i an index * @return {@code true} if {@code i} is an index on this priority queue; * {@code false} otherwise * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException unless {@code 0 <= i < maxN} */ public boolean contains(int i) { if (i < 0 || i >= maxN) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(); return qp[i] != -1; } /** * Returns the number of keys on this priority queue. * * @return the number of keys on this priority queue */ public int size() { return n; } /** * Associates key with index {@code i}. * * @param i an index * @param key the key to associate with index {@code i} * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException unless {@code 0 <= i < maxN} * @throws IllegalArgumentException if there already is an item associated * with index {@code i} */ public void insert(int i, Key key) { if (i < 0 || i >= maxN) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(); if (contains(i)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("index is already in the priority queue"); n++; qp[i] = n; pq[n] = i; keys[i] = key; swim(n); } /** * Returns an index associated with a minimum key. * * @return an index associated with a minimum key * @throws NoSuchElementException if this priority queue is empty */ public int minIndex() { if (n == 0) throw new NoSuchElementException("Priority queue underflow"); return pq[1]; } /** * Returns a minimum key. * * @return a minimum key * @throws NoSuchElementException if this priority queue is empty */ public Key minKey() { if (n == 0) throw new NoSuchElementException("Priority queue underflow"); return keys[pq[1]]; } /** * Removes a minimum key and returns its associated index. * @return an index associated with a minimum key * @throws NoSuchElementException if this priority queue is empty */ public int delMin() { if (n == 0) throw new NoSuchElementException("Priority queue underflow"); int min = pq[1]; exch(1, n--); sink(1); assert min == pq[n+1]; qp[min] = -1; // delete keys[min] = null; // to help with garbage collection pq[n+1] = -1; // not needed return min; } /** * Returns the key associated with index {@code i}. * * @param i the index of the key to return * @return the key associated with index {@code i} * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException unless {@code 0 <= i < maxN} * @throws NoSuchElementException no key is associated with index {@code i} */ public Key keyOf(int i) { if (i < 0 || i >= maxN) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(); if (!contains(i)) throw new NoSuchElementException("index is not in the priority queue"); else return keys[i]; } /** * Change the key associated with index {@code i} to the specified value. * * @param i the index of the key to change * @param key change the key associated with index {@code i} to this key * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException unless {@code 0 <= i < maxN} * @throws NoSuchElementException no key is associated with index {@code i} */ public void changeKey(int i, Key key) { if (i < 0 || i >= maxN) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(); if (!contains(i)) throw new NoSuchElementException("index is not in the priority queue"); keys[i] = key; swim(qp[i]); sink(qp[i]); } /** * Change the key associated with index {@code i} to the specified value. * * @param i the index of the key to change * @param key change the key associated with index {@code i} to this key * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException unless {@code 0 <= i < maxN} * @deprecated Replaced by {@code changeKey(int, Key)}. */ @Deprecated public void change(int i, Key key) { changeKey(i, key); } /** * Decrease the key associated with index {@code i} to the specified value. * * @param i the index of the key to decrease * @param key decrease the key associated with index {@code i} to this key * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException unless {@code 0 <= i < maxN} * @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code key >= keyOf(i)} * @throws NoSuchElementException no key is associated with index {@code i} */ public void decreaseKey(int i, Key key) { if (i < 0 || i >= maxN) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(); if (!contains(i)) throw new NoSuchElementException("index is not in the priority queue"); if (keys[i].compareTo(key) <= 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Calling decreaseKey() with given argument would not strictly decrease the key"); keys[i] = key; swim(qp[i]); } /** * Increase the key associated with index {@code i} to the specified value. * * @param i the index of the key to increase * @param key increase the key associated with index {@code i} to this key * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException unless {@code 0 <= i < maxN} * @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code key <= keyOf(i)} * @throws NoSuchElementException no key is associated with index {@code i} */ public void increaseKey(int i, Key key) { if (i < 0 || i >= maxN) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(); if (!contains(i)) throw new NoSuchElementException("index is not in the priority queue"); if (keys[i].compareTo(key) >= 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Calling increaseKey() with given argument would not strictly increase the key"); keys[i] = key; sink(qp[i]); } /** * Remove the key associated with index {@code i}. * * @param i the index of the key to remove * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException unless {@code 0 <= i < maxN} * @throws NoSuchElementException no key is associated with index {@code i} */ public void delete(int i) { if (i < 0 || i >= maxN) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(); if (!contains(i)) throw new NoSuchElementException("index is not in the priority queue"); int index = qp[i]; exch(index, n--); swim(index); sink(index); keys[i] = null; qp[i] = -1; } /*************************************************************************** * General helper functions. ***************************************************************************/ private boolean greater(int i, int j) { return keys[pq[i]].compareTo(keys[pq[j]]) > 0; } private void exch(int i, int j) { int swap = pq[i]; pq[i] = pq[j]; pq[j] = swap; qp[pq[i]] = i; qp[pq[j]] = j; } /*************************************************************************** * Heap helper functions. ***************************************************************************/ private void swim(int k) { while (k > 1 && greater(k/2, k)) { exch(k, k/2); k = k/2; } } private void sink(int k) { while (2*k <= n) { int j = 2*k; if (j < n && greater(j, j+1)) j++; if (!greater(k, j)) break; exch(k, j); k = j; } } /*************************************************************************** * Iterators. ***************************************************************************/ /** * Returns an iterator that iterates over the keys on the * priority queue in ascending order. * The iterator doesn't implement {@code remove()} since it's optional. * * @return an iterator that iterates over the keys in ascending order */ public Iterator<Integer> iterator() { return new HeapIterator(); } private class HeapIterator implements Iterator<Integer> { // create a new pq private IndexMinPQ<Key> copy; // add all elements to copy of heap // takes linear time since already in heap order so no keys move public HeapIterator() { copy = new IndexMinPQ<Key>(pq.length - 1); for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) copy.insert(pq[i], keys[pq[i]]); } public boolean hasNext() { return !copy.isEmpty(); } public void remove() { throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); } public Integer next() { if (!hasNext()) throw new NoSuchElementException(); return copy.delMin(); } } /** * Unit tests the {@code IndexMinPQ} data type. * * @param args the command-line arguments */ public static void main(String[] args) { // insert a bunch of strings String[] strings = { "it", "was", "the", "best", "of", "times", "it", "was", "the", "worst" }; IndexMinPQ<String> pq = new IndexMinPQ<String>(strings.length); for (int i = 0; i < strings.length; i++) { pq.insert(i, strings[i]); } // delete and print each key while (!pq.isEmpty()) { int i = pq.delMin(); StdOut.println(i + " " + strings[i]); } StdOut.println(); // reinsert the same strings for (int i = 0; i < strings.length; i++) { pq.insert(i, strings[i]); } // print each key using the iterator for (int i : pq) { StdOut.println(i + " " + strings[i]); } while (!pq.isEmpty()) { pq.delMin(); } } } /****************************************************************************** * Copyright 2002-2016, Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne. * * This file is part of algs4.jar, which accompanies the textbook * * Algorithms, 4th edition by Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne, * Addison-Wesley Professional, 2011, ISBN 0-321-57351-X. * http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu * * * algs4.jar is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or * (at your option) any later version. * * algs4.jar is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the * GNU General Public License for more details. * * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License * along with algs4.jar. If not, see http://www.gnu.org/licenses. ******************************************************************************/

/****************************************************************************** * Compilation: javac Stack.java * Execution: java Stack < input.txt * Dependencies: StdIn.java StdOut.java * Data files: http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/13stacks/tobe.txt * * A generic stack, implemented using a singly-linked list. * Each stack element is of type Item. * * This version uses a static nested class Node (to save 8 bytes per * Node), whereas the version in the textbook uses a non-static nested * class (for simplicity). * * % more tobe.txt * to be or not to - be - - that - - - is * * % java Stack < tobe.txt * to be not that or be (2 left on stack) * ******************************************************************************/ package edu.princeton.cs.algs4; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.NoSuchElementException; /** * The {@code Stack} class represents a last-in-first-out (LIFO) stack of generic items. * It supports the usual <em>push</em> and <em>pop</em> operations, along with methods * for peeking at the top item, testing if the stack is empty, and iterating through * the items in LIFO order. * <p> * This implementation uses a singly-linked list with a static nested class for * linked-list nodes. See {@link LinkedStack} for the version from the * textbook that uses a non-static nested class. * The <em>push</em>, <em>pop</em>, <em>peek</em>, <em>size</em>, and <em>is-empty</em> * operations all take constant time in the worst case. * <p> * For additional documentation, * see <a href="http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/13stacks">Section 1.3</a> of * <i>Algorithms, 4th Edition</i> by Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne. * * @author Robert Sedgewick * @author Kevin Wayne * * @param <Item> the generic type of an item in this stack */ public class Stack<Item> implements Iterable<Item> { private Node<Item> first; // top of stack private int n; // size of the stack // helper linked list class private static class Node<Item> { private Item item; private Node<Item> next; } /** * Initializes an empty stack. */ public Stack() { first = null; n = 0; } /** * Returns true if this stack is empty. * * @return true if this stack is empty; false otherwise */ public boolean isEmpty() { return first == null; } /** * Returns the number of items in this stack. * * @return the number of items in this stack */ public int size() { return n; } /** * Adds the item to this stack. * * @param item the item to add */ public void push(Item item) { Node<Item> oldfirst = first; first = new Node<Item>(); first.item = item; first.next = oldfirst; n++; } /** * Removes and returns the item most recently added to this stack. * * @return the item most recently added * @throws NoSuchElementException if this stack is empty */ public Item pop() { if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("Stack underflow"); Item item = first.item; // save item to return first = first.next; // delete first node n--; return item; // return the saved item } /** * Returns (but does not remove) the item most recently added to this stack. * * @return the item most recently added to this stack * @throws NoSuchElementException if this stack is empty */ public Item peek() { if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("Stack underflow"); return first.item; } /** * Returns a string representation of this stack. * * @return the sequence of items in this stack in LIFO order, separated by spaces */ public String toString() { StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder(); for (Item item : this) { s.append(item); s.append(' '); } return s.toString(); } /** * Returns an iterator to this stack that iterates through the items in LIFO order. * * @return an iterator to this stack that iterates through the items in LIFO order */ public Iterator<Item> iterator() { return new ListIterator<Item>(first); } // an iterator, doesn't implement remove() since it's optional private class ListIterator<Item> implements Iterator<Item> { private Node<Item> current; public ListIterator(Node<Item> first) { current = first; } public boolean hasNext() { return current != null; } public void remove() { throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); } public Item next() { if (!hasNext()) throw new NoSuchElementException(); Item item = current.item; current = current.next; return item; } } /** * Unit tests the {@code Stack} data type. * * @param args the command-line arguments */ public static void main(String[] args) { Stack<String> stack = new Stack<String>(); while (!StdIn.isEmpty()) { String item = StdIn.readString(); if (!item.equals("-")) stack.push(item); else if (!stack.isEmpty()) StdOut.print(stack.pop() + " "); } StdOut.println("(" + stack.size() + " left on stack)"); } } /****************************************************************************** * Copyright 2002-2016, Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne. * * This file is part of algs4.jar, which accompanies the textbook * * Algorithms, 4th edition by Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne, * Addison-Wesley Professional, 2011, ISBN 0-321-57351-X. * http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu * * * algs4.jar is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or * (at your option) any later version. * * algs4.jar is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the * GNU General Public License for more details. * * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License * along with algs4.jar. If not, see http://www.gnu.org/licenses. ******************************************************************************/

package com.cx.graph; public class DirectedEdge { private final int v,w; private final double weight; public DirectedEdge(int v,int w,double weight) { //有向边的起点,终点和权重 this.v=v; this.w=w; this.weight=weight; } public int from() { return v; } public int to() { return w; } public double weight() { return weight; } }
4.说明:该算法在最坏的情况下需要的空间与V成正比,所需的时间与ElogV成正比。
5.Dijkstra算法在右负数权重的边时不起作用。

一个尝试:给每条边添加一个相等的权重,使得没有负数权重的边存在。
例如对上面的图,每条边加上9.得到如下图形:
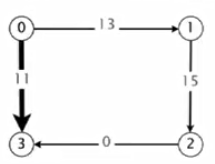
但是,依然是0处理完后处理3,会得到0->3,但它不是最短路。所以这种方式依然不可取。
三.拓扑排序算法
1.算法前提:只能用该算法处理无环的加权有向图,能够保证在线性时间内(和E+V成正比)解决单点最短路径问题
2.算法思想:(边的放松顺序为点的拓扑顺序)
(1)按照拓扑顺序考虑点
(2)将其他从这个点出发的边进行边的松弛操作。
3.举例
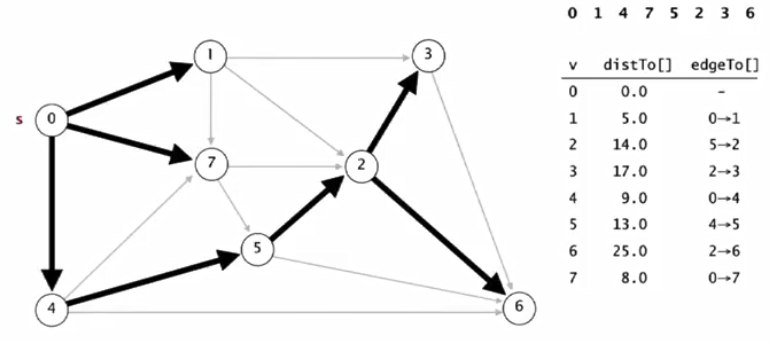
4.代码实现

package com.cx.graph; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.Stack; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.Topological; public class AcyclicSP { private DirectedEdge[] edgeTo; private double[] distTo; public AcyclicSP(EdgeWeightedDigraph G,int s) { edgeTo=new DirectedEdge[G.V()]; distTo=new double[G.V()]; for(int v=0;v<G.V();v++) distTo[v]=Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY; distTo[s]=0.0; //获得拓扑顺序 Topological topological=new Topological(G); for(int v:topological.order()) for(DirectedEdge e:G.adj(v)) relax(e); } private void relax(DirectedEdge e) { int v=e.from(),w=e.to(); //边的松弛 if(distTo[w]>distTo[v]+e.weight()) { //更新distTo和edgeTo distTo[w]=distTo[v]+e.weight(); edgeTo[w]=e; } } private double distTo(int v) { return distTo[v]; } public boolean hasPathTo(int v) { return distTo[v]<Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY; } public Iterable<DirectedEdge> pathTo(int v){ if(!hasPathTo(v)) return null; Stack<DirectedEdge> path=new Stack<DirectedEdge>(); for(DirectedEdge e=edgeTo[v];e!=null;e=edgeTo[e.from()]) path.push(e); return path; } }
5.应用

6.无环加权有向图中的最长路径问题:(因为这里允许负数的权重,所有可以用与无环加权有向图中的最短路径问题几乎相同的方法解决该问题)
(1)将所有权重取相反数
(2)找出最短路径
(3)将结果的权重取相反数
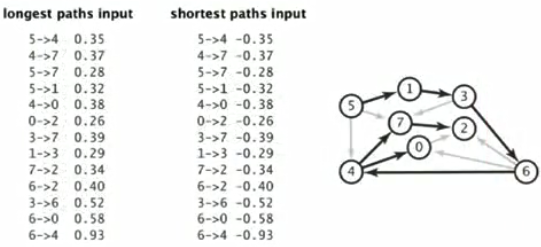
7.无环加权有向图中的最长路径问题的应用:优先级限制下的并行任务调度问题
(1)问题描述:给定一组需要完成的任务和每个任务所需要的时间,以及任务完成的先后次序的优先级限制。如何在若干相同的处理器上(数量不限)安排任务(需要对于每一个任务确定开始时间)并在最短的时间内完成所有的任务?
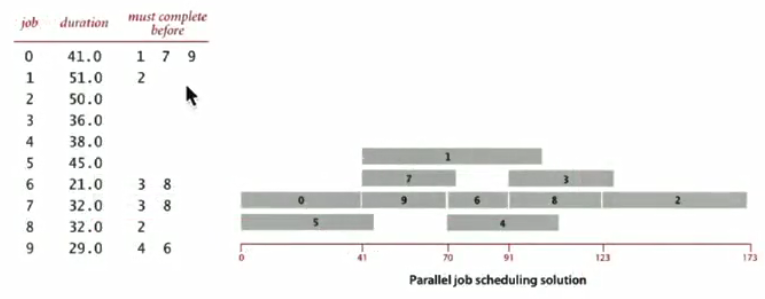
这个问题类似于工厂生产汽车,每道工序需要时间,有些工序受到优先级的限制,例如刷漆受到必须在组装完成以后。任务在满足条件的情况下可以并行的进行,希望合理调配从而更快的加工完汽车。
(2)为了解决优先级限制下的并行任务调度问题,可以构建一个边赋权的有向无环图
①添加一个总任务开始和总任务结束(source-end)的顶点
②对于每个任务来说,用两个顶点表示(开始和结束start-end)
③对于每个任务有三种边
-开始到结束(start-end),权重和任务需要的时间相等
-总任务开始source到开始start,权重为0
-结束end到总任务结束sink,权重为0
④对于每一个优先级限制来说用一条边表示,权重为0
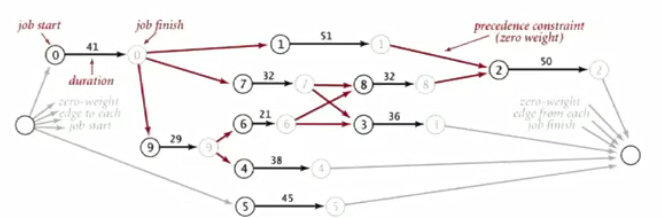
⑤每个任务的开始时间即为从起点到它的起始顶点的最长距离。
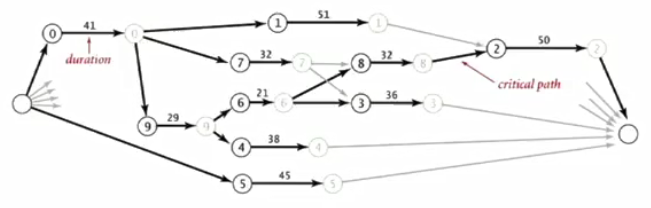
(3)转化以后可以在线性时间内解决该问题。
四.Bellman-Ford算法
1.负权重环:一个总权重(环上所有边的权重之和)为负的有向环。
2.最短路径存在当且仅当没有负权重环存在。因为,在负权重环存在时,可以用这个负权重环构造任意小的路径,此时最短路径问题没有意义。
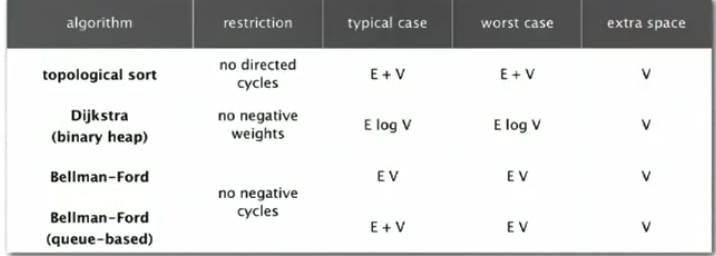
3.Bellman-Ford算法:重复V轮,每一轮以任意的顺序(假设都是按照0-V-1的顺序)放松所有的边。需要的时间和EV成正比。
代码实现:

for(int pass=0;pass<G.V();pass++) for(int v=0;v<G.V();v++) for(DirectedEdge e:G.adj(v)) relax(e);
4.改进:
(1)可以观察到:如果distTo[v]在第i轮不改变,那么在第i+!轮也没有必要对从v射出的边进行放松操作。
(2)因此,可以维持一个队列,在这个队列存放distTo[v]改变的顶点。值得注意的是对于队列中的每个顶点最多只能有一个份。
(3)性能:虽然在最坏的情况下,所需的时间依然与E*V成正比,但是在实际使用中,比最坏情况快得多
5.总结: