4.3 最小生成树
一.最小生成树的简介(Minimum spanning trees)
1.最小生成树:给定一幅无向图,它的边具有不同的权值。最小生成树指具有最小权值之和的生成树。
生成树指包含所有顶点的无环连通子图。
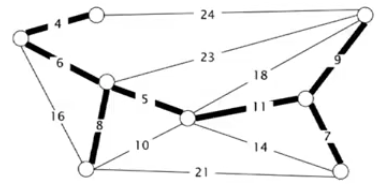
2.两个假定:为了简化讨论,以保证MST存在并且唯一
(1)边的权重是不同的
(2)只考虑连通图
3.切分(cut):指将图的所有顶点分为两个非空且不重叠的两个集合。
横切边(crossing edge)是一条连接两个属于不同集合的顶点的边
4.切分定理:给定任意的切分,它的横切边中权重最小者必然属于图的最小生成树
5.贪心算法:利用上面的切分定理,有如下算法:
(1)初始所有边涂为灰色
(2)找到没有黑色横切边的切分,并将它的最小权重的边涂为黑色
(3)重复上述过程直到V-1条边被涂为黑色
6.基于上述贪心算法的思想,有如下几种有效的实现算法:
(1)Kruskal's algorithm
(2)Prim's algorithm
(3)Boruvka's algorithm
7.加权无向图的表示。在不带权的无向图中是在Bag中放顶点,这里是在Bag中放Edge对象。每个Edge对象使用两个端点和边的权重构成的。

package com.cx.graph; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.Bag; //无向图的表示 public class EdgeWeightedGraph { private final int V; //Bag组成的数组,Bag中每一个元素时Edge类 private Bag<Edge>[] adj; //初始化V个顶点的图 public EdgeWeightedGraph(int V) { this.V=V; adj=(Bag<Edge>[])new Bag[V]; //将每个元素初始化,不然会为null for(int v=0;v<V;v++) { adj[v]=new Bag<Edge>(); } } //传入一条边,从而给对应的端点添加该边 public void addEdge(Edge edge) { //获得这条边的两个端点 int v=edge.either(); int w=edge.other(v); adj[v].add(edge); adj[w].add(edge); } //包含该顶点的所有边 public Iterable<Edge> adj(int v){ return adj[v]; } public int V() { return V; } //返回加权无向图的所有边 public Iterable<Edge> edges(){ Bag<Edge> bag=new Bag<Edge>(); for(int v=0;v<V;v++) for(Edge e:adj[v]) if(e.other(v)>v) bag.add(e); return bag; } }

package com.cx.graph; public class Edge implements Comparable<Edge>{ //定义边的两个端点以及边的权重 private final int v,w; private final double weight; public Edge(int v,int w,double weight) { this.v=v; this.w=w; this.weight=weight; } //返回边两端的顶点之一 public int either() { return v; } //返回边的另一个顶点 public int other(int vertex) { if(vertex==v) return w; else return v; } public int compareTo(Edge that) { if(this.weight>that.weight) return 1; else if(this.weight<that.weight) return -1; else return 0; } }
二.Kruskal算法
1.思想:将边按照权重大小按照递增的顺序排列,只要不形成环,就将下一条边加入到树T中。直到V-1条边被加入到T中为止。
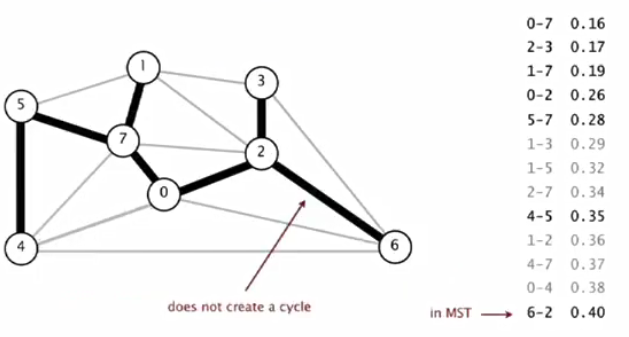
2.关键问题:添加一条边v-w到T是否会形成环?
法一:使用4.1中的方法,以v为起点,使用DFS,判断添加边之前w是否可达。若可达,则添加边以后会形成环。(这里进行一次判断的时间与V成正比)
法二:使用之前的union-find数据结构,即(这里进行一次判断的时间logV)
(1)对T中每一个连通分量维持一个集合
(2)如果v和w在相同的集合中,那么增加v-w会形成环(uf.connected(v, w))
(3)否则将v-w加入到T,并将v和w的集合合并(uf.union(v, w))
3.实现代码:

package com.cx.graph; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.MinPQ; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.Queue; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.UF; public class KruskalMST { private Queue<Edge> mst =new Queue<Edge>(); public KruskalMST(EdgeWeightedGraph G) { MinPQ<Edge> pq=new MinPQ<Edge>(); for(Edge e:G.edges()) //使用优先级队列来维持边 pq.insert(e); UF uf=new UF(G.V()); //直到mst的元素个数为V-1 while(!pq.isEmpty() && mst.size()<G.V()-1) { //每次取最小的边 Edge e=pq.delMin(); int v=e.either(), w=e.other(v); //判断e的两个顶点是否会在T中形成环 //不在相同的连通分量中即可加入T if(!uf.connected(v, w)) { //union两个连通分量 uf.union(v, w); //将边放入mst mst.enqueue(e); } } } public Iterable<Edge> edges(){ return mst; } }

/****************************************************************************** * Compilation: javac Queue.java * Execution: java Queue < input.txt * Dependencies: StdIn.java StdOut.java * Data files: http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/13stacks/tobe.txt * * A generic queue, implemented using a linked list. * * % java Queue < tobe.txt * to be or not to be (2 left on queue) * ******************************************************************************/ package edu.princeton.cs.algs4; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.NoSuchElementException; /** * The {@code Queue} class represents a first-in-first-out (FIFO) * queue of generic items. * It supports the usual <em>enqueue</em> and <em>dequeue</em> * operations, along with methods for peeking at the first item, * testing if the queue is empty, and iterating through * the items in FIFO order. * <p> * This implementation uses a singly-linked list with a static nested class for * linked-list nodes. See {@link LinkedQueue} for the version from the * textbook that uses a non-static nested class. * The <em>enqueue</em>, <em>dequeue</em>, <em>peek</em>, <em>size</em>, and <em>is-empty</em> * operations all take constant time in the worst case. * <p> * For additional documentation, see <a href="http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/13stacks">Section 1.3</a> of * <i>Algorithms, 4th Edition</i> by Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne. * * @author Robert Sedgewick * @author Kevin Wayne * * @param <Item> the generic type of an item in this queue */ public class Queue<Item> implements Iterable<Item> { private Node<Item> first; // beginning of queue private Node<Item> last; // end of queue private int n; // number of elements on queue // helper linked list class private static class Node<Item> { private Item item; private Node<Item> next; } /** * Initializes an empty queue. */ public Queue() { first = null; last = null; n = 0; } /** * Returns true if this queue is empty. * * @return {@code true} if this queue is empty; {@code false} otherwise */ public boolean isEmpty() { return first == null; } /** * Returns the number of items in this queue. * * @return the number of items in this queue */ public int size() { return n; } /** * Returns the item least recently added to this queue. * * @return the item least recently added to this queue * @throws NoSuchElementException if this queue is empty */ public Item peek() { if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("Queue underflow"); return first.item; } /** * Adds the item to this queue. * * @param item the item to add */ public void enqueue(Item item) { Node<Item> oldlast = last; last = new Node<Item>(); last.item = item; last.next = null; if (isEmpty()) first = last; else oldlast.next = last; n++; } /** * Removes and returns the item on this queue that was least recently added. * * @return the item on this queue that was least recently added * @throws NoSuchElementException if this queue is empty */ public Item dequeue() { if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("Queue underflow"); Item item = first.item; first = first.next; n--; if (isEmpty()) last = null; // to avoid loitering return item; } /** * Returns a string representation of this queue. * * @return the sequence of items in FIFO order, separated by spaces */ public String toString() { StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder(); for (Item item : this) { s.append(item); s.append(' '); } return s.toString(); } /** * Returns an iterator that iterates over the items in this queue in FIFO order. * * @return an iterator that iterates over the items in this queue in FIFO order */ public Iterator<Item> iterator() { return new ListIterator<Item>(first); } // an iterator, doesn't implement remove() since it's optional private class ListIterator<Item> implements Iterator<Item> { private Node<Item> current; public ListIterator(Node<Item> first) { current = first; } public boolean hasNext() { return current != null; } public void remove() { throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); } public Item next() { if (!hasNext()) throw new NoSuchElementException(); Item item = current.item; current = current.next; return item; } } /** * Unit tests the {@code Queue} data type. * * @param args the command-line arguments */ public static void main(String[] args) { Queue<String> queue = new Queue<String>(); while (!StdIn.isEmpty()) { String item = StdIn.readString(); if (!item.equals("-")) queue.enqueue(item); else if (!queue.isEmpty()) StdOut.print(queue.dequeue() + " "); } StdOut.println("(" + queue.size() + " left on queue)"); } } /****************************************************************************** * Copyright 2002-2016, Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne. * * This file is part of algs4.jar, which accompanies the textbook * * Algorithms, 4th edition by Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne, * Addison-Wesley Professional, 2011, ISBN 0-321-57351-X. * http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu * * * algs4.jar is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or * (at your option) any later version. * * algs4.jar is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the * GNU General Public License for more details. * * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License * along with algs4.jar. If not, see http://www.gnu.org/licenses. ******************************************************************************/

/****************************************************************************** * Compilation: javac MinPQ.java * Execution: java MinPQ < input.txt * Dependencies: StdIn.java StdOut.java * Data files: http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/24pq/tinyPQ.txt * * Generic min priority queue implementation with a binary heap. * Can be used with a comparator instead of the natural order. * * % java MinPQ < tinyPQ.txt * E A E (6 left on pq) * * We use a one-based array to simplify parent and child calculations. * * Can be optimized by replacing full exchanges with half exchanges * (ala insertion sort). * ******************************************************************************/ package edu.princeton.cs.algs4; import java.util.Comparator; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.NoSuchElementException; /** * The {@code MinPQ} class represents a priority queue of generic keys. * It supports the usual <em>insert</em> and <em>delete-the-minimum</em> * operations, along with methods for peeking at the minimum key, * testing if the priority queue is empty, and iterating through * the keys. * <p> * This implementation uses a binary heap. * The <em>insert</em> and <em>delete-the-minimum</em> operations take * logarithmic amortized time. * The <em>min</em>, <em>size</em>, and <em>is-empty</em> operations take constant time. * Construction takes time proportional to the specified capacity or the number of * items used to initialize the data structure. * <p> * For additional documentation, see <a href="http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/24pq">Section 2.4</a> of * <i>Algorithms, 4th Edition</i> by Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne. * * @author Robert Sedgewick * @author Kevin Wayne * * @param <Key> the generic type of key on this priority queue */ public class MinPQ<Key> implements Iterable<Key> { private Key[] pq; // store items at indices 1 to n private int n; // number of items on priority queue private Comparator<Key> comparator; // optional comparator /** * Initializes an empty priority queue with the given initial capacity. * * @param initCapacity the initial capacity of this priority queue */ public MinPQ(int initCapacity) { pq = (Key[]) new Object[initCapacity + 1]; n = 0; } /** * Initializes an empty priority queue. */ public MinPQ() { this(1); } /** * Initializes an empty priority queue with the given initial capacity, * using the given comparator. * * @param initCapacity the initial capacity of this priority queue * @param comparator the order to use when comparing keys */ public MinPQ(int initCapacity, Comparator<Key> comparator) { this.comparator = comparator; pq = (Key[]) new Object[initCapacity + 1]; n = 0; } /** * Initializes an empty priority queue using the given comparator. * * @param comparator the order to use when comparing keys */ public MinPQ(Comparator<Key> comparator) { this(1, comparator); } /** * Initializes a priority queue from the array of keys. * <p> * Takes time proportional to the number of keys, using sink-based heap construction. * * @param keys the array of keys */ public MinPQ(Key[] keys) { n = keys.length; pq = (Key[]) new Object[keys.length + 1]; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) pq[i+1] = keys[i]; for (int k = n/2; k >= 1; k--) sink(k); assert isMinHeap(); } /** * Returns true if this priority queue is empty. * * @return {@code true} if this priority queue is empty; * {@code false} otherwise */ public boolean isEmpty() { return n == 0; } /** * Returns the number of keys on this priority queue. * * @return the number of keys on this priority queue */ public int size() { return n; } /** * Returns a smallest key on this priority queue. * * @return a smallest key on this priority queue * @throws NoSuchElementException if this priority queue is empty */ public Key min() { if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("Priority queue underflow"); return pq[1]; } // helper function to double the size of the heap array private void resize(int capacity) { assert capacity > n; Key[] temp = (Key[]) new Object[capacity]; for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { temp[i] = pq[i]; } pq = temp; } /** * Adds a new key to this priority queue. * * @param x the key to add to this priority queue */ public void insert(Key x) { // double size of array if necessary if (n == pq.length - 1) resize(2 * pq.length); // add x, and percolate it up to maintain heap invariant pq[++n] = x; swim(n); assert isMinHeap(); } /** * Removes and returns a smallest key on this priority queue. * * @return a smallest key on this priority queue * @throws NoSuchElementException if this priority queue is empty */ public Key delMin() { if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("Priority queue underflow"); exch(1, n); Key min = pq[n--]; sink(1); pq[n+1] = null; // avoid loitering and help with garbage collection if ((n > 0) && (n == (pq.length - 1) / 4)) resize(pq.length / 2); assert isMinHeap(); return min; } /*************************************************************************** * Helper functions to restore the heap invariant. ***************************************************************************/ private void swim(int k) { while (k > 1 && greater(k/2, k)) { exch(k, k/2); k = k/2; } } private void sink(int k) { while (2*k <= n) { int j = 2*k; if (j < n && greater(j, j+1)) j++; if (!greater(k, j)) break; exch(k, j); k = j; } } /*************************************************************************** * Helper functions for compares and swaps. ***************************************************************************/ private boolean greater(int i, int j) { if (comparator == null) { return ((Comparable<Key>) pq[i]).compareTo(pq[j]) > 0; } else { return comparator.compare(pq[i], pq[j]) > 0; } } private void exch(int i, int j) { Key swap = pq[i]; pq[i] = pq[j]; pq[j] = swap; } // is pq[1..N] a min heap? private boolean isMinHeap() { return isMinHeap(1); } // is subtree of pq[1..n] rooted at k a min heap? private boolean isMinHeap(int k) { if (k > n) return true; int left = 2*k; int right = 2*k + 1; if (left <= n && greater(k, left)) return false; if (right <= n && greater(k, right)) return false; return isMinHeap(left) && isMinHeap(right); } /** * Returns an iterator that iterates over the keys on this priority queue * in ascending order. * <p> * The iterator doesn't implement {@code remove()} since it's optional. * * @return an iterator that iterates over the keys in ascending order */ public Iterator<Key> iterator() { return new HeapIterator(); } private class HeapIterator implements Iterator<Key> { // create a new pq private MinPQ<Key> copy; // add all items to copy of heap // takes linear time since already in heap order so no keys move public HeapIterator() { if (comparator == null) copy = new MinPQ<Key>(size()); else copy = new MinPQ<Key>(size(), comparator); for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) copy.insert(pq[i]); } public boolean hasNext() { return !copy.isEmpty(); } public void remove() { throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); } public Key next() { if (!hasNext()) throw new NoSuchElementException(); return copy.delMin(); } } /** * Unit tests the {@code MinPQ} data type. * * @param args the command-line arguments */ public static void main(String[] args) { MinPQ<String> pq = new MinPQ<String>(); while (!StdIn.isEmpty()) { String item = StdIn.readString(); if (!item.equals("-")) pq.insert(item); else if (!pq.isEmpty()) StdOut.print(pq.delMin() + " "); } StdOut.println("(" + pq.size() + " left on pq)"); } } /****************************************************************************** * Copyright 2002-2016, Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne. * * This file is part of algs4.jar, which accompanies the textbook * * Algorithms, 4th edition by Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne, * Addison-Wesley Professional, 2011, ISBN 0-321-57351-X. * http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu * * * algs4.jar is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or * (at your option) any later version. * * algs4.jar is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the * GNU General Public License for more details. * * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License * along with algs4.jar. If not, see http://www.gnu.org/licenses. ******************************************************************************/

/****************************************************************************** * Compilation: javac UF.java * Execution: java UF < input.txt * Dependencies: StdIn.java StdOut.java * Data files: http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/15uf/tinyUF.txt * http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/15uf/mediumUF.txt * http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/15uf/largeUF.txt * * Weighted quick-union by rank with path compression by halving. * * % java UF < tinyUF.txt * 4 3 * 3 8 * 6 5 * 9 4 * 2 1 * 5 0 * 7 2 * 6 1 * 2 components * ******************************************************************************/ package edu.princeton.cs.algs4; /** * The {@code UF} class represents a <em>union鈥揻ind data type</em> * (also known as the <em>disjoint-sets data type</em>). * It supports the <em>union</em> and <em>find</em> operations, * along with a <em>connected</em> operation for determining whether * two sites are in the same component and a <em>count</em> operation that * returns the total number of components. * <p> * The union鈥揻ind data type models connectivity among a set of <em>n</em> * sites, named 0 through <em>n</em>−1. * The <em>is-connected-to</em> relation must be an * <em>equivalence relation</em>: * <ul> * <li> <em>Reflexive</em>: <em>p</em> is connected to <em>p</em>. * <li> <em>Symmetric</em>: If <em>p</em> is connected to <em>q</em>, * then <em>q</em> is connected to <em>p</em>. * <li> <em>Transitive</em>: If <em>p</em> is connected to <em>q</em> * and <em>q</em> is connected to <em>r</em>, then * <em>p</em> is connected to <em>r</em>. * </ul> * <p> * An equivalence relation partitions the sites into * <em>equivalence classes</em> (or <em>components</em>). In this case, * two sites are in the same component if and only if they are connected. * Both sites and components are identified with integers between 0 and * <em>n</em>−1. * Initially, there are <em>n</em> components, with each site in its * own component. The <em>component identifier</em> of a component * (also known as the <em>root</em>, <em>canonical element</em>, <em>leader</em>, * or <em>set representative</em>) is one of the sites in the component: * two sites have the same component identifier if and only if they are * in the same component. * <ul> * <li><em>union</em>(<em>p</em>, <em>q</em>) adds a * connection between the two sites <em>p</em> and <em>q</em>. * If <em>p</em> and <em>q</em> are in different components, * then it replaces * these two components with a new component that is the union of * the two. * <li><em>find</em>(<em>p</em>) returns the component * identifier of the component containing <em>p</em>. * <li><em>connected</em>(<em>p</em>, <em>q</em>) * returns true if both <em>p</em> and <em>q</em> * are in the same component, and false otherwise. * <li><em>count</em>() returns the number of components. * </ul> * <p> * The component identifier of a component can change * only when the component itself changes during a call to * <em>union</em>鈥攊t cannot change during a call * to <em>find</em>, <em>connected</em>, or <em>count</em>. * <p> * This implementation uses weighted quick union by rank with path compression * by halving. * Initializing a data structure with <em>n</em> sites takes linear time. * Afterwards, the <em>union</em>, <em>find</em>, and <em>connected</em> * operations take logarithmic time (in the worst case) and the * <em>count</em> operation takes constant time. * Moreover, the amortized time per <em>union</em>, <em>find</em>, * and <em>connected</em> operation has inverse Ackermann complexity. * For alternate implementations of the same API, see * {@link QuickUnionUF}, {@link QuickFindUF}, and {@link WeightedQuickUnionUF}. * * <p> * For additional documentation, see <a href="http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/15uf">Section 1.5</a> of * <i>Algorithms, 4th Edition</i> by Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne. * * @author Robert Sedgewick * @author Kevin Wayne */ public class UF { private int[] parent; // parent[i] = parent of i private byte[] rank; // rank[i] = rank of subtree rooted at i (never more than 31) private int count; // number of components /** * Initializes an empty union鈥揻ind data structure with {@code n} sites * {@code 0} through {@code n-1}. Each site is initially in its own * component. * * @param n the number of sites * @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code n < 0} */ public UF(int n) { if (n < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException(); count = n; parent = new int[n]; rank = new byte[n]; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { parent[i] = i; rank[i] = 0; } } /** * Returns the component identifier for the component containing site {@code p}. * * @param p the integer representing one site * @return the component identifier for the component containing site {@code p} * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException unless {@code 0 <= p < n} */ public int find(int p) { validate(p); while (p != parent[p]) { parent[p] = parent[parent[p]]; // path compression by halving p = parent[p]; } return p; } /** * Returns the number of components. * * @return the number of components (between {@code 1} and {@code n}) */ public int count() { return count; } /** * Returns true if the the two sites are in the same component. * * @param p the integer representing one site * @param q the integer representing the other site * @return {@code true} if the two sites {@code p} and {@code q} are in the same component; * {@code false} otherwise * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException unless * both {@code 0 <= p < n} and {@code 0 <= q < n} */ public boolean connected(int p, int q) { return find(p) == find(q); } /** * Merges the component containing site {@code p} with the * the component containing site {@code q}. * * @param p the integer representing one site * @param q the integer representing the other site * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException unless * both {@code 0 <= p < n} and {@code 0 <= q < n} */ public void union(int p, int q) { int rootP = find(p); int rootQ = find(q); if (rootP == rootQ) return; // make root of smaller rank point to root of larger rank if (rank[rootP] < rank[rootQ]) parent[rootP] = rootQ; else if (rank[rootP] > rank[rootQ]) parent[rootQ] = rootP; else { parent[rootQ] = rootP; rank[rootP]++; } count--; } // validate that p is a valid index private void validate(int p) { int n = parent.length; if (p < 0 || p >= n) { throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("index " + p + " is not between 0 and " + (n-1)); } } /** * Reads in a an integer {@code n} and a sequence of pairs of integers * (between {@code 0} and {@code n-1}) from standard input, where each integer * in the pair represents some site; * if the sites are in different components, merge the two components * and print the pair to standard output. * * @param args the command-line arguments */ public static void main(String[] args) { int n = StdIn.readInt(); UF uf = new UF(n); while (!StdIn.isEmpty()) { int p = StdIn.readInt(); int q = StdIn.readInt(); if (uf.connected(p, q)) continue; uf.union(p, q); StdOut.println(p + " " + q); } StdOut.println(uf.count() + " components"); } } /****************************************************************************** * Copyright 2002-2016, Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne. * * This file is part of algs4.jar, which accompanies the textbook * * Algorithms, 4th edition by Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne, * Addison-Wesley Professional, 2011, ISBN 0-321-57351-X. * http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu * * * algs4.jar is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or * (at your option) any later version. * * algs4.jar is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the * GNU General Public License for more details. * * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License * along with algs4.jar. If not, see http://www.gnu.org/licenses. ******************************************************************************/
4.在最坏的情况下,Kruskal算法计算MST需要的时间和ElogE成正比

三.Prim算法
1.思想:
(1)从0号顶点开始,按照下面的步骤贪心的增长树T
(2)在恰好一个端点在T中的边中,选一条权重最小的边加入到T
(3)重复上述过程直到T中有V-1条边
2.关键问题:如何在恰好一个端点在T中的边中,找到一条权重最小的边?
法一:lazy implementation
法二:eager implementation
3.lazy implementation
(1)思想:
①维持一个边的优先级队列PQ,这些边至少有一个端点在T中
②不断删除PQ最小的边,如果这个边的两个端点都已经在T中,则直接将它丢弃,不加入到T
③否则(表明只有一个端点在T中,假设不在T中的点是w),将与w相连的所有边(以前未加入到PQ的边)加入到PQ中,并将w和该边加入到T
④重复上述过程直到T中包含V-1条边
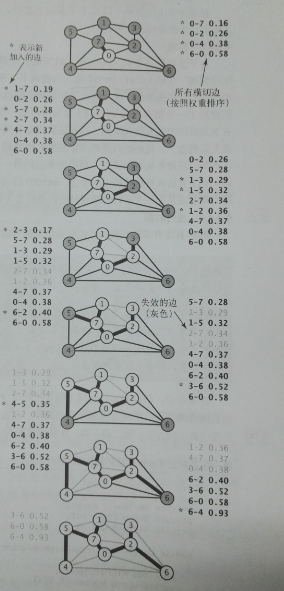
(2)代码实现:使用队列mst保存最小生成树中的边,使用优先级队列pq维持一个边的队列,这些边至少有一个端点在T中,使用marked[]对点进行标记,值是true的表示该点在mst中。

package com.cx.graph; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.MinPQ; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.Queue; public class LazyPrimMST { //用来标记点在T中 private boolean[] marked; //mst用于保存最小生成树中的边 private Queue<Edge> mst; //用于维持边的PQ,这些边至少有一个端点在T中 private MinPQ<Edge> pq; public LazyPrimMST(EdgeWeightedGraph G) { pq=new MinPQ<Edge>(); mst=new Queue<>(); marked=new boolean[G.V()]; //初始化,标记顶点0并将与0相连的所有边加入到pq visited(G, 0); //直到最小生成树有V-1条边为止 while(mst.size()!=(G.V()-1)) { //获得权重最小的边 Edge e=pq.delMin(); int v=e.either(),w=e.other(v); //如果两个点都被标记,则去掉该边继续 if(marked[v]&&marked[w]) continue; //否则,将该边加入到mst中,并将未被标记的点相邻的边加入pq mst.enqueue(e); if(!marked[v]) visited(G, v); if(!marked[w]) visited(G, w); } } //标记顶点v并将v相连的所有边(另一个顶点未被标记)加入到pq private void visited(EdgeWeightedGraph G,int v) { marked[v]=true; for(Edge e:G.adj(v)) { //另一个顶点未被标记 if(!marked[e.other(v)]) pq.insert(e); } } }
(3)性能:最坏情况下,prim算法需要的时间为ElogE,空间为E
4.Eage implementation
(1)思想:
①维持一个顶点的优先级队列PQ,这些顶点连接了T中的一条边,并且点v的优先级等于连接v的最短边的权重
②不断删除最小v和它所关联的边(这些边在T中)
③更新PQ,通过考虑所有与v关联的边e=v-x
-如果点x已经在T中,忽略这个x
-如果不在T中,将x加入到PQ
-如果x-v变为了T中连接x的最短路,降低x的优先级
(2)举例(黑色粗线表示在mst中的边,红线表示在优先级队列中的边)
①0出队列,并将与0相邻的顶点(7,2,4,6)加入PQ(按照边的权重维持优先级)。
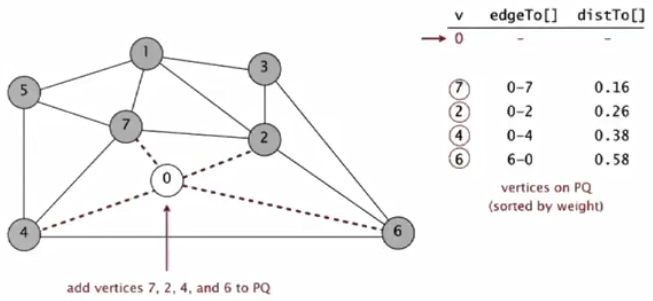
②最小权重7出队列PQ,将与7相邻且不在T的点入队列。对于0来说已经在T,不考虑。对于2和4来说,已经具有较小边(0-2和0-4),维持权重不变。对于1和5来说入队列,并赋权(7-1,7-5)。
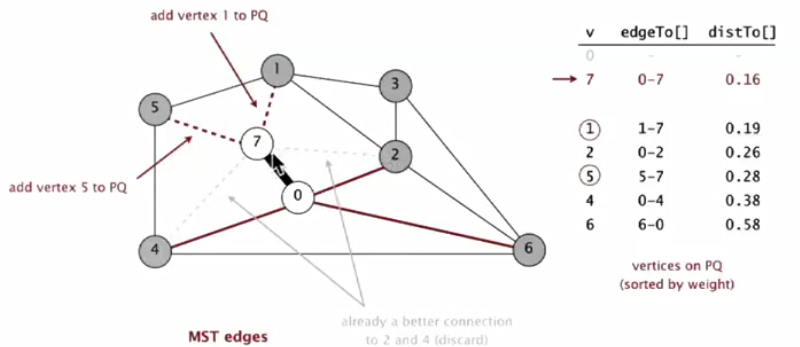
③最小权重1出队列PQ,将与7相邻且不在T的点入队列。7在T中不考虑。对于2和5来说,已经具有较小边(2-7,5-7)维持权重不变。对于3来说入队列,并赋权(1-3)。
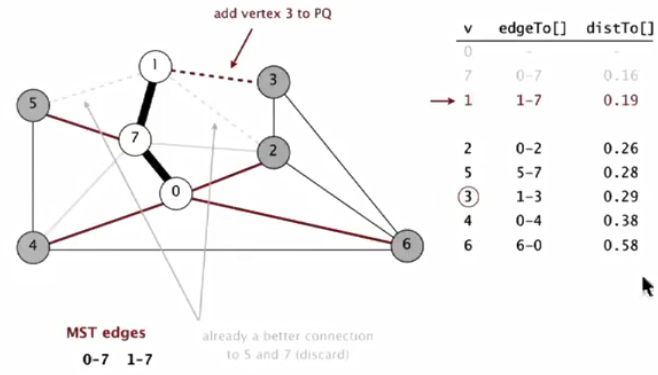
④最小权重2出队列PQ,将与2相邻且不在T的点入队列。0,7,1在T中不考虑。对于3来说,2-3的权重更小(比1-3),更新3的权重。同样对于6来说,2-6的权重更小(比0-6),更新6的权重
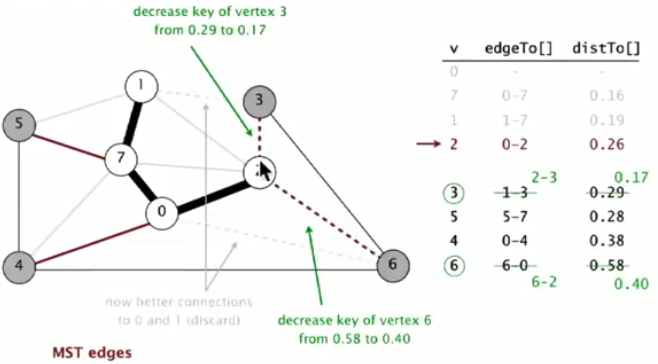
⑤最小权重3出队列PQ,将与3相邻且不在T的点入队列。1,2在T中不考虑。对于6来说,已经具有较小边(2-6)维持权重不变。
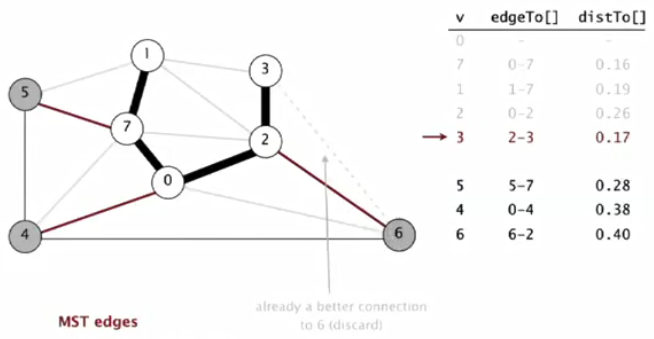
⑥最小权重5出队列PQ,将与5相邻且不在T的点入队列。1,7在T中不考虑。对于4来说,4-5的权重更小(比0-4),更新4的权重。
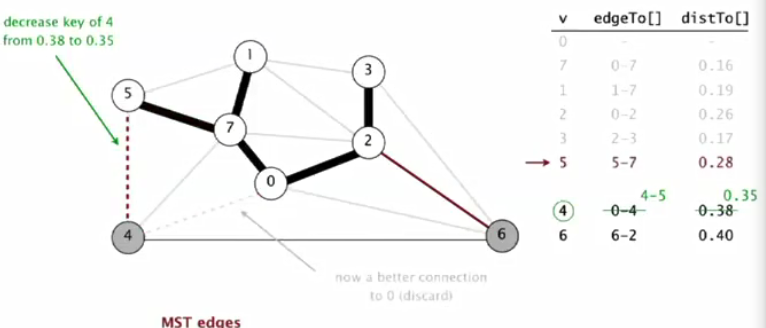
⑦最小权重4出队列PQ,将与4相邻且不在T的点入队列。0,5,7在T中不考虑。对于6来说,已经具有较小边(2-6)维持权重不变。
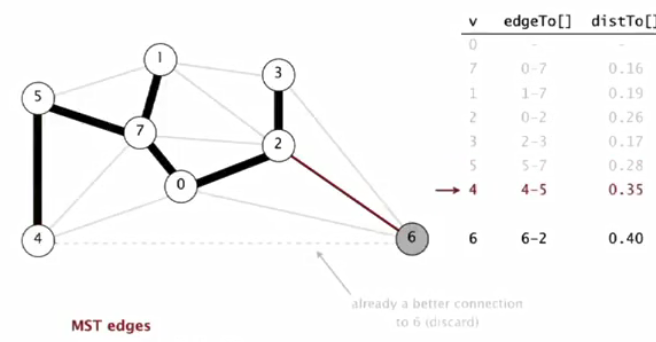
⑧最小权重6出队列PQ,完成整个过程。
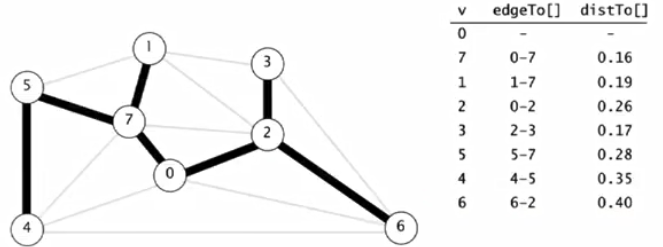
(3)性能:最坏情况下,所需的时间与ElogV成正比,所需的空间与V成正比
(4)代码实现:(没有完全弄懂)

package com.cx.graph; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.IndexMinPQ; public class EagePrimMST { //可能在树T中的边 private Edge[] edgeTo; //这个点的权重w=这条边的权重edgeTo[w].weight()=distTo[w] private double[] distTo; //true表明已经在mst中了 private boolean[] marked; //维持点的优先级队列 private IndexMinPQ<Double> pq; public EagePrimMST(EdgeWeightedGraph G) { //初始化 edgeTo=new Edge[G.V()]; distTo=new double[G.V()]; marked=new boolean[G.V()]; for(int v=0;v<G.V();v++) { distTo[v]=Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY; } pq=new IndexMinPQ<Double>(G.V()); distTo[0]=0.0; //用顶点0来初始化pq pq.insert(0, 0.0); while(!pq.isEmpty()) visit(G,pq.delMin()); } private void visit(EdgeWeightedGraph G,int v) { //将v加入T,并更新顶点和边 marked[v]=true; for(Edge e:G.adj(v)) { int w=e.other(v); //w已经在T中,continue if(marked[w]) continue; //e的权重小于distTo[w],更新点的权重 if(e.weight()<distTo[w]) { //更新最佳边 edgeTo[w]=e; //更新点的权重 distTo[w]=e.weight(); if(pq.contains(w)) pq.change(w, distTo[w]); else pq.insert(w, distTo[w]); } } } }

/****************************************************************************** * Compilation: javac IndexMinPQ.java * Execution: java IndexMinPQ * Dependencies: StdOut.java * * Minimum-oriented indexed PQ implementation using a binary heap. * ******************************************************************************/ package edu.princeton.cs.algs4; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.NoSuchElementException; /** * The {@code IndexMinPQ} class represents an indexed priority queue of generic keys. * It supports the usual <em>insert</em> and <em>delete-the-minimum</em> * operations, along with <em>delete</em> and <em>change-the-key</em> * methods. In order to let the client refer to keys on the priority queue, * an integer between {@code 0} and {@code maxN - 1} * is associated with each key鈥攖he client uses this integer to specify * which key to delete or change. * It also supports methods for peeking at the minimum key, * testing if the priority queue is empty, and iterating through * the keys. * <p> * This implementation uses a binary heap along with an array to associate * keys with integers in the given range. * The <em>insert</em>, <em>delete-the-minimum</em>, <em>delete</em>, * <em>change-key</em>, <em>decrease-key</em>, and <em>increase-key</em> * operations take logarithmic time. * The <em>is-empty</em>, <em>size</em>, <em>min-index</em>, <em>min-key</em>, * and <em>key-of</em> operations take constant time. * Construction takes time proportional to the specified capacity. * <p> * For additional documentation, see <a href="http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/24pq">Section 2.4</a> of * <i>Algorithms, 4th Edition</i> by Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne. * * @author Robert Sedgewick * @author Kevin Wayne * * @param <Key> the generic type of key on this priority queue */ public class IndexMinPQ<Key extends Comparable<Key>> implements Iterable<Integer> { private int maxN; // maximum number of elements on PQ private int n; // number of elements on PQ private int[] pq; // binary heap using 1-based indexing private int[] qp; // inverse of pq - qp[pq[i]] = pq[qp[i]] = i private Key[] keys; // keys[i] = priority of i /** * Initializes an empty indexed priority queue with indices between {@code 0} * and {@code maxN - 1}. * @param maxN the keys on this priority queue are index from {@code 0} * {@code maxN - 1} * @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code maxN < 0} */ public IndexMinPQ(int maxN) { if (maxN < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException(); this.maxN = maxN; n = 0; keys = (Key[]) new Comparable[maxN + 1]; // make this of length maxN?? pq = new int[maxN + 1]; qp = new int[maxN + 1]; // make this of length maxN?? for (int i = 0; i <= maxN; i++) qp[i] = -1; } /** * Returns true if this priority queue is empty. * * @return {@code true} if this priority queue is empty; * {@code false} otherwise */ public boolean isEmpty() { return n == 0; } /** * Is {@code i} an index on this priority queue? * * @param i an index * @return {@code true} if {@code i} is an index on this priority queue; * {@code false} otherwise * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException unless {@code 0 <= i < maxN} */ public boolean contains(int i) { if (i < 0 || i >= maxN) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(); return qp[i] != -1; } /** * Returns the number of keys on this priority queue. * * @return the number of keys on this priority queue */ public int size() { return n; } /** * Associates key with index {@code i}. * * @param i an index * @param key the key to associate with index {@code i} * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException unless {@code 0 <= i < maxN} * @throws IllegalArgumentException if there already is an item associated * with index {@code i} */ public void insert(int i, Key key) { if (i < 0 || i >= maxN) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(); if (contains(i)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("index is already in the priority queue"); n++; qp[i] = n; pq[n] = i; keys[i] = key; swim(n); } /** * Returns an index associated with a minimum key. * * @return an index associated with a minimum key * @throws NoSuchElementException if this priority queue is empty */ public int minIndex() { if (n == 0) throw new NoSuchElementException("Priority queue underflow"); return pq[1]; } /** * Returns a minimum key. * * @return a minimum key * @throws NoSuchElementException if this priority queue is empty */ public Key minKey() { if (n == 0) throw new NoSuchElementException("Priority queue underflow"); return keys[pq[1]]; } /** * Removes a minimum key and returns its associated index. * @return an index associated with a minimum key * @throws NoSuchElementException if this priority queue is empty */ public int delMin() { if (n == 0) throw new NoSuchElementException("Priority queue underflow"); int min = pq[1]; exch(1, n--); sink(1); assert min == pq[n+1]; qp[min] = -1; // delete keys[min] = null; // to help with garbage collection pq[n+1] = -1; // not needed return min; } /** * Returns the key associated with index {@code i}. * * @param i the index of the key to return * @return the key associated with index {@code i} * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException unless {@code 0 <= i < maxN} * @throws NoSuchElementException no key is associated with index {@code i} */ public Key keyOf(int i) { if (i < 0 || i >= maxN) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(); if (!contains(i)) throw new NoSuchElementException("index is not in the priority queue"); else return keys[i]; } /** * Change the key associated with index {@code i} to the specified value. * * @param i the index of the key to change * @param key change the key associated with index {@code i} to this key * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException unless {@code 0 <= i < maxN} * @throws NoSuchElementException no key is associated with index {@code i} */ public void changeKey(int i, Key key) { if (i < 0 || i >= maxN) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(); if (!contains(i)) throw new NoSuchElementException("index is not in the priority queue"); keys[i] = key; swim(qp[i]); sink(qp[i]); } /** * Change the key associated with index {@code i} to the specified value. * * @param i the index of the key to change * @param key change the key associated with index {@code i} to this key * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException unless {@code 0 <= i < maxN} * @deprecated Replaced by {@code changeKey(int, Key)}. */ @Deprecated public void change(int i, Key key) { changeKey(i, key); } /** * Decrease the key associated with index {@code i} to the specified value. * * @param i the index of the key to decrease * @param key decrease the key associated with index {@code i} to this key * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException unless {@code 0 <= i < maxN} * @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code key >= keyOf(i)} * @throws NoSuchElementException no key is associated with index {@code i} */ public void decreaseKey(int i, Key key) { if (i < 0 || i >= maxN) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(); if (!contains(i)) throw new NoSuchElementException("index is not in the priority queue"); if (keys[i].compareTo(key) <= 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Calling decreaseKey() with given argument would not strictly decrease the key"); keys[i] = key; swim(qp[i]); } /** * Increase the key associated with index {@code i} to the specified value. * * @param i the index of the key to increase * @param key increase the key associated with index {@code i} to this key * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException unless {@code 0 <= i < maxN} * @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code key <= keyOf(i)} * @throws NoSuchElementException no key is associated with index {@code i} */ public void increaseKey(int i, Key key) { if (i < 0 || i >= maxN) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(); if (!contains(i)) throw new NoSuchElementException("index is not in the priority queue"); if (keys[i].compareTo(key) >= 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Calling increaseKey() with given argument would not strictly increase the key"); keys[i] = key; sink(qp[i]); } /** * Remove the key associated with index {@code i}. * * @param i the index of the key to remove * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException unless {@code 0 <= i < maxN} * @throws NoSuchElementException no key is associated with index {@code i} */ public void delete(int i) { if (i < 0 || i >= maxN) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(); if (!contains(i)) throw new NoSuchElementException("index is not in the priority queue"); int index = qp[i]; exch(index, n--); swim(index); sink(index); keys[i] = null; qp[i] = -1; } /*************************************************************************** * General helper functions. ***************************************************************************/ private boolean greater(int i, int j) { return keys[pq[i]].compareTo(keys[pq[j]]) > 0; } private void exch(int i, int j) { int swap = pq[i]; pq[i] = pq[j]; pq[j] = swap; qp[pq[i]] = i; qp[pq[j]] = j; } /*************************************************************************** * Heap helper functions. ***************************************************************************/ private void swim(int k) { while (k > 1 && greater(k/2, k)) { exch(k, k/2); k = k/2; } } private void sink(int k) { while (2*k <= n) { int j = 2*k; if (j < n && greater(j, j+1)) j++; if (!greater(k, j)) break; exch(k, j); k = j; } } /*************************************************************************** * Iterators. ***************************************************************************/ /** * Returns an iterator that iterates over the keys on the * priority queue in ascending order. * The iterator doesn't implement {@code remove()} since it's optional. * * @return an iterator that iterates over the keys in ascending order */ public Iterator<Integer> iterator() { return new HeapIterator(); } private class HeapIterator implements Iterator<Integer> { // create a new pq private IndexMinPQ<Key> copy; // add all elements to copy of heap // takes linear time since already in heap order so no keys move public HeapIterator() { copy = new IndexMinPQ<Key>(pq.length - 1); for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) copy.insert(pq[i], keys[pq[i]]); } public boolean hasNext() { return !copy.isEmpty(); } public void remove() { throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); } public Integer next() { if (!hasNext()) throw new NoSuchElementException(); return copy.delMin(); } } /** * Unit tests the {@code IndexMinPQ} data type. * * @param args the command-line arguments */ public static void main(String[] args) { // insert a bunch of strings String[] strings = { "it", "was", "the", "best", "of", "times", "it", "was", "the", "worst" }; IndexMinPQ<String> pq = new IndexMinPQ<String>(strings.length); for (int i = 0; i < strings.length; i++) { pq.insert(i, strings[i]); } // delete and print each key while (!pq.isEmpty()) { int i = pq.delMin(); StdOut.println(i + " " + strings[i]); } StdOut.println(); // reinsert the same strings for (int i = 0; i < strings.length; i++) { pq.insert(i, strings[i]); } // print each key using the iterator for (int i : pq) { StdOut.println(i + " " + strings[i]); } while (!pq.isEmpty()) { pq.delMin(); } } } /****************************************************************************** * Copyright 2002-2016, Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne. * * This file is part of algs4.jar, which accompanies the textbook * * Algorithms, 4th edition by Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne, * Addison-Wesley Professional, 2011, ISBN 0-321-57351-X. * http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu * * * algs4.jar is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or * (at your option) any later version. * * algs4.jar is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the * GNU General Public License for more details. * * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License * along with algs4.jar. If not, see http://www.gnu.org/licenses. ******************************************************************************/




