组合求和
给定一个无重复元素的数组 candidates 和一个目标数 target ,找出 candidates 中所有可以使数字和为 target 的组合。
candidates 中的数字可以无限制重复被选取。
说明:
- 所有数字(包括
target)都是正整数。 - 解集不能包含重复的组合。
示例 1:
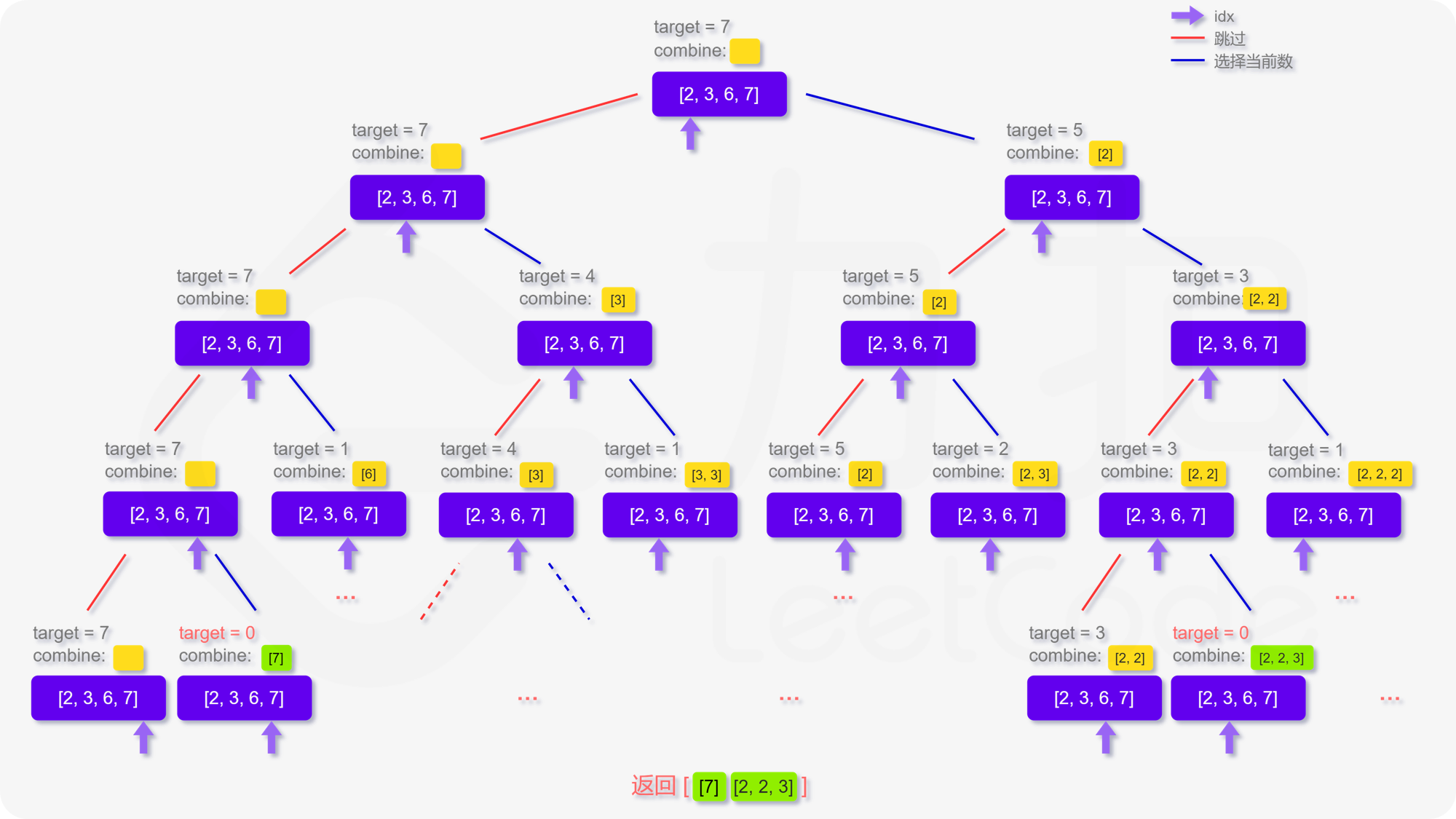
输入:candidates = [2,3,6,7],target = 7,
输出:[ [7], [2,2,3] ]
示例 2:
输入:candidates = [2,3,5], target = 8,
输出:[ [2,2,2,2], [2,3,3], [3,5] ]
提示:
- 1 <= candidates.length <= 30
- 1 <= candidates[i] <= 200
- candidate 中的每个元素都是独一无二的。
- 1 <= target <= 500
思路与算法
对于这类寻找所有可行解的题,我们都可以尝试用「搜索回溯」的方法来解决。
回到本题,我们定义递归函数 dfs(target, combine, idx) 表示当前在 candidates 数组的第 idx 位,还剩 target 要组合,已经组合的列表为 combine。递归的终止条件为 target <= 0 或者 candidates 数组被全部用完。那么在当前的函数中,每次我们可以选择跳过不用第 idx 个数,即执行 dfs(target, combine, idx + 1)。也可以选择使用第 idx 个数,即执行 dfs(target - candidates[idx], combine, idx),注意到每个数字可以被无限制重复选取,因此搜索的下标仍为 idx。
更形象化地说,如果我们将整个搜索过程用一个树来表达,即如下图呈现,每次的搜索都会延伸出两个分叉,直到递归的终止条件,这样我们就能不重复且不遗漏地找到所有可行解:
代码实现:
candidate = [1,2,3,6,7] tar = 7 def solve(candidates,target): ans = [] def dfs(target,combination,idx): if idx == len(candidates): return if target <= 0: ans.append(combination) return else: dfs(target,combination,idx+1) if target-candidates[idx]>=0: dfs(target-candidates[idx],combination+[candidates[idx]],idx) dfs(target,[],0) return ans print(solve(tar,candidate))




