MyBatis3
一.MyBatis 实现多表查询
1.Mybatis 实现多表查询方式
1)业务装配.对两个表编写单表查询语句,在业务(Service)把查询的两个结果进行关联.
2)使用AutoMapping特性,在实现两表联合查询时通过别名完成映射.
3)使用 MyBatis 的<resultMap>标签进行实现.
2.多表查询时,类中包含另一个类的对象的分类
1)单个对象
2)集合对象
二.resultMap 标签
1. <resultMap>标签写在mapper.xml中,由程序员控制SQL查询结果与实体类的映射关系.
默认 MyBatis 使用 AutoMapping 特性.
2. 使用<resultMap>标签时,<select>标签不写 resultType 属性,而是使用 resultMap 属性引用<resultMap>标签.
3. 使用 resultMap 实现单表映射关系
1)数据库设计
表名:teacher 表字段:id , name
2)实体类设计
public class Teacher{ private int id1; private String name1; }
3)mapper.xml代码
<resultMap type="teacher" id="mymap"> <!-- 主键使用 id 标签配置映射关系 --> <id column="id" property="id1" /> <!-- 其他列使用 result 标签配置映射关系 --> <result column="name" property="name1"/> </resultMap> <select id="selAll" resultMap="mymap"> select * from teacher </select>
4. 使用 resultMap 实现关联单个对象(N+1 方式)
1)N+1 查询方式,先查询出某个表的全部信息,根据这个表的信息查询另一个表的信息.
2)与业务装配的区别:
在 service 里面写的代码,由 mybatis 完成装配
3)实现步骤:
在 Student 实现类中包含了一个 Teacher 对象
public class Student { private int id; private String name; private int age; private int tid; private Teacher teacher;
在 TeacherMapper 中提供一个查询
<select id="selById" resultType="teacher" parameterType="int"> select * from teacher where id=#{0} </select>
在 StudentMapper 中
<association> 装配一个对象时使用
property: 对象在类中的属性名
select:通过哪个查询查询出这个对象的信息
column: 把当前表的哪个列的值做为参数传递给另一个查询
<resultMap type="student" id="stuMap"> <id property="id" column="id"/> <result property="name" column="name"/> <result property="age" column="age"/> <result property="tid" column="tid"/> <!-- 如果关联一个对象 --> <association property="teacher" select="com.su.mapper.TeacherMapper.selById" column="tid"></association> </resultMap> <select id="selAll" resultMap="stuMap"> select * from student </select>
大前提使用 N+1 方式.时如果列名和属性名相同可以不配置,使用 Automapping 特性.但是 mybatis 默认只会给列装配一次。把上面代码简化成:
<resultMap type="student" id="stuMap"> <result property="tid" column="tid"/> <!-- 如果关联一个对象 --> <association property="teacher" select="com.su.mapper.TeacherMapper.selById" column="tid"></association> </resultMap> <select id="selAll" resultMap="stuMap"> select * from student </select>
5. 使用 resultMap 实现关联单个对象(联合查询方式)
1)只需要编写一个 SQL,在 StudentMapper 中添加下面效果
<association/>只要专配一个对象就用这个标签
此时把<association/>当做小的<resultMap>看待
javaType 属性:<association/>装配完后返回一个什么类型的对象.取值是一个类(或类的别名)
<resultMap type="Student" id="stuMap1"> <id column="sid" property="id"/> <result column="sname" property="name"/> <result column="age" property="age"/> <result column="tid" property="tid"/> <association property="teacher" javaType="Teacher" > <id column="tid" property="id"/> <result column="tname" property="name"/> </association> </resultMap> <select id="selAll1" resultMap="stuMap1"> select s.id sid,s.name sname,age age,t.id tid,t.name tname FROM student s left outer join teacher t on s.tid=t.id </select>
6. N+1 方式和联合查询方式对比
1)N+1:需求不确定时.
2)联合查询:需求中确定查询时两个表一定都查询.
7. N+1 名称由来
1)举例:学生中有 3 条数据
需求:查询所有学生信息级授课老师信息
需要执行的 SQL 命令:
查询全部学生信息:select * from 学生
执行 3 遍 select * from 老师 where id=学生的外键
使用多条 SQL命令查询两表数据时,如果希望把需要的数据都查询出来,需要执行 N+1 条 SQL才能把所有数据库查询出来.
2)缺点:效率低
3)优点:
如果有的时候不需要查询学生时同时查询老师.只需要执行一个 select * from student;
4)适用场景: 有的时候需要查询学生同时查询老师,有的时候只需要查询学生.
5)如何解决 N+1 查询带来的效率低的问题:
默认带的前提: 每次都是两个都查询.使用两表联合查询.
三.使用<resultMap>查询关联集合对象(N+1)
1. 在 Teacher 中添加 List<Student>
public class Teacher { private int id; private String name; private List<Student> list;
2. 在 StudentMapper.xml 中添加通过 tid 查询
<select id="selByTid" parameterType="int" resultType="student"> select * from student where tid=#{0} </select>
3. 在 TeacherMapper.xml 中添加查询全部
<collection/> 当属性是集合类型时使用的标签.
<resultMap type="teacher" id="mymap"> <id column="id" property="id"/> <result column="name" property="name"/> <collection property="list" select="com.su.mapper.StudentMapper.selByTid" column="id"></collection> </resultMap> <select id="selAll" resultMap="mymap"> select * from teacher </select>
四.使用<resultMap>实现加载集合数据(联合查询方式)
1.在 teacherMapper.xml 中添加
1)mybatis 可以通过主键判断对象是否被加载过
2)不需要担心创建重复 Teacher
3)ofType 属性:表示集合的泛型是什么 (这里表示student)
<resultMap type="teacher" id="mymap1"> <id column="tid" property="id"/> <result column="tname" property="name"/> <collection property="list" ofType="student" > <id column="sid" property="id"/> <result column="sname" property="name"/> <result column="age" property="age"/> <result column="tid" property="tid"/> </collection> </resultMap> <select id="selAll1" resultMap="mymap1"> select t.id tid,t.name tname,s.id sid,s.name sname,age,tid from teacher t LEFT JOIN student s on t.id=s.tid; </select>
五.使用 AutoMapping 结合别名实现多表查询
1.只能使用多表联合查询方式.
2.要求:查询出的列名和属性名相同.
3.实现方式
1)在 Student 实现类中包含了一个 Teacher 对象
public class Student { private int id; private String name; private int age; private int tid; private Teacher teacher;
2)在 SQL 是关键字符,两侧添加反单引号
<select id="selAll" resultType="student"> select t.id `teacher.id`,t.name `teacher.name`,s.id id,s.name name,age,tid from student s LEFT JOIN teacher t on t.id=s.tid </select>
六.MyBatis 注解
1. 注解:为了简化配置文件.
2. Mybatis 的注解简化 mapper.xml 文件.
如果涉及动态 SQL 依然使用 mapper.xml
3. mapper.xml 和注解可以共存.
4. 使用注解时 mybatis.xml 中<mappers>使用
<package/>
<mapper class="com.su.mapper.TeacherMapper"/> :接口名
5. 实现查询
在TeacherMapper接口:
@Select("select * from teacher")
List<Teacher> selAll();
6. 实现新增
在TeacherMapper接口:
@Insert("insert into teacher values(default,#{name})")
int insTeacher(Teacher teacher);
7. 实现修改
在TeacherMapper接口:
@Update("update teacher set name=#{name} where id=#{id}")
int updTeacher(Teacher teacher);
8. 实现删除
在TeacherMapper接口:
@Delete("delete from teacher where id=#{0}")
int delById(int id);
9. 使用注解实现<resultMap>功能
1)以 N+1 举例
2)在 StudentMapper 接口添加查询
@Select("select * from student where tid=#{0}")
List<Student> selByTid(int tid);
3)在 TeacherMapper 接口添加
@Results() 相当于<resultMap>
@Result() 相当于<id/>或<result/>
@Result(id=true) 相当于<id/>
@Many() 相当于<collection/>
@One() 相当于<association/>
@Results(value={ @Result(id=true,property="id",column="id"), @Result(property="name",column="name"), @Result(property="list",column="id",many=@Many(select="com.su.mapper.StudentMapper.selByTid"))
}) @Select("select * from teacher") List<Teacher> selTeacher();
七. MyBatis运行原理
1. 运行过程中涉及到的类
Resources:MyBatis中IO流的工具类
加载配置文件
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder():构建器
作用:创建 SqlSessionFactory 接口的实现类
XMLConfigBuilder:MyBatis 全局配置文件内容构建器类
作用负责读取流内容并转换为 JAVA 代码.
Configuration:封装了全局配置文件所有配置信息.
全局配置文件内容存放在 Configuration 中
DefaultSqlSessionFactory:是SqlSessionFactory接口的实现类
Transaction:事务类
每一个 SqlSession 会带有一个 Transaction 对象.
TransactionFactory:事务工厂
负责生产 Transaction
Executor :MyBatis 执行器
作用:负责执行 SQL 命令
相当于 JDBC 中 statement 对象(或 PreparedStatement或 CallableStatement)
默认的执行器 SimpleExcutor
批量操作 BatchExcutor
通过 openSession(参数控制)
DefaultSqlSession:是 SqlSession 接口的实现类
ExceptionFactory:MyBatis 中异常工厂
2. 流程图
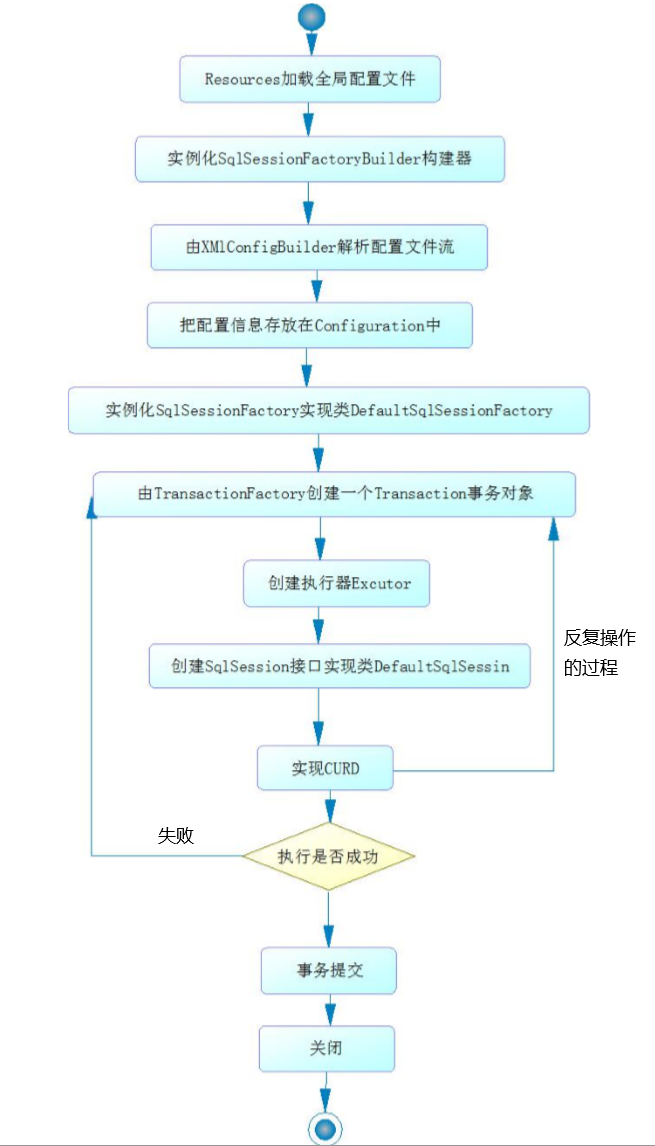
3.文字解释
在 MyBatis 运行开始时需要先通过 Resources 加载全局配置文件.
下面需要实例化 SqlSessionFactoryBuilder 构建器.帮助 SqlSessionFactory 接口实现类 DefaultSqlSessionFactory.
在实例化 DefaultSqlSessionFactory 之前需要先创建 XmlConfigBuilder解析全局配置文件流,并把解析结果存放在 Configuration 中.之后把Configuration传递给 DefaultSqlSessionFactory.到此 SqlSessionFactory 工厂创建成功.
由 SqlSessionFactory 工厂创建 SqlSession.
每次创建 SqlSession 时,都需要由 TransactionFactory 创建 Transaction对象,同时还需要创建 SqlSession 的执行器 Excutor,最后实例化DefaultSqlSession,传递给 SqlSession 接口.
根据项目需求使用 SqlSession 接口中的 API 完成具体的事务操作.
如果事务执行失败,需要进行 rollback 回滚事务.
如果事务执行成功提交给数据库.关闭 SqlSession
到此就是 MyBatis 的运行原理.






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· Manus爆火,是硬核还是营销?
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 单元测试从入门到精通