


package main import ( "fmt" ) //声明/定义一个接口 type Usb interface { //声明了两个没有实现的方法 Start() Stop() } //声明/定义一个接口 type Usb2 interface { //声明了两个没有实现的方法 Start() Stop() Test() } type Phone struct { } //让Phone 实现 Usb接口的方法 func (p Phone) Start() { fmt.Println("手机开始工作。。。") } func (p Phone) Stop() { fmt.Println("手机停止工作。。。") } type Camera struct { } //让Camera 实现 Usb接口的方法 func (c Camera) Start() { fmt.Println("相机开始工作~~~。。。") } func (c Camera) Stop() { fmt.Println("相机停止工作。。。") } //计算机 type Computer struct { } //编写一个方法Working 方法,接收一个Usb接口类型变量 //只要是实现了 Usb接口 (所谓实现Usb接口,就是指实现了 Usb接口声明所有方法) func (c Computer) Working(usb Usb) { //通过usb接口变量来调用Start和Stop方法 usb.Start() usb.Stop() } func main() { //测试 //先创建结构体变量 computer := Computer{} phone := Phone{} camera := Camera{} //关键点 computer.Working(phone) computer.Working(camera) // }






1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 | package mainimport "fmt"type Ainterface interface { Say()}type Binterface interface { Hello()}type Monster struct {}func (m Monster) Hello() { fmt.Println("hello ()")}func (m Monster) Say() { fmt.Println("Say ()")}func main() { var monster Monster var a Ainterface = monster var b Binterface = monster a.Say() b.Hello()} |



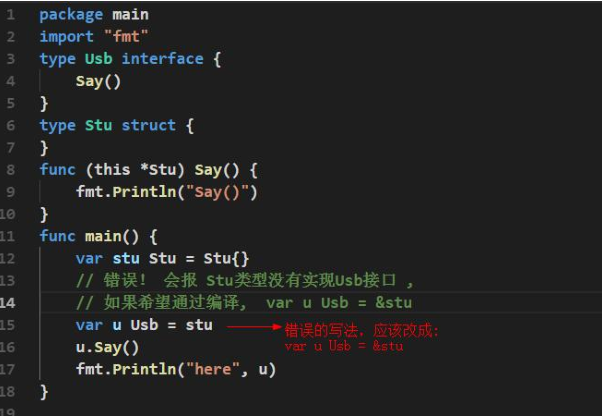
本文来自博客园,作者:孙龙-程序员,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/sunlong88/p/11180555.html






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本
· C#/.NET/.NET Core优秀项目和框架2025年2月简报
· DeepSeek在M芯片Mac上本地化部署
· 葡萄城 AI 搜索升级:DeepSeek 加持,客户体验更智能