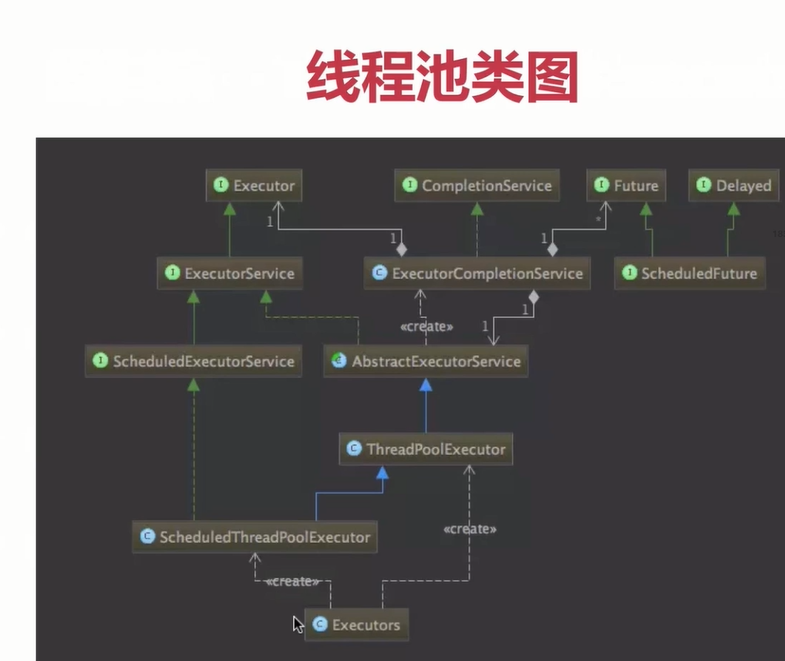
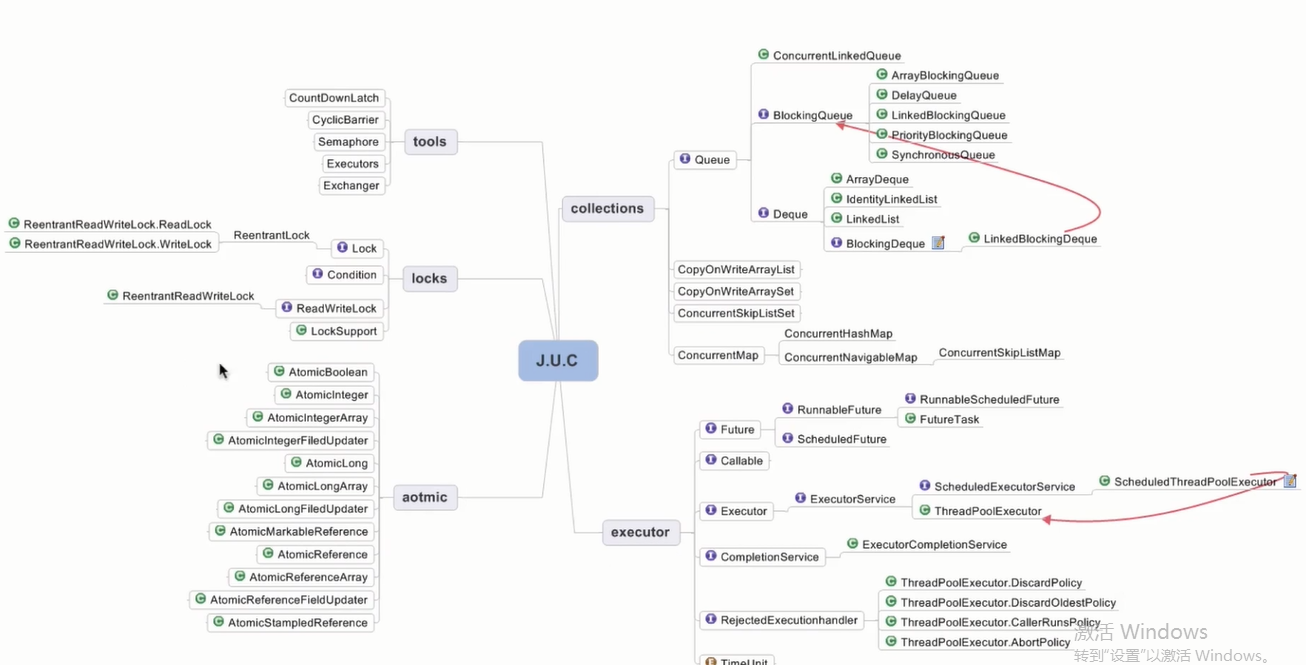
Java线程池

缺少更多功能,如更多执行,定期执行,线程中断





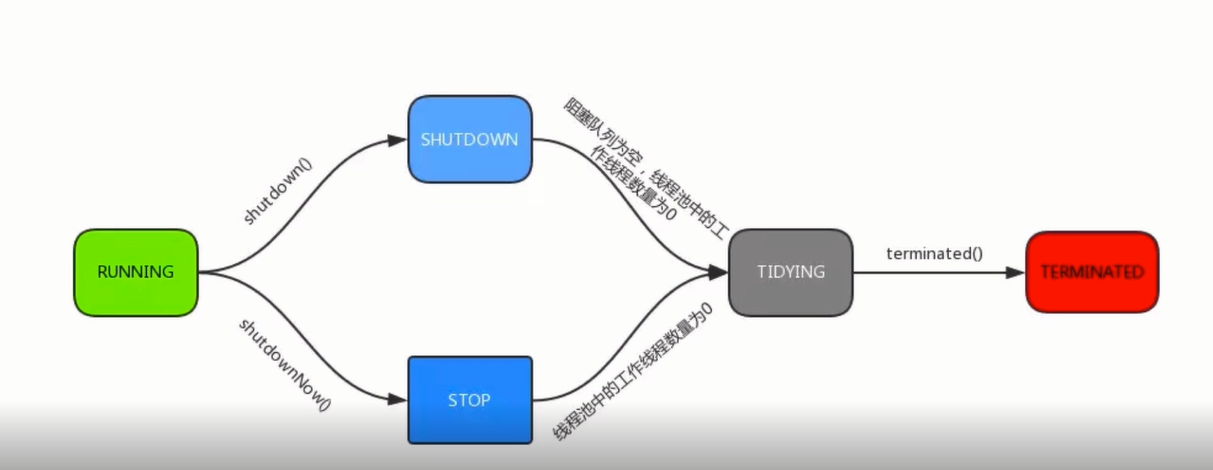
线程池中的状态:













import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Timer;
import java.util.TimerTask;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@Slf4j
public class ThreadPoolExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// ExecutorService executorService= Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
// ExecutorService executorService=Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
//ExecutorService executorService=Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
ExecutorService executorService=Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(3);
executorService.schedule(new Runnable(){
@Override
public void run(){
log.warn("schedule run");
}
},3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
//延迟一秒每隔一秒执行
executorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable(){
@Override
public void run(){
log.warn("schedule run");
}
},1,3,TimeUnit.SECONDS);
Timer timer=new Timer();
timer.schedule(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
log.warn("schedule run");
}
},new Date(),5*1000);
// for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
// final int index=i;
// executorService.execute(new Runnable() {
// @Override
// public void run() {
// log.info("task:{}",index);
// }
// });
// }
executorService.shutdown();
}
}

死锁案例:
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
@Slf4j
public class DeadLock implements Runnable {
public int flag=1;
private static Object o1=new Object(),o2=new Object();
@Override
public void run(){
log.info("flag:",flag);
if(flag==1){
synchronized (o1){
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
synchronized (o2){
log.info("1");
}
}
}
if(flag==0){
synchronized (o2){
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
synchronized (o1){
log.info("0");
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
DeadLock td1=new DeadLock();
DeadLock td2=new DeadLock();
td1.flag=1;
td2.flag=0;
new Thread(td1).start();
new Thread(td2).start();
}
}
多线程并发的实践:
1.使用本地变量
2.使用不可变类
3.最小化锁的作用域范围
4.使用线程池的Executor,而不是直接new Thread执行
5.宁可使用同步,也不使用线程的wait和notify
6.使用BlockingQueue实现生产消费模式
7.使用并发集合不是加了锁的同步集合
8.使用Semaphore创建有界的访问
9.宁可使用同步代码块,也不使用同步的方法
10避免使用静态变量





