类型转换
-
由于Java是强类型语言,所以要进行有些运算的时候时,需要用到类型转换。
- 低——>高
-
byte、short、char——>int——>long——>folat——>double
-
运算中,不同类型的数据先转化为同一类型,然后进行运算。
-
强制类型转换
-
自动类型转换
public class Demo04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 128;
double d = i;//内存溢出
//强制转换 (类型)变量
//自动转换 低--高
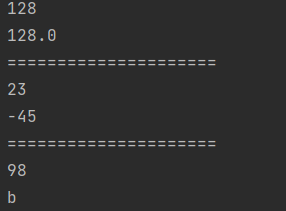
System.out.println(i);
System.out.println(d);
/*
注意点:
1.不能对布尔值进行转换
2.不能把对象类型转换为不相干的类型
3.在把高容量转换到低容量的时候,强制转换
4。转换的时候可能存在内存溢出或者精度问题!
*/
System.out.println("=====================");
System.out.println((int) 23.7);
System.out.println((int)-45.89f);
System.out.println("=====================");
char c = 'a';
int d1 = c+1;
System.out.println(d1);
System.out.println((char)d1);
}
}
public class Demo05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//操作比较大的数的时候,注意溢出问题
//JDK7新特性,数字之间可以用下划线分割
int money = 10_0000_0000;
int years = 20;
int total = money*years;//-1474836480,计算的时候溢出
long total2 = money*years;//默认是int,转换之前已经存在问题了
long total3 = money*((long)years);//先把一个数转换为long
System.out.println(total);
System.out.println(total2);
System.out.println(total3);
}
}






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· Docker 太简单,K8s 太复杂?w7panel 让容器管理更轻松!