SIFT算法
首先感谢 会飞的吴克 在B站中的教学视频,本篇博客只用于交流学习
在这里贴出参考教学视频的网址SIFT(尺度不变特征变换)
下面所有标红的部分都是目前暂时不是很理解的部分,等待后面有时间必须将这一部分了解透彻
SIFT过程
1建立高斯差分金字塔
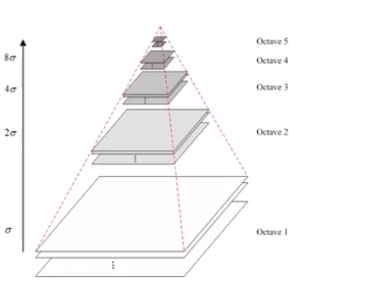
图1
首先如图1所示,这是高斯金字塔。我们可以看到其是由很多组组成,每一组包含很多层,其中每一组的层代表的是一张照片,每一组的照片的大小尺寸是相同的。
可以使用不同的方差计算高斯核
用不同的方差的高斯核对原图片进行卷积就能得到第一组的所有层,也就是图1中最下面的Octave1组,也就是第一组的每一层都是由不同尺度方差的高斯核计算得到的。
第二层的初始第一张图片是由第一组的图片进行降采样得到的。降采样就是隔点取点,也就是第一个像素点留下,第二个去掉,第三个留下,第四个去掉,依次这么做,最后第二层的图片的长宽都是第一层的1/2,之后再用不同尺度的高斯核进行卷积。之后的每一组都是这么顺序操作。这样得到的图1就是高斯金字塔,这个金字塔也可以叫做尺度空间。
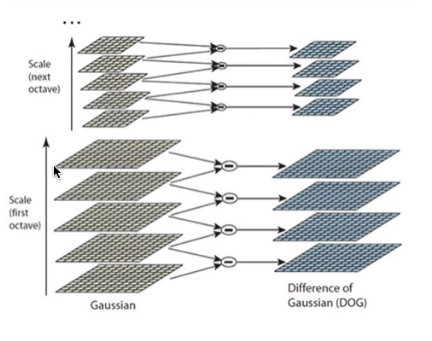
图2
在得到的图1的高斯金字塔上的同一组的每一层相减,就是单纯对应位置的四则减法运算,得到的就是高斯差分金字塔,如图2所示。
对于高斯金字塔中应该由多少组,每组应该有多少层,算法的发明者在论文中的建议值为
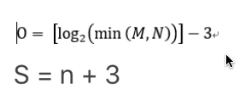
图3
如图3所示,o表示多少组,M N表示原图片的长和宽,S是层数
n表示希望提取几个尺度的极值点(具体意义和作用暂不理解知道)
S=n+3的由来是:
在图2中S=5,所以只能提取到两张图片中的特征,找特征点实际上是在高斯差分金字塔中进行寻找,此时高斯差分金字塔中是4张图片,在三个方向中找极值点。三个方向是图片的两个方向x y,以及尺度方向,也就是图2中的竖着的方向,因为差分金字塔的最上面一层没有向上的竖着的方向,所以无法求导,同理最下面一层也没有向下的方向,所以也无法求导,因为找极值点就是求导,无法求导就是不能寻找极值点,所以需要再减2.这样得到的n+3
为什么建立高斯金字塔,高斯差分金字塔?
SIFT应该有远近不变性,也就是不管是离着远拍还是离着仅拍,同一个物品都应该是能识别出来的。金字塔其实就是模拟的近大远小。高斯核卷积模拟的是近处清晰,远处模糊。在数学上有个证明,高斯核是唯一可以模拟近处清晰,远处模糊的线性核。
每次卷积的时候的尺度怎么定?高斯核的标准差怎么定?
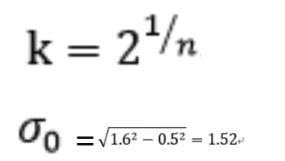
图4
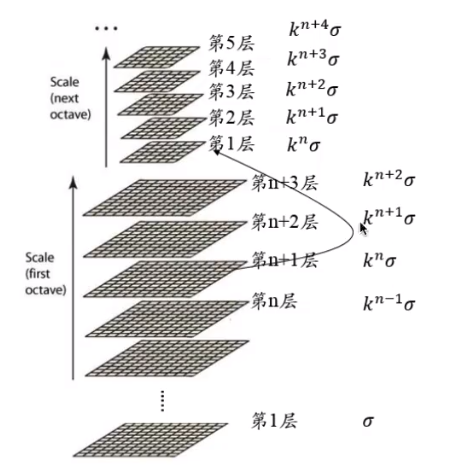
图5
由图4和图5可知,第一组的子一层是标准差0,第二层就是k标准差,依次类推。第二组的第一层是k的指数与第一组的倒数第三层一样,这个时候系数为2,也就是为了凑一个2标准差.也就是2标注差的图片隔点取点得到第二组第一层的图片。
标准差0,照相机照相的时候也不是完全清晰的,自带一个模糊尺度,认为这个尺度是0.5,希望第一次高斯核卷积之后能达到1.6,这样就出来了标准差的公式。也就是用0.5尺度卷积,再用1.52尺度卷积得到的结果与直接用1.6尺度卷积得到的效果一样。
2关键点位置的确定
关键点是稳定的点,变化少,有稳定性质的点,包含很多信息的点,这些点通常是在极值位置,可以是极大值,也可以是极小值。
2.1 阈值化

图6
首先进行阈值化,每个像素点的绝对值满足上面的要求,如果不满足,我们认为是极值点的可能性非常小。
2.2在高斯差分金字塔中找极值
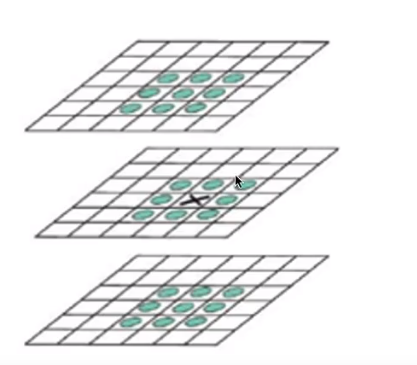
图7
图7找的极值点是离散的极值点,因为我们的空间是一个像素一个像素的,是离散的。
在图7中如果是在27个像素点中找到一个最大的,那么这就是一个离散的极值点,并不是一个真正的极值点。
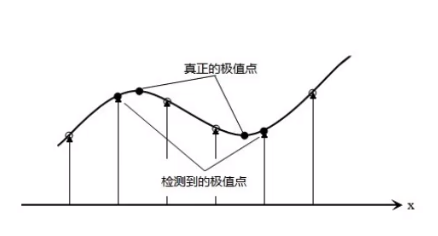
图8
按照图7极值点的求取办法是找到一个真正极值点的附近的一个点,我们需要找到一个更准确的亚像素位置的极值点。
2.3 调整极值点的位置
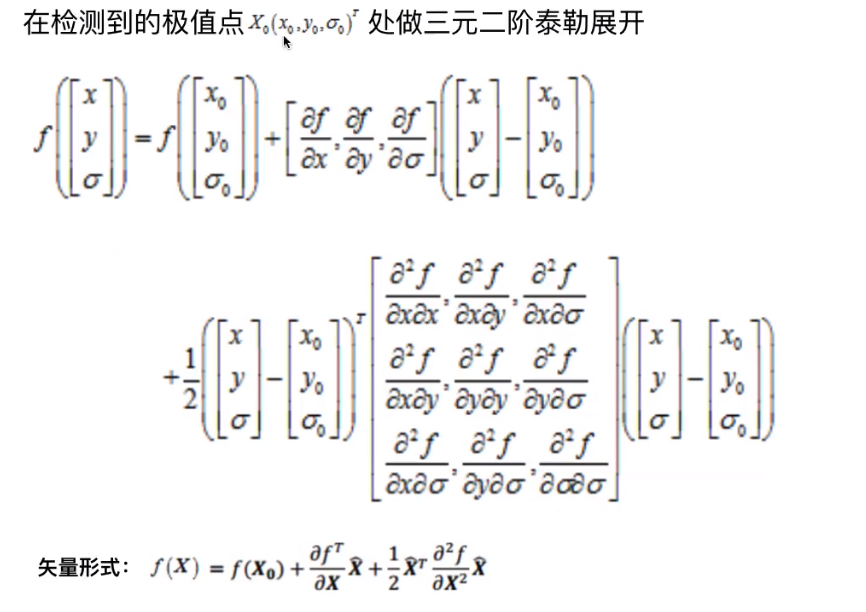
图9
上面的X0就是在图7中检测到的极值点。表示成矢量的形式是为了找到极值点的精确位置,泰勒展开的f(x)是在X0处原函数的近似,在这里就认为是原函数。

图10
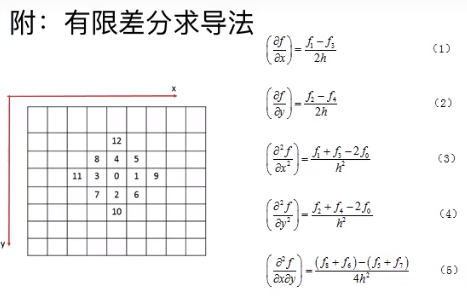
图11
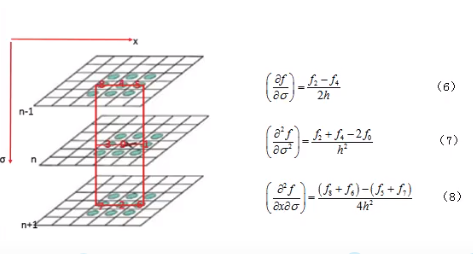
图12
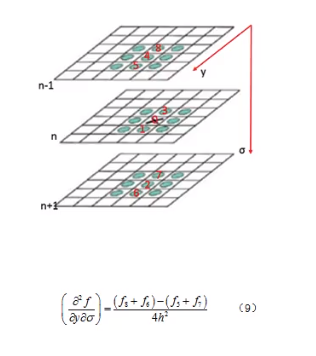
图13
如上图所示,求导使用差商来代替,例如0处对x的求导,其中f1=3,f3=1,至于h取什么值暂时无所谓。
因为X(上面图片中的X上有一个小弧线,在博客园中暂时打不出,所以之后都使用加粗倾斜的X表示)是X-X0,所以得到的解X是真正的极值点相对于检测到的极值点的位移量。最后求出的f(X)是真正极值点对应的值。
算法实现的时候是迭代的过程,会涉及一些细节问题,这里暂时不讨论,我也不太理解。
当X的三个分量都小于0.5的时候,就认为已经比较接近真正的极值点,就不需要再进行迭代了。如果超出迭代次数限制,三个分量都没有小于0.5,认为它可能收敛不了了,就直接舍去这个点。如果最后收敛了,但是解超出了一定范围(因为这个泰克展开只能在找到的极值点的附近拟合原函数),也进行舍去操作。
2.4 舍去低对比度的点
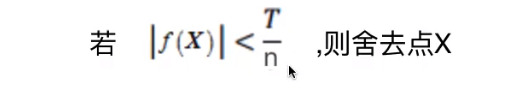
图14
如果最后的f(x)的绝对值满足图14的条件,则直接舍去。
2.5 边缘效应的去除
需要用到海森矩阵
图15
海森矩阵可以描述曲线的曲率,在两个方向上的曲率差不多的时候才可以,否则很可能是一个边缘。海森矩阵的特征值和曲率成正比,这里使用Tr(H)和Set(H)来代替进行操作
其中α β就是两个特征值。
若Det(H)《0,这时特征值异号了,此时有边缘效应了。
图15最下面的Tr(H)少写一个平方
需要注意的是例如在第二层求出的极值点,映射到第一层其x 和 y分别乘2
3 为关键点赋予方向
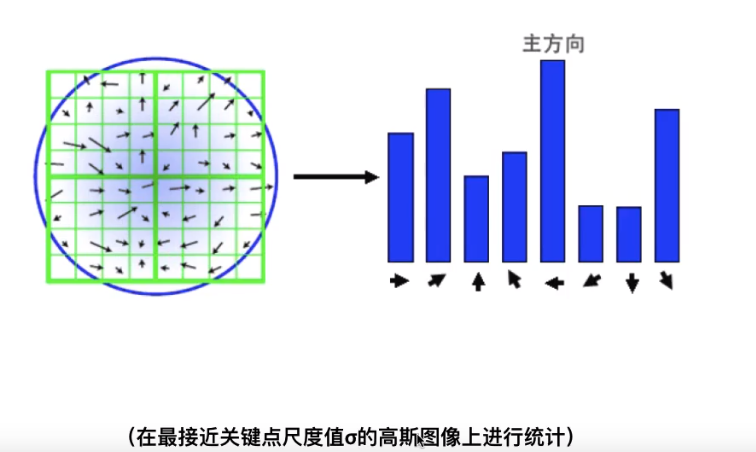
图16
统计以特征点为圆心,以该特征点所在的高斯图像的尺度1.5倍为半径的圆内的所有的像素的梯度的方向及其梯度赋值,并作1.5标准差的高斯滤波。
关键点的参数是 (x, y, 标准差),可以都不是整数,标准差也可以不落在某一层上
因为关键点的标准差可能在亚像素上,也就是并不在当前组的某一层上,所以统计的高斯图像是最接近这个标准差的某一层(在高斯金字塔中找,而不是在高斯差分金字塔中)。
统计其梯度方向和大小,方向有360°,但是最后统计成8个方向,落在那个区间就是在哪个方向。
做高斯滤波是为了越接近特征点的权重就越大
在实际的代码中分成了36个方向,每十度是一个方向,从其中选择主方向,主方向就是最后的权重最大的方向,有时也会存在一个辅方向(权重大于等于主方向的80%)
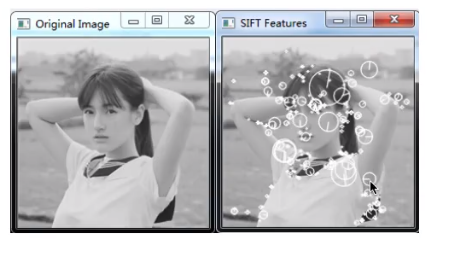
图17
此时就可以得到如图17所示的图像
提取出了一张图片中的特征点,位置代表了特征点的位置,圆圈的大小代表了尺度的大小,线代表了主方向。有两个方向就是存在一个辅方向,辅方向的处理方法是当作两个特征点进行处理。
4构建关键点描述符
关键点的参数(x,y,标准差,主方向)
在一张图片中找到关键点不算完,要在两张图片中分别找到它们的关键点,把对应的关键点进行匹配,这个时候就需要通过描述符进行匹配。
在SIT算法中描述符是一个128维的向量,也就是128个数。
使用k近邻(KNN)算法进行匹配
其实就是找最近的两个向量。
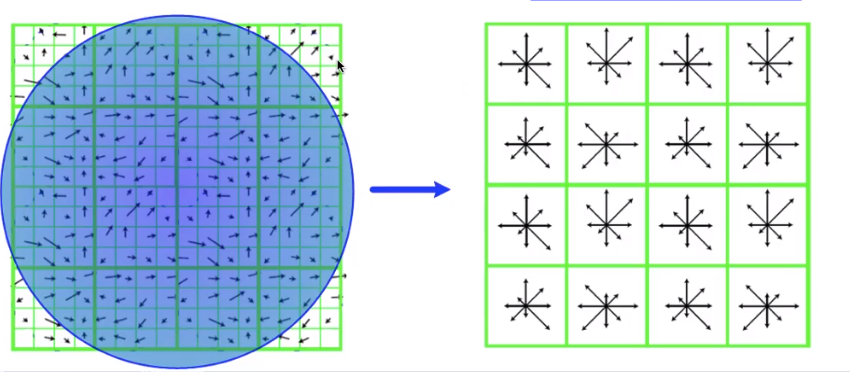
图18
在关键点周围的一个区域,如图18所示。一共分成了16个子区域,每一个最小格是一个像素。在每个子区域内统计八个方向(东、南、西、北、东北、东南、西北、西南)上的梯度(也是经过高斯加权)的长度,所以共有8*16=128个数,这128个数按照顺序写出来就是描述符
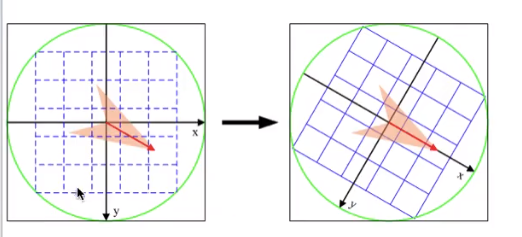
图19
图18的区域并不是直接拿关键点周围的高斯图像区域,而是首先把关键点周围的某个区域旋转到主方向上,为了SIFT的描述符具有旋转不变性(我的理解是可能比较的两张图片中其中一张存在旋转,这样我们将其区域都相对于主方向进行旋转,那么这个关键点周围区域的两张图片就是同一个方向,也就是旋转到了同一个方向),才可以得到稳定的描述符。
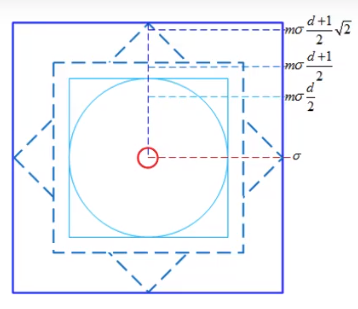
图20
图20是为了确定关键点周围区域的大小,插值的方式。
m一般取3,d有几个小区域(横着算竖着算)d=4
5程序运行结果示例

图21
如图21所示,可以将几个对应位置对应起来。
6 代码
点击查看代码
# coding: utf-8
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore") #忽略警告
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
from PIL import Image
def convolve(filter,mat,padding,strides):
result = None
filter_size = filter.shape
mat_size = mat.shape
if len(filter_size) == 2:
if len(mat_size) == 3:
channel = []
for i in range(mat_size[-1]):
pad_mat = np.pad(mat[:,:,i], ((padding[0], padding[1]), (padding[2], padding[3])), 'constant')
temp = []
for j in range(0,mat_size[0],strides[1]):
temp.append([])
for k in range(0,mat_size[1],strides[0]):
val = (filter*pad_mat[j:j+filter_size[0],k:k+filter_size[1]]).sum()
temp[-1].append(val)
channel.append(np.array(temp))
channel = tuple(channel)
result = np.dstack(channel)
elif len(mat_size) == 2:
channel = []
pad_mat = np.pad(mat, ((padding[0], padding[1]), (padding[2], padding[3])), 'constant')
for j in range(0, mat_size[0], strides[1]):
channel.append([])
for k in range(0, mat_size[1], strides[0]):
val = (filter * pad_mat[j:j + filter_size[0],k:k + filter_size[1]]).sum()
channel[-1].append(val)
result = np.array(channel)
return result
def downsample(img,step = 2):
return img[::step,::step]
def GuassianKernel(sigma , dim):
'''
:param sigma: Standard deviation
:param dim: dimension(must be positive and also an odd number)
:return: return the required Gaussian kernel.
'''
temp = [t - (dim//2) for t in range(dim)]
assistant = []
for i in range(dim):
assistant.append(temp)
# print(type(assistant))
# print(assistant)
assistant = np.array(assistant)
# print(type(assistant))
# print(assistant)
temp = 2*sigma*sigma
result = (1.0/(temp*np.pi))*np.exp(-(assistant**2+(assistant.T)**2)/temp)
return result
# 返回高斯金字塔和高斯差分金字塔
def getDoG(img,n,sigma0,S = None,O = None):
'''
:param img: the original img.
:param sigma0: sigma of the first stack of the first octave. default 1.52 for complicate reasons.
:param n: how many stacks of feature that you wanna extract.
:param S: how many stacks does every octave have. S must bigger than 3.
:param k: the ratio of two adjacent stacks' scale.
:param O: how many octaves do we have.
:return: the DoG Pyramid
'''
# 确定高斯金字塔的组数O和每层的层数S
if S == None:
S = n + 3
if O == None:
O = int(np.log2(min(img.shape[0], img.shape[1]))) - 3
k = 2 ** (1.0 / n)
# 两维列表,第一维表示第几组,第二维表示第几层 直接将每一组的每一层的方差计算出来了
sigma = [[(k**s)*sigma0*(1<<o) for s in range(S)] for o in range(O)]
samplePyramid = [downsample(img, 1 << o) for o in range(O)]
# 高斯金字塔的初始化,是列表的形式
GuassianPyramid = []
for i in range(O): # 遍历每一组 每组的层数是相同的
GuassianPyramid.append([]) # 高斯金字塔添加当前组的初始化列表
for j in range(S): # 遍历每一层
dim = int(6*sigma[i][j] + 1)
if dim % 2 == 0:
dim += 1
# 这里-1表示的是上面刚加入的当前组的初始化列表
GuassianPyramid[-1].append(convolve(GuassianKernel(sigma[i][j], dim),samplePyramid[i],[dim//2,dim//2,dim//2,dim//2],[1,1]))
DoG = [[GuassianPyramid[o][s+1] - GuassianPyramid[o][s] for s in range(S - 1)] for o in range(O)]
return DoG,GuassianPyramid
def adjustLocalExtrema(DoG,o,s,x,y,contrastThreshold,edgeThreshold,sigma,n,SIFT_FIXPT_SCALE):
SIFT_MAX_INTERP_STEPS = 5
SIFT_IMG_BORDER = 5
point = []
img_scale = 1.0 / (255 * SIFT_FIXPT_SCALE)
deriv_scale = img_scale * 0.5
second_deriv_scale = img_scale
cross_deriv_scale = img_scale * 0.25
img = DoG[o][s]
i = 0
while i < SIFT_MAX_INTERP_STEPS:
if s < 1 or s > n or y < SIFT_IMG_BORDER or y >= img.shape[1] - SIFT_IMG_BORDER or x < SIFT_IMG_BORDER or x >= img.shape[0] - SIFT_IMG_BORDER:
return None,None,None,None
img = DoG[o][s]
prev = DoG[o][s - 1]
next = DoG[o][s + 1]
dD = [ (img[x,y + 1] - img[x, y - 1]) * deriv_scale,
(img[x + 1, y] - img[x - 1, y]) * deriv_scale,
(next[x, y] - prev[x, y]) * deriv_scale ]
v2 = img[x, y] * 2
dxx = (img[x, y + 1] + img[x, y - 1] - v2) * second_deriv_scale
dyy = (img[x + 1, y] + img[x - 1, y] - v2) * second_deriv_scale
dss = (next[x, y] + prev[x, y] - v2) * second_deriv_scale
dxy = (img[x + 1, y + 1] - img[x + 1, y - 1] - img[x - 1, y + 1] + img[x - 1, y - 1]) * cross_deriv_scale
dxs = (next[x, y + 1] - next[x, y - 1] - prev[x, y + 1] + prev[x, y - 1]) * cross_deriv_scale
dys = (next[x + 1, y] - next[x - 1, y] - prev[x + 1, y] + prev[x - 1, y]) * cross_deriv_scale
H=[ [dxx, dxy, dxs],
[dxy, dyy, dys],
[dxs, dys, dss]]
X = np.matmul(np.linalg.pinv(np.array(H)),np.array(dD))
xi = -X[2]
xr = -X[1]
xc = -X[0]
if np.abs(xi) < 0.5 and np.abs(xr) < 0.5 and np.abs(xc) < 0.5:
break
y += int(np.round(xc))
x += int(np.round(xr))
s += int(np.round(xi))
i+=1
if i >= SIFT_MAX_INTERP_STEPS:
return None,x,y,s
if s < 1 or s > n or y < SIFT_IMG_BORDER or y >= img.shape[1] - SIFT_IMG_BORDER or x < SIFT_IMG_BORDER or x >= \
img.shape[0] - SIFT_IMG_BORDER:
return None, None, None, None
t = (np.array(dD)).dot(np.array([xc, xr, xi]))
contr = img[x,y] * img_scale + t * 0.5
if np.abs( contr) * n < contrastThreshold:
return None,x,y,s
# 利用Hessian矩阵的迹和行列式计算主曲率的比值
tr = dxx + dyy
det = dxx * dyy - dxy * dxy
if det <= 0 or tr * tr * edgeThreshold >= (edgeThreshold + 1) * (edgeThreshold + 1) * det:
return None,x,y,s
point.append((x + xr) * (1 << o))
point.append((y + xc) * (1 << o))
point.append(o + (s << 8) + (int(np.round((xi + 0.5)) * 255) << 16))
point.append(sigma * np.power(2.0, (s + xi) / n)*(1 << o) * 2)
return point,x,y,s
def GetMainDirection(img,r,c,radius,sigma,BinNum):
expf_scale = -1.0 / (2.0 * sigma * sigma)
X = []
Y = []
W = []
temphist = []
for i in range(BinNum):
temphist.append(0.0)
# 图像梯度直方图统计的像素范围
k = 0
for i in range(-radius,radius+1):
y = r + i
if y <= 0 or y >= img.shape[0] - 1:
continue
for j in range(-radius,radius+1):
x = c + j
if x <= 0 or x >= img.shape[1] - 1:
continue
dx = (img[y, x + 1] - img[y, x - 1])
dy = (img[y - 1, x] - img[y + 1, x])
X.append(dx)
Y.append(dy)
W.append((i * i + j * j) * expf_scale)
k += 1
length = k
W = np.exp(np.array(W))
Y = np.array(Y)
X = np.array(X)
Ori = np.arctan2(Y,X)*180/np.pi
Mag = (X**2+Y**2)**0.5
# 计算直方图的每个bin
for k in range(length):
bin = int(np.round((BinNum / 360.0) * Ori[k]))
if bin >= BinNum:
bin -= BinNum
if bin < 0:
bin += BinNum
temphist[bin] += W[k] * Mag[k]
# smooth the histogram
# 高斯平滑
temp = [temphist[BinNum - 1], temphist[BinNum - 2], temphist[0], temphist[1]]
temphist.insert(0, temp[0])
temphist.insert(0, temp[1])
temphist.insert(len(temphist), temp[2])
temphist.insert(len(temphist), temp[3]) # padding
hist = []
for i in range(BinNum):
hist.append((temphist[i] + temphist[i+4]) * (1.0 / 16.0) + (temphist[i+1] + temphist[i+3]) * (4.0 / 16.0) + temphist[i+2] * (6.0 / 16.0))
# 得到主方向
maxval = max(hist)
return maxval,hist
def LocateKeyPoint(DoG,sigma,GuassianPyramid,n,BinNum = 36,contrastThreshold = 0.04,edgeThreshold = 10.0):
SIFT_ORI_SIG_FCTR = 1.52
SIFT_ORI_RADIUS = 3 * SIFT_ORI_SIG_FCTR
SIFT_ORI_PEAK_RATIO = 0.8
SIFT_INT_DESCR_FCTR = 512.0
# SIFT_FIXPT_SCALE = 48
SIFT_FIXPT_SCALE = 1
KeyPoints = []
O = len(DoG)
S = len(DoG[0])
for o in range(O):
for s in range(1,S-1):
threshold = 0.5*contrastThreshold/(n*255*SIFT_FIXPT_SCALE)
img_prev = DoG[o][s-1]
img = DoG[o][s]
img_next = DoG[o][s+1]
for i in range(img.shape[0]):
for j in range(img.shape[1]):
val = img[i,j]
eight_neiborhood_prev = img_prev[max(0, i - 1):min(i + 2, img_prev.shape[0]), max(0, j - 1):min(j + 2, img_prev.shape[1])]
eight_neiborhood = img[max(0, i - 1):min(i + 2, img.shape[0]), max(0, j - 1):min(j + 2, img.shape[1])]
eight_neiborhood_next = img_next[max(0, i - 1):min(i + 2, img_next.shape[0]), max(0, j - 1):min(j + 2, img_next.shape[1])]
if np.abs(val) > threshold and \
((val > 0 and (val >= eight_neiborhood_prev).all() and (val >= eight_neiborhood).all() and (val >= eight_neiborhood_next).all())
or (val < 0 and (val <= eight_neiborhood_prev).all() and (val <= eight_neiborhood).all() and (val <= eight_neiborhood_next).all())):
#精调关键点位置
point,x,y,layer = adjustLocalExtrema(DoG,o,s,i,j,contrastThreshold,edgeThreshold,sigma,n,SIFT_FIXPT_SCALE)
if point == None:
continue
scl_octv = point[-1]*0.5/(1 << o)
#确定主方向
omax,hist = GetMainDirection(GuassianPyramid[o][layer],x,y,int(np.round(SIFT_ORI_RADIUS * scl_octv)),SIFT_ORI_SIG_FCTR * scl_octv,BinNum)
mag_thr = omax * SIFT_ORI_PEAK_RATIO
for k in range(BinNum):
if k > 0:
l = k - 1
else:
l = BinNum - 1
if k < BinNum - 1:
r2 = k + 1
else:
r2 = 0
if hist[k] > hist[l] and hist[k] > hist[r2] and hist[k] >= mag_thr:
bin = k + 0.5 * (hist[l]-hist[r2]) /(hist[l] - 2 * hist[k] + hist[r2])
if bin < 0:
bin = BinNum + bin
else:
if bin >= BinNum:
bin = bin - BinNum
temp = point[:]
temp.append((360.0/BinNum) * bin)
KeyPoints.append(temp)
return KeyPoints
def calcSIFTDescriptor(img,ptf,ori,scl,d,n,SIFT_DESCR_SCL_FCTR = 3.0,SIFT_DESCR_MAG_THR = 0.2,SIFT_INT_DESCR_FCTR = 512.0,FLT_EPSILON = 1.19209290E-07):
dst = []
pt = [int(np.round(ptf[0])), int(np.round(ptf[1]))] # 坐标点取整
cos_t = np.cos(ori * (np.pi / 180)) # 余弦值
sin_t = np.sin(ori * (np.pi / 180)) # 正弦值
bins_per_rad = n / 360.0
exp_scale = -1.0 / (d * d * 0.5)
hist_width = SIFT_DESCR_SCL_FCTR * scl
radius = int(np.round(hist_width * 1.4142135623730951 * (d + 1) * 0.5))
cos_t /= hist_width
sin_t /= hist_width
rows = img.shape[0]
cols = img.shape[1]
hist = [0.0]*((d+2)*(d+2)*(n+2))
X = []
Y = []
RBin = []
CBin = []
W = []
k = 0
for i in range(-radius,radius+1):
for j in range(-radius,radius+1):
c_rot = j * cos_t - i * sin_t
r_rot = j * sin_t + i * cos_t
rbin = r_rot + d // 2 - 0.5
cbin = c_rot + d // 2 - 0.5
r = pt[1] + i
c = pt[0] + j
if rbin > -1 and rbin < d and cbin > -1 and cbin < d and r > 0 and r < rows - 1 and c > 0 and c < cols - 1:
dx = (img[r, c+1] - img[r, c-1])
dy = (img[r-1, c] - img[r+1, c])
X.append(dx)
Y.append(dy)
RBin.append(rbin)
CBin.append(cbin)
W.append((c_rot * c_rot + r_rot * r_rot) * exp_scale)
k+=1
length = k
Y = np.array(Y)
X = np.array(X)
Ori = np.arctan2(Y,X)*180/np.pi
Mag = (X ** 2 + Y ** 2) ** 0.5
W = np.exp(np.array(W))
for k in range(length):
rbin = RBin[k]
cbin = CBin[k]
obin = (Ori[k] - ori) * bins_per_rad
mag = Mag[k] * W[k]
r0 = int(rbin)
c0 = int(cbin)
o0 = int(obin)
rbin -= r0
cbin -= c0
obin -= o0
if o0 < 0:
o0 += n
if o0 >= n:
o0 -= n
# histogram update using tri-linear interpolation
v_r1 = mag * rbin
v_r0 = mag - v_r1
v_rc11 = v_r1 * cbin
v_rc10 = v_r1 - v_rc11
v_rc01 = v_r0 * cbin
v_rc00 = v_r0 - v_rc01
v_rco111 = v_rc11 * obin
v_rco110 = v_rc11 - v_rco111
v_rco101 = v_rc10 * obin
v_rco100 = v_rc10 - v_rco101
v_rco011 = v_rc01 * obin
v_rco010 = v_rc01 - v_rco011
v_rco001 = v_rc00 * obin
v_rco000 = v_rc00 - v_rco001
idx = ((r0 + 1) * (d + 2) + c0 + 1) * (n + 2) + o0
hist[idx] += v_rco000
hist[idx+1] += v_rco001
hist[idx + (n+2)] += v_rco010
hist[idx + (n+3)] += v_rco011
hist[idx+(d+2) * (n+2)] += v_rco100
hist[idx+(d+2) * (n+2)+1] += v_rco101
hist[idx+(d+3) * (n+2)] += v_rco110
hist[idx+(d+3) * (n+2)+1] += v_rco111
# finalize histogram, since the orientation histograms are circular
for i in range(d):
for j in range(d):
idx = ((i+1) * (d+2) + (j+1)) * (n+2)
hist[idx] += hist[idx+n]
hist[idx+1] += hist[idx+n+1]
for k in range(n):
dst.append(hist[idx+k])
# copy histogram to the descriptor,
# apply hysteresis thresholding
# and scale the result, so that it can be easily converted
# to byte array
nrm2 = 0
length = d * d * n
for k in range(length):
nrm2 += dst[k] * dst[k]
thr = np.sqrt(nrm2) * SIFT_DESCR_MAG_THR
nrm2 = 0
for i in range(length):
val = min(dst[i], thr)
dst[i] = val
nrm2 += val * val
nrm2 = SIFT_INT_DESCR_FCTR / max(np.sqrt(nrm2), FLT_EPSILON)
for k in range(length):
dst[k] = min(max(dst[k] * nrm2,0),255)
return dst
def calcDescriptors(gpyr,keypoints,SIFT_DESCR_WIDTH = 4,SIFT_DESCR_HIST_BINS = 8):
# SIFT_DESCR_WIDTH = 4,描述直方图的宽度
# SIFT_DESCR_HIST_BINS = 8
d = SIFT_DESCR_WIDTH
n = SIFT_DESCR_HIST_BINS
descriptors = []
for i in range(len(keypoints)):
kpt = keypoints[i]
o = kpt[2] & 255
s = (kpt[2] >> 8) & 255 # 该特征点所在的组序号和层序号
scale = 1.0 / (1 << o) # 缩放倍数
size = kpt[3] * scale # 该特征点所在组的图像尺寸
ptf = [kpt[1] * scale, kpt[0] * scale] # 该特征点在金字塔组中的坐标
img = gpyr[o][s] # 该点所在的金字塔图像
descriptors.append(calcSIFTDescriptor(img, ptf, kpt[-1], size * 0.5, d, n))
return descriptors
def SIFT(img,showDoGimgs = False): # he
SIFT_SIGMA = 1.6 # 想要得到的尺度
SIFT_INIT_SIGMA = 0.5 # 假设的摄像头的尺度
sigma0 = np.sqrt(SIFT_SIGMA**2-SIFT_INIT_SIGMA**2)
n = 3
# 得到高斯差分金字塔
DoG,GuassianPyramid = getDoG(img, n, sigma0) # he
#展示高斯差分金字塔
if showDoGimgs:
for i in DoG:
print(i)
for j in i:
plt.imshow(j.astype(np.uint8), cmap='gray')
plt.axis('off')
# plt.show()
# 关键点定位
KeyPoints = LocateKeyPoint(DoG, SIFT_SIGMA, GuassianPyramid, n) # he
# 计算描述符
discriptors = calcDescriptors(GuassianPyramid,KeyPoints) # he
return KeyPoints,discriptors
def Lines(img,info,color = (255,0,0),err = 700):
if len(img.shape) == 2:
result = np.dstack((img,img,img))
else:
result = img
k = 0
for i in range(result.shape[0]):
for j in range(result.shape[1]):
temp = (info[:,1]-info[:,0])
A = (j - info[:,0])*(info[:,3]-info[:,2])
B = (i - info[:,2])*(info[:,1]-info[:,0])
temp[temp == 0] = 1e-9
t = (j-info[:,0])/temp
e = np.abs(A-B)
temp = e < err
if (temp*(t >= 0)*(t <= 1)).any():
result[i,j] = color
k+=1
print(k)
return result
def drawLines(X1,X2,Y1,Y2,dis,img,num = 10):
info = list(np.dstack((X1,X2,Y1,Y2,dis))[0])
info = sorted(info,key=lambda x:x[-1])
info = np.array(info)
info = info[:min(num,info.shape[0]),:]
img = Lines(img,info)
#plt.imsave('./sift/3.jpg', img)
if len(img.shape) == 2:
plt.imshow(img.astype(np.uint8),cmap='gray')
else:
plt.imshow(img.astype(np.uint8))
plt.axis('off')
#plt.plot([info[:,0], info[:,1]], [info[:,2], info[:,3]], 'c')
# fig = plt.gcf()
# fig.set_size_inches(int(img.shape[0]/100.0),int(img.shape[1]/100.0))
#plt.savefig('./sift/2.jpg')
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
print("********start**********")
print("read the first image")
origimg = plt.imread('./SIFTimg/1.jpeg')
if len(origimg.shape) == 3:
img = origimg.mean(axis=-1)
else:
img = origimg
# 计算图片的关键点和描述符
keyPoints,discriptors = SIFT(img)
print("read the second image")
origimg2 = plt.imread('./SIFTimg/2.jpeg')
if len(origimg.shape) == 3:
img2 = origimg2.mean(axis=-1)
else:
img2 = origimg2
ScaleRatio = img.shape[0]*1.0/img2.shape[0] #第一张图片和第二张图片的比例大小
print(img.shape,img2.shape,ScaleRatio)
img2 = np.array(Image.fromarray(img2).resize((int(round(ScaleRatio * img2.shape[1])),img.shape[0]), Image.BICUBIC))
print(img2.shape)
keyPoints2, discriptors2 = SIFT(img2,True)
# 使用knn算法进行匹配,然后将匹配结果放入画线函数
print("start knn")
knn = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=1)
print("type"+str(type(knn)))
print("content"+str(knn))
print(knn)
knn.fit(discriptors,[0]*len(discriptors))
match = knn.kneighbors(discriptors2,n_neighbors=1,return_distance=True)
# print("match")
# print(match)
keyPoints = np.array(keyPoints)[:,:2]
keyPoints2 = np.array(keyPoints2)[:,:2]
keyPoints2[:, 1] = img.shape[1] + keyPoints2[:, 1]
origimg2 = np.array(Image.fromarray(origimg2).resize((img2.shape[1],img2.shape[0]), Image.BICUBIC))
result = np.hstack((origimg,origimg2))
keyPoints = keyPoints[match[1][:,0]]
X1 = keyPoints[:, 1]
X2 = keyPoints2[:, 1]
Y1 = keyPoints[:, 0]
Y2 = keyPoints2[:, 0]
drawLines(X1,X2,Y1,Y2,match[0][:,0],result,6)
最后再次感谢 会飞的吴克,给出完整可运行代码
代码链接
作者:孙建钊
出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/sunjianzhao/
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文连接,否则保留追究法律责任的权利。



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 25岁的心里话
· 闲置电脑爆改个人服务器(超详细) #公网映射 #Vmware虚拟网络编辑器
· 零经验选手,Compose 一天开发一款小游戏!
· 因为Apifox不支持离线,我果断选择了Apipost!
· 通过 API 将Deepseek响应流式内容输出到前端