多用户登录限制
代码下载:login_limit
最近闲来没事,但就这么闲着心里老不踏实,总得找点事干干啊,大好时光不能白白浪费啊,于是乎捋了捋平时工作会遇到的一些常见问题,首先想到了多用户登录限制问题,下面就对此问题做一点思考讲解。
1、设计场景
1)同一时刻不允许某个用户多地登录
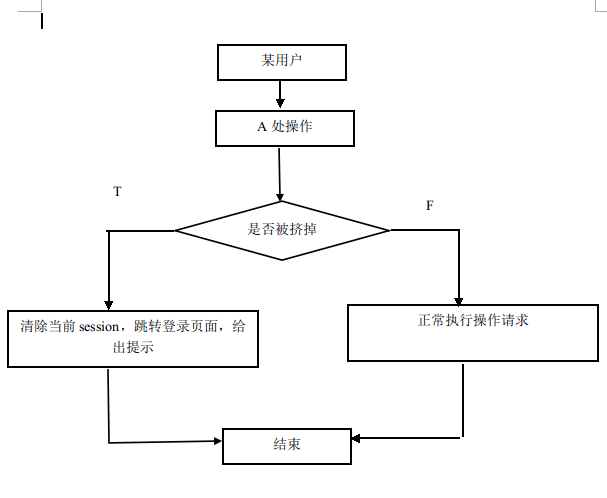
2)用户已在A处登录,现在从B处登录是允许的,但会把A处挤掉(考虑到用户在A处登录后因某些情况跑到了B处,但还想继续之前的工作,所以需要登录系统)
3)B处挤掉A后,A再做其它操作的时候系统会给出提示,该用户在别处登录,如不是本人操作可能密码泄漏,请修改密码。
2、思路导图
每个用户登录的时候,通常我们会将用户信息存入session,以便用户进行操作的时候系统方便得到用户的基本信息。但这个session具有私有性,只对当前用户可见(如果同意用户在不同浏览器登录会得到不同的session,这也是为什么可以多用户登录的根源所在)。那么接着问题就来了,某个用户登录的时候如何能知道自己是否在线,相信聪明的你已经想到,这还不好半,把在线的用户信息存储在一个公共的地方问题不就迎刃而解了么,网上一查,解决方案无出其右,大致为以下两种
1)数据库中标识在线用户
2)存储到application中
经过重重考虑,我们会发现方案一需要解决许多棘手的问题(用户异常退出未来得及修改状态,频繁访问数据库影响性能等),这对于一个要求完美的你来说显然是不合时宜的,于是我们采用了方案二,将在线用户信息保存到application中,具体设计如下。
1)登录流程图
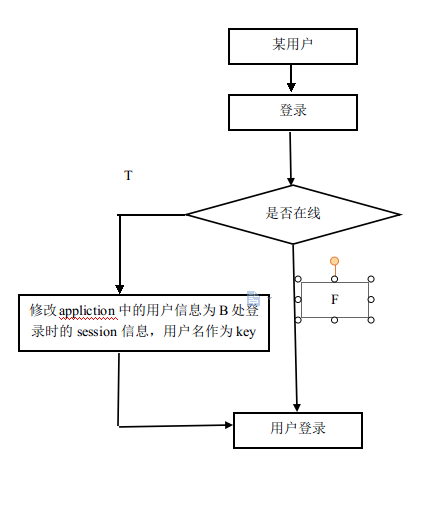
2)被挤掉后操作流程图
3、代码
1)登录方法
@RequestMapping(value = "/login", method = RequestMethod.POST) public String login(String userName, String password, RedirectAttributes redirectAttributes, HttpServletRequest request) { //判断用户是否已经在线及处理(已在线则剔除) String loginLimite = limiteLogin.loginLimite(request, userName); //判断用户名、密码是否正确 String result = userService.login(userName, password); if (result.equals("success")) { request.getSession().setAttribute("now_user", userService.findByUserName(userName));
//用户掉线,登录后重定向到保存的链接 Object url = request.getSession().getAttribute("redirect_link"); if (url != null) { request.getSession().removeAttribute("redirect_link"); return "redirect:" + url.toString(); } return "index"; } redirectAttributes.addFlashAttribute("message", result); return "redirect:/other/toLogin"; }
2)登录判断是否已经在线
@Service @Transactional public class LimiteLogin { private static Logger log = Logger.getLogger(SessionListener.class); private static Map<String, String> loginUserMap = new HashMap<>();//存储在线用户 private static Map<String, String> loginOutTime = new HashMap<>();//存储剔除用户时间 @Autowired private UserService userService; public String loginLimite(HttpServletRequest request, String userName) { User user = userService.findByUserName(userName); String sessionId = request.getSession().getId(); for (String key : loginUserMap.keySet()) { //用户已在另一处登录 if (key.equals(user.getUserName()) && !loginUserMap.containsValue(sessionId)) { log.info("用户:" + user.getUserName() + ",于" + DateUtil.dateFormat(new Date(), "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss") + "被剔除!"); loginOutTime.put(user.getUserName(), DateUtil.dateFormat(new Date(), "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")); loginUserMap.remove(user.getUserName()); break; } } loginUserMap.put(user.getUserName(), sessionId); request.getSession().getServletContext().setAttribute("loginUserMap", loginUserMap); request.getSession().getServletContext().setAttribute("loginOutTime", loginOutTime); return "success"; } }
3)登录拦截器(未登录跳转登录页)
public class LoginInterceptor extends HandlerInterceptorAdapter { @Override public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { HttpSession session = request.getSession(); User user = (User) session.getAttribute("now_user"); if (session.getAttribute("now_user") == null) { response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath() + "/other/toLogin"); return false; } //多用户登录限制判断,并给出提示信息 boolean isLogin = false; if (user != null) { Map<String, String> loginUserMap = (Map<String, String>) session.getServletContext().getAttribute("loginUserMap"); String sessionId = session.getId(); for (String key : loginUserMap.keySet()) { //用户已在另一处登录 if (key.equals(user.getUserName()) && !loginUserMap.containsValue(sessionId)) { isLogin = true; break; } } } if (isLogin) { Map<String, String> loginOutTime = (Map<String, String>) session.getServletContext().getAttribute("loginOutTime"); session.setAttribute("mess", "用户:" + user.getUserName() + ",于 " + loginOutTime.get(user.getUserName()) + " 已在别处登录!"); loginOutTime.remove(user.getUserName()); session.getServletContext().setAttribute("loginUserMap", loginOutTime); response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath() + "/other/toLogin"); return false; } return super.preHandle(request, response, handler); } @Override public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception { super.postHandle(request, response, handler, modelAndView); } @Override public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception { super.afterCompletion(request, response, handler, ex); } }
4)在session销毁的时候,把loginUserMap中保存的键值对清除
public class SessionListener implements HttpSessionListener { private static Logger log = Logger.getLogger(SessionListener.class); @Override public void sessionCreated(HttpSessionEvent event) { } @Override public void sessionDestroyed(HttpSessionEvent event) { HttpSession session = event.getSession(); String sessionId = session.getId(); //在session销毁的时候,把loginUserMap中保存的键值对清除 User user = (User) session.getAttribute("now_user"); if (user != null) { Map<String, String> loginUserMap = (Map<String, String>) event.getSession().getServletContext().getAttribute("loginUserMap"); if(loginUserMap.get(user.getUserName()).equals(sessionId)){ log.info("clean user from application : " + user.getUserName()); loginUserMap.remove(user.getUserName()); event.getSession().getServletContext().setAttribute("loginUserMap", loginUserMap); } } } }
5)web.xml
<!-- session listener 多用户登录限制,退出清除session信息的同时清除application中存放用户登录信息-->
<listener>
<listener-class>com.service.limitelogin.SessionListener</listener-class>
</listener>
6)页面代码(用于给出提示的同时,清除被挤掉用户的session信息,否则提示信息会一直显示)
<script type="text/javascript"> $(document).ready(function () { var message='${mess}'; if (message != "") { $.ajax({ type: 'GET', async: false, cache: false, url: '/other/clearUserSession', dataType: '', data: {}, success: function (data) { } }); $('#mess').html(message); } }); </script>
7)清除挤掉用户session代码
/** * 多用户登录限制,清除session信息(登录信息、提示信息) * * @param request * @return */ @ResponseBody @RequestMapping(value = "/clearUserSession") public String clearUserSession(HttpServletRequest request) { HttpSession httpSession = request.getSession(); //httpSession.invalidate(); httpSession.removeAttribute("now_user"); httpSession.removeAttribute("mess"); return "success"; }
到此开发工作完成
4、运行结果





