算法数据结构系列-实践篇-链表算法
@
微信公众号:JavaTomStudio
1、尾插法创建链表
Node head = null;
public void add(int data){
Node newNode = new Node(data);
if(head == null){//头结点是否为空
head = newNode;
return;
}
Node temp = head;//查找添加位
while(temp.next != null){
temp = temp.next;
}
temp.next = newNode;
}
2、删除链表指定节点
public Boolean delete(int index){
if(index < 0 || index>length()) {
return false;
}
//删除链表的第一个元素
if(index == 0){
head = head.next;
return true;
}
//删除第一个以外的元素
Node pre = head;
Node cur = head.next;
int i=1;
while(cur != null){
if(i == index){
pre.next = cur.next;
return true;
}
pre=cur;
cur=cur.next;
i++;//别忘了
}
return true;
}
3、排序链表
public Node orderList(Node head){
Node seq = null;
Node cur = head;
while(cur.next != null){//遍历选择
seq = cur.next;
while(seq != null) {//选出最小点
if(cur.data>seq.data){
int temp = cur.data;
cur.data=seq.data;
seq.data=temp;
}
seq=seq.next;//不要忘了,移动到下一点继续
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return head;
}
4、普通链表去重
public ListNode deleteDuplication(ListNode pHead){
if(head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<Integer>();
ListNode cur = pHead;
ListNode pre = null;
while(cur != null) {
if (!set.contains(cur.val)) {
set.add(cur.val);
pre = cur;//pre总指向当前添加的节点,永远指向尾部
}
if(set.contains(cur.val)) {
pre.next = cur.next;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return pHead;
}
// 方法二
public void deleteDuplecate2(){
Node cur = head;
while(cur != null){
Node pre = cur;
Node seq = cur.next;//这样是为了有前驱
while(seq != null){//若没有后继则不必考虑去重
if(seq.data == cur.data){
pre.next = seq.next;
}
if(seq.data != cur.data){
pre = seq;
}
seq = seq.next;
}
cur=cur.next;
}
}
5、排序链表去重
public void duplication(LinkList linkList) {
LinkListNode cur = linkList.getHead();
LinkListNode seq = null;
LinkListNode pre = null;
while (cur != null) {//遍历
seq = cur.getNext();
if (seq == null) {
break;
}
if (seq.getVal() != cur.getVal()) {
cur = cur.getNext();
continue;
}
do {
pre = seq;
seq = seq.getNext();
} while (seq != null && seq.getVal() == cur.getVal());
if (seq == null) {
cur.setNext(null);
break;
}
pre.setNext(null);
cur.setNext(seq);
cur = seq;
}
}
6、不知道头指针情况下删除节点
public boolean deleteNode(Node node) {
if(node==null || node.next==null) {
return false;
}
//与后继节点交换元素
int temp = node.data;
node.data = node.next.data;
node.next.data = temp;
node.next=node.next.next;
return true;
}
7、分割链表
编写代码,以给定值x为基准将链表分割成两部分,所有小于x的结点排在大于或等于x的结点之前
public ListNode partition(ListNode pHead, int x) {
// write code here
if (pHead == null) {
return pHead;
}
ListNode cur = pHead;
ListNode head1 = null;
ListNode pre1 = null;
ListNode head2 = null;
ListNode pre2 = null;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val < x && head1 == null) {
head1 = cur;
pre1 = cur;
}
if (cur.val >= x && head2 == null) {
head2 = cur;
pre2 = cur;
}
if (cur.val < x&& head1 != null) {
pre1.next = cur;
pre1 = cur;
}
if (cur.val >= x&& head1 != null) {
pre2.next = cur;
pre2 = cur;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
if (head1 == null) {
return head2;
}
if (head2 == null) {
return head1;
}
pre2.next = null;//next不是rear
pre1.next = head2;//next啊亲啊
return head1;
}
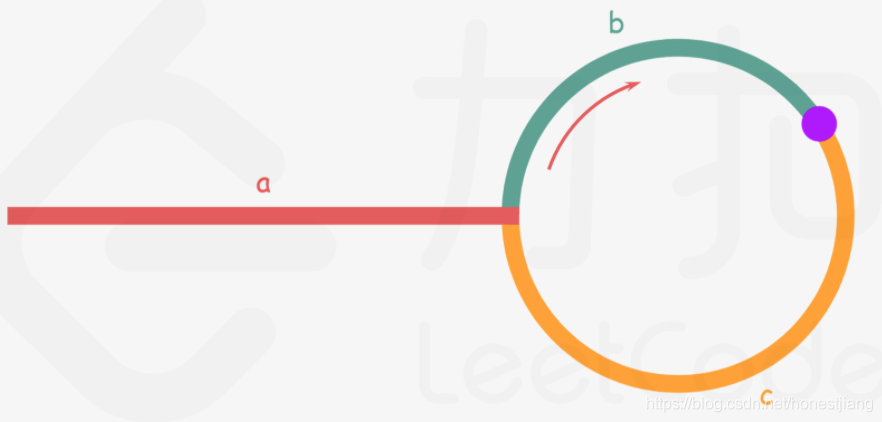
8、快慢指针求链表环的入口点
等量关系:a+(n+1)b+nc=2(a+b) ⟹ a=c+(n−1)(b+c) ⟹ a= c + (n-1)*R式,从相遇点到入环点的距离加上 n-1 圈的环长 R ,恰好等于从链表头部到入环点的距离。
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
boolean hasCycle = false;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if (fast == slow) {
hasCycle = true;
break;
}
}
if (!hasCycle) {
return null;
}
slow = head;
while (fast != slow) {
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
9、快慢指针求链表的中间节点
public ListNode searchMid(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head, quick = head;
while (quick != null && quick.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
quick = quick.next.next;
}
return slow;
}
10、快慢指针判断回文链表
// 最简单的办法,通过堆栈来实现,放入栈在遍历一次
public boolean chkPalindrome(ListNode head) {
// write code here
if (head == null) {
return false;
}
ListNode rear = searchMid(head);
ListNode cur = rear.next
ListNode seq = null;
while (cur != null) {
seq = cur.next;//保存后继
cur.next = rear;//逆置
rear = cur;//移动
cur = seq;//该算法不需要返回最后节点
}
while (head != rear) {
if (head.val != rear.val) {
return false;
}
if (head.next == rear && head.val == rear.val) {
return true;
}
rear = rear.next;
head = head.next;
}
return true;
}
11、求两个链表的交点
public ListNode FindFirstCommonNode(ListNode pHead1, ListNode pHead2) {
if (pHead1 == null || pHead2 == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode tail1 = pHead1;
ListNode tail2 = pHead2;
while (tail1.next != null) {
tail1 = tail1.next;
}
while (tail2.next != null) {
tail2 = tail2.next;
}
if (tail1 != tail2) {
return null;
}
ListNode cur1 = pHead1;
ListNode cur2 = pHead2;
int l1 = getLen(pHead1);
int l2 = getLen(pHead2);
int delta = l1 - l2;
while (delta > 0) {
cur1 = cur1.next;
delta--;
}
while (delta < 0) {
cur2 = cur2.next;
delta++;
}
while (cur1 != cur2) {
cur1 = cur1.next;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
return cur1;
}
12、Offer-06 从尾到头打印链表
问题描述:输入一个链表的头节点,从尾到头反过来返回每个节点的值(用数组返回)。输入:head = [1,3,2],输出:[2,3,1]。
public int[] reversePrint(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return new int[]{};
}
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
ListNode p = head;
while (p != null) {
stack.push(p.val);
p = p.next;
}
int[] result = new int[stack.size()];
int k = 0;
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
result[k++] = stack.pop();
}
return result;
}
13、Offer-24 反转链表
剑指 Offer 24. 反转链表:定义一个函数,输入一个链表的头节点,反转该链表并输出反转后链表的头节点。示例:输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL,输出: 5->4->3->2->1->NULL
public ListNode ReverseList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode pre = head, cur = head.next;
ListNode seq = null, newHead = null;
head.next = null;
while (cur != null) {
seq = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
if (seq == null) {
newHead = cur;
}
cur = seq;
}
return newHead;
}
14、Offer-22 链表中倒数第k个节点
剑指 Offer 22. 链表中倒数第k个节点:输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个节点。为了符合大多数人的习惯,本题从1开始计数,即链表的尾节点是倒数第1个节点。
例如,一个链表有 6 个节点,从头节点开始,它们的值依次是 1、2、3、4、5、6。这个链表的倒数第 3 个节点是值为 4 的节点。
public ListNode FindKthToTail(ListNode head, int k) {
if (head == null || getLen(head) < k || k <= 0) {
return null;
}
ListNode cur1 = head;
ListNode cur2 = head;
for (int i = 1; i < k; i++) {
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
while (cur2.next != null) {
cur2 = cur2.next;
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
return cur1;
}
15、Offer-18. 删除链表的节点
剑指 Offer 18. 删除链表的节点:给定单向链表的头指针和一个要删除的节点的值,定义一个函数删除该节点。返回删除后的链表的头节点。
示例:
输入: head = [4,5,1,9], val = 5
输出: [4,1,9]
解释: 给定你链表中值为 5 的第二个节点,那么在调用了你的函数之后,该链表应变为 4 -> 1 -> 9.
/**
* 考虑头结点为删除节点+非头结点删除
*/
public ListNode deleteNode(ListNode head, int val) {
if (head == null) {
return head;
}
if (head.val == val) {
return head.next;
}
ListNode pre = head, cur = head.next;
while (cur != null && cur.val != val) {
pre = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
if (cur != null) {
pre.next = cur.next;
}
return head;
}
16、Offer-25 合并两个排序的链表
剑指 Offer 25. 合并两个排序的链表:输入两个递增排序的链表,合并这两个链表并使新链表中的节点仍然是递增排序的。示例1:输入:1->2->4, 1->3->4,输出:1->1->2->3->4->4。
public ListNode Merge(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
if (list1 == null) {
return list2;
}
if (list2 == null) {
return list1;
}
ListNode head = null;
if (list1.val < list2.val) {
head = list1;
head.next = Merge(list1.next, list2);
} else {
head = list2;
head.next = Merge(list1, list2.next);
}
return head;
}
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
if (l1 == null) {
return l2;
}
if (l2 == null) {
return l1;
}
ListNode dum = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode cur = dum;
while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
int l1v = l1.val, l2v = l2.val;
if (l1v <= l2v) {
cur.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
}
if (l1v > l2v) {
cur.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = l1 == null ? l2 : l1;
return dum.next;
}
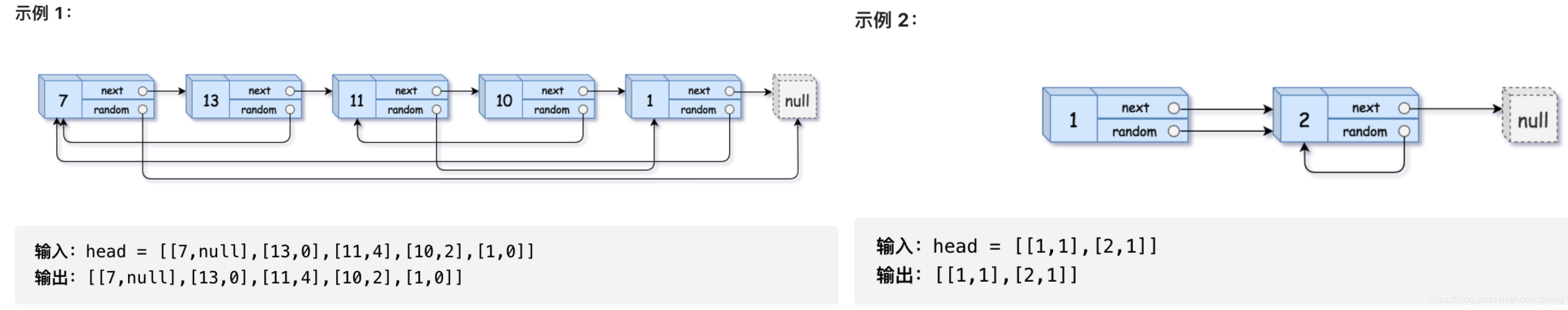
17、Offer-35 复杂链表的复制
剑指 Offer 35. 复杂链表的复制:请实现 copyRandomList 函数,复制一个复杂链表。在复杂链表中,每个节点除了有一个 next 指针指向下一个节点,还有一个 random 指针指向链表中的任意节点或者 null。
// 普通链表复制
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
Node cur = head;
Node dum = new Node(0), pre = dum;
while(cur != null) {
Node node = new Node(cur.val); // 复制节点 cur
pre.next = node; // 新链表的 前驱节点 -> 当前节点
// pre.random = "???"; // 新链表的 「 前驱节点 -> 当前节点 」 无法确定
cur = cur.next; // 遍历下一节点
pre = node; // 保存当前新节点
}
return dum.next;
}
// 复杂链表复制:哈希表法
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return head;
}
// 复制各节点,并建立 “原节点 -> 新节点” 的 Map 映射
Node cur = head;
Map<Node, Node> nodeMap = new HashMap<>();
while(cur != null) {
nodeMap.put(cur, new Node(cur.val));
cur = cur.next;
}
cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
nodeMap.get(cur).next = nodeMap.get(cur.next);
nodeMap.get(cur).random = nodeMap.get(cur.random);
cur = cur.next;
}
return nodeMap.get(head); // 返回新链表的头节点
}
// 复杂链表复制:链表合并拆分法 原节点 1 -> 新节点 1 -> 原节点 2 -> 新节点 2 ->
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if(head == null) return null;
Node cur = head;
// 1. 复制各节点,并构建拼接链表
while(cur != null) {
Node tmp = new Node(cur.val);
tmp.next = cur.next;
cur.next = tmp;
cur = tmp.next;
}
// 2. 构建各新节点的 random 指向
cur = head;
while(cur != null) {
if(cur.random != null)
cur.next.random = cur.random.next;
cur = cur.next.next;
}
// 3. 拆分两链表
cur = head.next;
Node pre = head, res = head.next;
while(cur.next != null) {
pre.next = pre.next.next;
cur.next = cur.next.next;
pre = pre.next;
cur = cur.next;
}
pre.next = null; // 单独处理原链表尾节点
return res; // 返回新链表头节点
}
本文由mdnice多平台发布

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号