【C++】weak_ptr
weak_ptr 详解
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
class CB;
class CA
{
public:
CA() { std::cout << "CA()" << std::endl; }
~CA() { std::cout << "~CA()" << std::endl; }
void set_ptr(std::shared_ptr<CB> &ptr) { m_ptr_b = ptr; }
private:
std::shared_ptr<CB> m_ptr_b;
};
class CB
{
public:
CB() { std::cout << "CB()" << std::endl; }
~CB() { std::cout << "~CB()" << std::endl; }
void set_ptr(std::shared_ptr<CA> &ptr) { m_ptr_a = ptr; }
private:
std::shared_ptr<CA> m_ptr_a;
};
int main()
{
std::shared_ptr<CA> ptr_a(new CA());
std::shared_ptr<CB> ptr_b(new CB());
ptr_a->set_ptr(ptr_b);
ptr_b->set_ptr(ptr_a);
std::cout << ptr_a.use_count() << " " << ptr_b.use_count() << std::endl;
return 0;
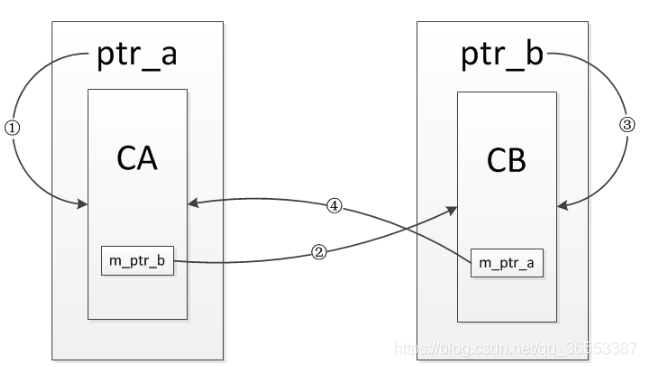
}既然析构函数没有调用,就说明ptr_a和ptr_b两个变量的引用计数都不是0。
分析一下引用情况
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
class CB;
class CA
{
public:
CA() { std::cout << "CA()" << std::endl; }
~CA() { std::cout << "~CA()" << std::endl; }
void set_ptr(std::shared_ptr<CB>& ptr) { m_ptr_b = ptr; }
private:
std::shared_ptr<CB> m_ptr_b;
};
class CB
{
public:
CB() { std::cout << "CB()" << std::endl; }
~CB() { std::cout << "~CB()" << std::endl; }
void set_ptr(std::shared_ptr<CA>& ptr) { m_ptr_a = ptr; }
private:
std::weak_ptr<CA> m_ptr_a;
};
int main()
{
std::shared_ptr<CA> ptr_a(new CA());
std::shared_ptr<CB> ptr_b(new CB());
ptr_a->set_ptr(ptr_b);
ptr_b->set_ptr(ptr_a);
std::cout << ptr_a.use_count() << " " << ptr_b.use_count() << std::endl;
return 0;
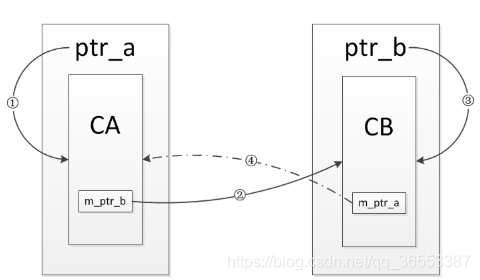
}流程与上一例子大体相似,但是不同的是4这条引用是通过weak_ptr建立的,并不会增加引用计数。也就是说,CA的对象只有一个引用计数,而CB的对象只有两个引用计数,当main函数返回时,对象ptr_a和ptr_b被销毁,也就是1,3两条引用会被断开,此时CA对象的引用计数会减为0,对象被销毁,进而解决了引用成环的问题。
参考资料


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号