Python操作MySQL:pymysql和SQLAlchemy
pymsql
pymsql是Python中操作MySQL的模块,其使用方法和MySQLdb几乎相同。
下载安装
1 pip3 install pymysql
使用操作
1、执行SQL
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- 3 import pymysql 4 5 # 创建连接 6 conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', passwd='123', db='t1') 7 # 创建游标 8 cursor = conn.cursor() 9 10 # 执行SQL,并返回收影响行数 11 effect_row = cursor.execute("update hosts set host = '1.1.1.2'") 12 13 # 执行SQL,并返回受影响行数 14 #effect_row = cursor.execute("update hosts set host = '1.1.1.2' where nid > %s", (1,)) 15 16 # 执行SQL,并返回受影响行数 17 #effect_row = cursor.executemany("insert into hosts(host,color_id)values(%s,%s)", [("1.1.1.11",1),("1.1.1.11",2)]) 18 19 20 # 提交,不然无法保存新建或者修改的数据 21 conn.commit() 22 23 # 关闭游标 24 cursor.close() 25 # 关闭连接 26 conn.close()
示例:
1 import pymysql 2 3 4 conn = pymysql.connect(host="10.37.129.3",port=3306,user="egon",passwd="123456",db="homework",charset="utf8") 5 6 cursor = conn.cursor() 7 8 9 #方式一: 10 11 sql = "select * from course where cid=1" 12 effect_row = cursor.execute(sql) 13 14 15 # 方式二: 16 sql = "select * from course where cid='%s'" %(1,) 17 effect_row = cursor.execute(sql) 18 19 20 # 方式三 普通 列表 21 sql = "select * from course where cid='%s'" 22 23 effect_row = cursor.execute(sql,1) 24 effect_row = cursor.execute(sql,[1]) 25 26 27 # 方式四 字典格式 28 29 sql = "select * from course where cid='%(u)s'" 30 effect_row = cursor.execute(sql,{"u":1}) 31 32 33 row_1 = cursor.fetchone() 34 35 cursor.close() 36 conn.close() 37 38 print(row_1)
2、获取新创建数据自增ID
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- 3 import pymysql 4 5 conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', passwd='123', db='t1') 6 cursor = conn.cursor() 7 cursor.executemany("insert into hosts(host,color_id)values(%s,%s)", [("1.1.1.11",1),("1.1.1.11",2)]) 8 conn.commit() 9 cursor.close() 10 conn.close() 11 12 # 获取最新自增ID 13 new_id = cursor.lastrowid
3、获取查询数据
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- 3 import pymysql 4 5 conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', passwd='123', db='t1') 6 cursor = conn.cursor() 7 cursor.execute("select * from hosts") 8 9 # 获取第一行数据 10 row_1 = cursor.fetchone() 11 12 # 获取前n行数据 13 # row_2 = cursor.fetchmany(3) 14 # 获取所有数据 15 # row_3 = cursor.fetchall() 16 17 conn.commit() 18 cursor.close() 19 conn.close()
注:在fetch数据时按照顺序进行,可以使用cursor.scroll(num,mode)来移动游标位置,如:
- cursor.scroll(1,mode='relative') # 相对当前位置移动
- cursor.scroll(2,mode='absolute') # 相对绝对位置移动
4、fetch数据类型
关于默认获取的数据是元祖类型,如果想要或者字典类型的数据,即:
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- 3 import pymysql 4 5 conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', passwd='123', db='t1') 6 7 # 游标设置为字典类型 8 cursor = conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) 9 r = cursor.execute("call p1()") 10 11 result = cursor.fetchone() 12 13 conn.commit() 14 cursor.close() 15 conn.close()
5、插入演示
1 import pymysql 2 3 4 conn = pymysql.connect(host="10.37.129.3",port=3306,user="egon",passwd="123456",db="student_info",charset="utf8") 5 6 cursor = conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) 7 8 9 #插入一行 10 # sql = "insert into student_info(sname,gender,class_id) VALUES('alex1','女',2)" 11 12 #插入多行 13 sql = "insert into student_info(sname,gender,class_id) VALUES('alex1','女',2),('alex2','女',2),('alex3','女',2)" 14 15 r = cursor.execute(sql) 16 17 #或 18 19 sql = "insert into userinfo(username,password) values(%s,%s)" 20 # 受影响的行数 21 r = cursor.executemany(sql,[('egon','sb'),('laoyao','BS')]) 22 23 24 25 26 conn.commit() 27 cursor.close() 28 conn.close() 29 30 print(r)
6、补充
1 # sql 注入 2 import pymysql 3 4 user = input("username:") 5 pwd = input("password:") 6 7 conn = pymysql.connect(host="localhost",user='root',password='',database="db3") #建立与客户端的链接 8 cursor = conn.cursor() 9 sql = "select * from userinfo where username='%s' and pwd='%s'" %(user,pwd,) #不要自己定义放置占位符user和pwd,防数据库被泄露 10 # select * from userinfo where username='uu' or 1=1 -- ' and password='%s' 11 #上面部分会理解成,第一部分:select * from userinfo where username='uu',第二部分:or 1=1,第三部分:-- 注释, 12 # 第四部分:' and password='%s',第四部分会当成注释内容。所以执行该程序会显示登录成功。 13 cursor.execute(sql) #执行sql语句 14 result = cursor.fetchone() #返回第一行内容 15 #关闭连接 16 cursor.close() 17 conn.close() 18 19 if result: 20 print('登录成功') 21 else: 22 print('登录失败')
1 import pymysql 2 user = input("username:") 3 pwd = input("password:") 4 5 conn = pymysql.connect(host="localhost",user='root',password='',database="db3") 6 cursor = conn.cursor() 7 sql = "select * from userinfo where username=%s and pwd=%s" 8 # cursor.execute(sql,(user,pwd)) 9 cursor.execute(sql,[user,pwd]) #cursor.execute(sql,user,pwd)也可写成cursor.execute(sql,[user,pwd]),效果一样 10 # cursor.execute(sql,{'u':user,'p':pwd}) #sql中加入key值,打印结果就会变成字典的格式而不是元组格式 11 result = cursor.fetchone() #取一行 12 cursor.close() 13 conn.close() 14 if result: 15 print('登录成功') 16 else: 17 print('登录失败') 18 19 print(result) 20
1 import pymysql 2 3 # 增加,删,该 4 #增 5 # conn = pymysql.connect(host="localhost",user='root',password='',database="db3") 6 # cursor = conn.cursor() 7 # sql = "insert into userinfo(username,pwd) values('root','123123')" 8 # 受影响的行数 9 # r = cursor.execute(sql) 10 # # ****** 11 # conn.commit() #对数据库有改变均要执行conn.commit()命令,提交给数据库。所以增删改均需有这条命令,查不需要。 12 # cursor.close() 13 # conn.close() 14 15 # conn = pymysql.connect(host="localhost",user='root',password='',database="db3") 16 # cursor = conn.cursor() 17 # # sql = "insert into userinfo(username,pwd) values(%s,%s)" 18 # # cursor.execute(sql,(user,pwd,)) 19 # 20 # sql = "insert into userinfo(username,password) values(%s,%s)" 21 # # 受影响的行数 22 # r = cursor.executemany(sql,[('egon','sb'),('laoyao','BS')]) 23 # # ****** 24 # conn.commit() 25 # cursor.close() 26 # conn.close() 27 28 29 30 31 # 查 32 # conn = pymysql.connect(host="localhost",user='root',password='',database="db666") 33 # cursor = conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) 34 # sql = "select * from userinfo" 35 # cursor.execute(sql) 36 37 # cursor.scroll(1,mode='relative') # 相对当前位置移动 38 # cursor.scroll(2,mode='absolute') # 相对绝对位置移动 39 # result = cursor.fetchone() 40 # print(result) 41 # result = cursor.fetchone() 42 # print(result) 43 # result = cursor.fetchone() 44 # print(result) 45 # result = cursor.fetchall() 46 # print(result) 47 48 49 # result = cursor.fetchmany(4) 50 # print(result) 51 # cursor.close() 52 # conn.close() 53 54 55 56 57 # 新插入数据的自增ID: cursor.lastrowid 58 # import pymysql 59 # 60 # conn = pymysql.connect(host="localhost",user='root',password='',database="db3") 61 # cursor = conn.cursor() 62 # sql = "insert into userinfo(username,pwd) values('asdfasdf','123123')" 63 # cursor.execute(sql) 64 # conn.commit() 65 # print(cursor.lastrowid) #lastrowid最后一个自增id 66 # cursor.close() 67 # conn.close()
SQLAchemy
SQLAlchemy是Python编程语言下的一款ORM框架,该框架建立在数据库API之上,使用关系对象映射进行数据库操作,简言之便是:将对象转换成SQL,然后使用数据API执行SQL并获取执行结果。
安装:
1 pip3 install SQLAlchemy
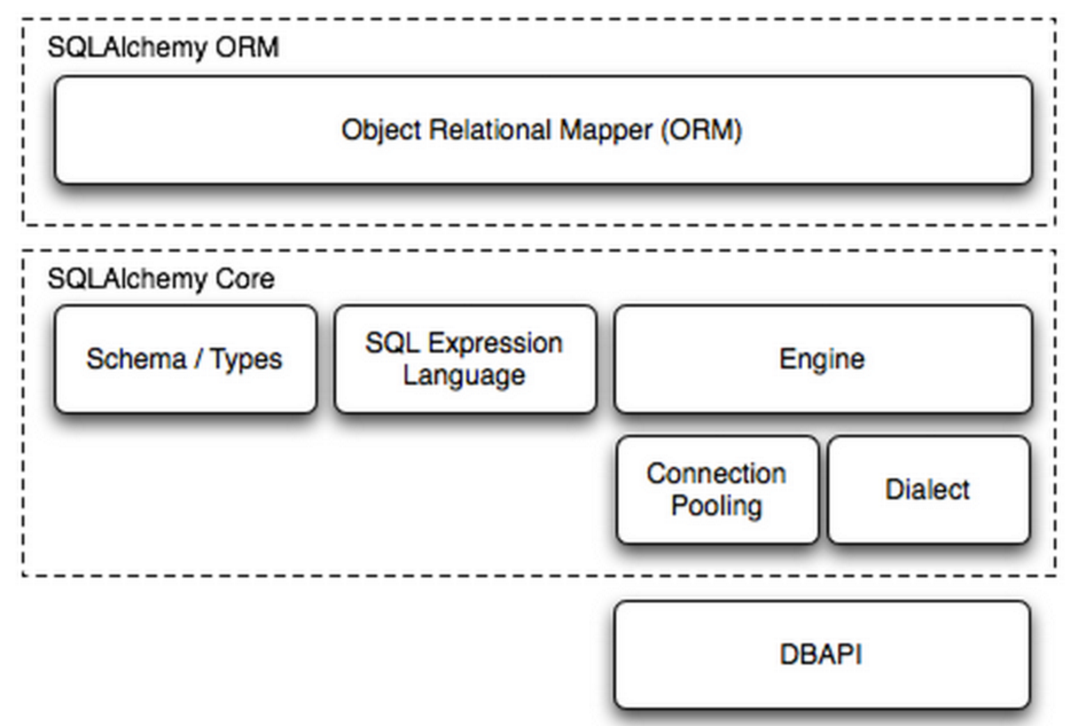
SQLAlchemy本身无法操作数据库,其必须以来pymsql等第三方插件,Dialect用于和数据API进行交流,根据配置文件的不同调用不同的数据库API,
从而实现对数据库的操作,如:
1 MySQL-Python 2 mysql+mysqldb://<user>:<password>@<host>[:<port>]/<dbname> 3 4 pymysql 5 mysql+pymysql://<username>:<password>@<host>/<dbname>[?<options>] 6 7 MySQL-Connector 8 mysql+mysqlconnector://<user>:<password>@<host>[:<port>]/<dbname> 9 10 cx_Oracle 11 oracle+cx_oracle://user:pass@host:port/dbname[?key=value&key=value...] 12 13 更多详见:http://docs.sqlalchemy.org/en/latest/dialects/index.html
一、内部处理
使用 Engine/ConnectionPooling/Dialect 进行数据库操作,Engine使用ConnectionPooling连接数据库,然后再通过Dialect执行SQL语句。
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- 3 from sqlalchemy import create_engine 4 5 6 engine = create_engine("mysql+pymysql://root:123@127.0.0.1:3306/t1", max_overflow=5) 7 8 # 执行SQL 9 # cur = engine.execute( 10 # "INSERT INTO hosts (host, color_id) VALUES ('1.1.1.22', 3)" 11 # ) 12 13 # 新插入行自增ID 14 # cur.lastrowid 15 16 # 执行SQL 17 # cur = engine.execute( 18 # "INSERT INTO hosts (host, color_id) VALUES(%s, %s)",[('1.1.1.22', 3),('1.1.1.221', 3),] 19 # ) 20 21 22 # 执行SQL 23 # cur = engine.execute( 24 # "INSERT INTO hosts (host, color_id) VALUES (%(host)s, %(color_id)s)", 25 # host='1.1.1.99', color_id=3 26 # ) 27 28 # 执行SQL 29 # cur = engine.execute('select * from hosts') 30 # 获取第一行数据 31 # cur.fetchone() 32 # 获取第n行数据 33 # cur.fetchmany(3) 34 # 获取所有数据 35 # cur.fetchall()
二、ORM功能使用
使用 ORM/Schema Type/SQL Expression Language/Engine/ConnectionPooling/Dialect 所有组件对数据进行操作。根据类创建对象,对象转换成SQL,执行SQL。
1、创建表
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- 3 from sqlalchemy.ext.declarative import declarative_base 4 from sqlalchemy import Column, Integer, String, ForeignKey, UniqueConstraint, Index 5 from sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmaker, relationship 6 from sqlalchemy import create_engine 7 8 engine = create_engine("mysql+pymysql://root:123@127.0.0.1:3306/t1", max_overflow=5) 9 10 Base = declarative_base() 11 12 # 创建单表 13 class Users(Base): 14 __tablename__ = 'users' 15 id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True) 16 name = Column(String(32)) 17 extra = Column(String(16)) 18 19 __table_args__ = ( 20 UniqueConstraint('id', 'name', name='uix_id_name'), 21 Index('ix_id_name', 'name', 'extra'), 22 ) 23 24 25 # 一对多 26 class Favor(Base): 27 __tablename__ = 'favor' 28 nid = Column(Integer, primary_key=True) 29 caption = Column(String(50), default='red', unique=True) 30 31 32 class Person(Base): 33 __tablename__ = 'person' 34 nid = Column(Integer, primary_key=True) 35 name = Column(String(32), index=True, nullable=True) 36 favor_id = Column(Integer, ForeignKey("favor.nid")) 37 38 39 # 多对多 40 class Group(Base): 41 __tablename__ = 'group' 42 id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True) 43 name = Column(String(64), unique=True, nullable=False) 44 port = Column(Integer, default=22) 45 46 47 class Server(Base): 48 __tablename__ = 'server' 49 50 id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True, autoincrement=True) 51 hostname = Column(String(64), unique=True, nullable=False) 52 53 54 class ServerToGroup(Base): 55 __tablename__ = 'servertogroup' 56 nid = Column(Integer, primary_key=True, autoincrement=True) 57 server_id = Column(Integer, ForeignKey('server.id')) 58 group_id = Column(Integer, ForeignKey('group.id')) 59 60 61 def init_db(): 62 Base.metadata.create_all(engine) 63 64 65 def drop_db(): 66 Base.metadata.drop_all(engine)
注:设置外检的另一种方式 ForeignKeyConstraint(['other_id'], ['othertable.other_id'])
2、操作表

1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- 3 from sqlalchemy.ext.declarative import declarative_base 4 from sqlalchemy import Column, Integer, String, ForeignKey, UniqueConstraint, Index 5 from sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmaker, relationship 6 from sqlalchemy import create_engine 7 8 engine = create_engine("mysql+pymysql://root:123@127.0.0.1:3306/t1", max_overflow=5) 9 10 Base = declarative_base() 11 12 # 创建单表 13 class Users(Base): 14 __tablename__ = 'users' 15 id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True) 16 name = Column(String(32)) 17 extra = Column(String(16)) 18 19 __table_args__ = ( 20 UniqueConstraint('id', 'name', name='uix_id_name'), 21 Index('ix_id_name', 'name', 'extra'), 22 ) 23 24 def __repr__(self): 25 return "%s-%s" %(self.id, self.name) 26 27 # 一对多 28 class Favor(Base): 29 __tablename__ = 'favor' 30 nid = Column(Integer, primary_key=True) 31 caption = Column(String(50), default='red', unique=True) 32 33 def __repr__(self): 34 return "%s-%s" %(self.nid, self.caption) 35 36 class Person(Base): 37 __tablename__ = 'person' 38 nid = Column(Integer, primary_key=True) 39 name = Column(String(32), index=True, nullable=True) 40 favor_id = Column(Integer, ForeignKey("favor.nid")) 41 # 与生成表结构无关,仅用于查询方便 42 favor = relationship("Favor", backref='pers') 43 44 # 多对多 45 class ServerToGroup(Base): 46 __tablename__ = 'servertogroup' 47 nid = Column(Integer, primary_key=True, autoincrement=True) 48 server_id = Column(Integer, ForeignKey('server.id')) 49 group_id = Column(Integer, ForeignKey('group.id')) 50 group = relationship("Group", backref='s2g') 51 server = relationship("Server", backref='s2g') 52 53 class Group(Base): 54 __tablename__ = 'group' 55 id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True) 56 name = Column(String(64), unique=True, nullable=False) 57 port = Column(Integer, default=22) 58 # group = relationship('Group',secondary=ServerToGroup,backref='host_list') 59 60 61 class Server(Base): 62 __tablename__ = 'server' 63 64 id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True, autoincrement=True) 65 hostname = Column(String(64), unique=True, nullable=False) 66 67 68 69 70 def init_db(): 71 Base.metadata.create_all(engine) 72 73 74 def drop_db(): 75 Base.metadata.drop_all(engine) 76 77 78 Session = sessionmaker(bind=engine) 79 session = Session() 80 81 表结构 + 数据库连接
增

1 obj = Users(name="alex0", extra='sb') 2 session.add(obj) 3 session.add_all([ 4 Users(name="alex1", extra='sb'), 5 Users(name="alex2", extra='sb'), 6 ]) 7 session.commit()
删

1 session.query(Users).filter(Users.id > 2).delete() 2 session.commit()
改

1 session.query(Users).filter(Users.id > 2).update({"name" : "099"}) 2 session.query(Users).filter(Users.id > 2).update({Users.name: Users.name + "099"}, synchronize_session=False) 3 session.query(Users).filter(Users.id > 2).update({"num": Users.num + 1}, synchronize_session="evaluate") 4 session.commit()
查

1 ret = session.query(Users).all() 2 ret = session.query(Users.name, Users.extra).all() 3 ret = session.query(Users).filter_by(name='alex').all() 4 ret = session.query(Users).filter_by(name='alex').first() 5 6 ret = session.query(Users).filter(text("id<:value and name=:name")).params(value=224, name='fred').order_by(User.id).all() 7 8 ret = session.query(Users).from_statement(text("SELECT * FROM users where name=:name")).params(name='ed').all()
补充

1 # 条件 2 ret = session.query(Users).filter_by(name='alex').all() 3 ret = session.query(Users).filter(Users.id > 1, Users.name == 'eric').all() 4 ret = session.query(Users).filter(Users.id.between(1, 3), Users.name == 'eric').all() 5 ret = session.query(Users).filter(Users.id.in_([1,3,4])).all() 6 ret = session.query(Users).filter(~Users.id.in_([1,3,4])).all() 7 ret = session.query(Users).filter(Users.id.in_(session.query(Users.id).filter_by(name='eric'))).all() 8 from sqlalchemy import and_, or_ 9 ret = session.query(Users).filter(and_(Users.id > 3, Users.name == 'eric')).all() 10 ret = session.query(Users).filter(or_(Users.id < 2, Users.name == 'eric')).all() 11 ret = session.query(Users).filter( 12 or_( 13 Users.id < 2, 14 and_(Users.name == 'eric', Users.id > 3), 15 Users.extra != "" 16 )).all() 17 18 19 # 通配符 20 ret = session.query(Users).filter(Users.name.like('e%')).all() 21 ret = session.query(Users).filter(~Users.name.like('e%')).all() 22 23 # 限制 24 ret = session.query(Users)[1:2] 25 26 # 排序 27 ret = session.query(Users).order_by(Users.name.desc()).all() 28 ret = session.query(Users).order_by(Users.name.desc(), Users.id.asc()).all() 29 30 # 分组 31 from sqlalchemy.sql import func 32 33 ret = session.query(Users).group_by(Users.extra).all() 34 ret = session.query( 35 func.max(Users.id), 36 func.sum(Users.id), 37 func.min(Users.id)).group_by(Users.name).all() 38 39 ret = session.query( 40 func.max(Users.id), 41 func.sum(Users.id), 42 func.min(Users.id)).group_by(Users.name).having(func.min(Users.id) >2).all() 43 44 # 连表 45 46 ret = session.query(Users, Favor).filter(Users.id == Favor.nid).all() 47 48 ret = session.query(Person).join(Favor).all() 49 50 ret = session.query(Person).join(Favor, isouter=True).all() 51 52 53 # 组合 54 q1 = session.query(Users.name).filter(Users.id > 2) 55 q2 = session.query(Favor.caption).filter(Favor.nid < 2) 56 ret = q1.union(q2).all() 57 58 q1 = session.query(Users.name).filter(Users.id > 2) 59 q2 = session.query(Favor.caption).filter(Favor.nid < 2) 60 ret = q1.union_all(q2).all()
更多功能参见文档,猛击这里下载PDF。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号