缓冲流(两类四种)
一、缓冲字节流
1、缓冲字节输出流(BufferedOutputStream)
1 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 2 /* 3 字节缓冲输出流使用步骤: 4 1:创建FileOutputStream对象,指定输出文件 5 2:创建BufferedOutputStream对象,对FileOutputStream进行“包装”,使其效率提高 6 3:使用BufferedOutputStream对象调用write方法,将数据写入内部缓冲区中 7 4:使用BufferedOutputStream对象调用flush方法,将内部缓冲区的数据刷新到文件中 8 5:释放资源(若释放资源,第4步flush可省略,因为在调用close时会先进行flush再释放资源) 9 */ 10 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("b.txt"); 11 BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos); 12 bos.write("字节缓冲输出流".getBytes()); 13 bos.flush(); 14 bos.close(); 15 // fos.close();// 不用手动释放,缓冲流释放资源时自动将其内部的字节流进行关闭 16 }
2、缓冲字节输入流(BufferedInputStream)
1 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 2 /* 3 字节缓冲输出流使用步骤: 4 1:创建FileInputStream对象,指定输出文件 5 2:创建BufferedInputStream对象,对FileInputStream进行“包装”,使其效率提高 6 3:使用BufferedInputStream对象调用read方法,将数据读入内部缓冲区中 7 4:释放资源 8 */ 9 10 //方式一: 11 /* 12 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("b.txt"); 13 BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis); 14 int len=0; 15 while((len=bis.read())!=-1){ 16 System.out.println(len); 17 } 18 bis.close(); 19 */ 20 21 //方式二: 22 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("b.txt"); 23 BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis); 24 int len = 0; 25 byte[] bytes = new byte[1024]; 26 while ((len = bis.read(bytes)) != -1) { 27 System.out.println(new String(bytes, 0, len)); 28 } 29 bis.close(); 30 }
3、测试缓冲流与字符流复制文件的速度
1 package demo09.buffer; 2 3 import java.io.*; 4 import java.util.Arrays; 5 6 public class demo07copy02 { 7 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 8 copy01(); 9 copy02(); 10 } 11 12 private static void copy02() throws IOException { 13 long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); 14 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("c:\\1.jpg"); 15 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("d:\\1.jpg"); 16 int len = 0; 17 while ((len = fis.read()) != -1) { 18 fos.write(len); 19 } 20 fos.close(); 21 fis.close(); 22 System.out.println("使用字节流花费时间:"+(System.currentTimeMillis()-start)); 23 } 24 25 private static void copy01() throws IOException { 26 long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); 27 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("c:\\1.jpg"); 28 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("d:\\1.jpg"); 29 BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis); 30 BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos); 31 int len = 0; 32 while ((len = bis.read()) != -1) { 33 bos.write(len); 34 } 35 bos.close(); 36 bis.close(); 37 System.out.println("使用缓冲流花费时间:"+(System.currentTimeMillis()-start)); 38 } 39 }
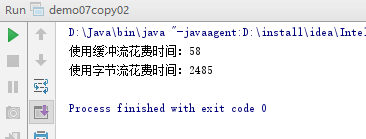
经测试:使用缓冲流比字节流速度要快的多。
注:如果在测试代码中都添加byte数组,则测试效果不明显。
二、缓冲字符流
1、字符缓冲输出流(BufferedWriter)
1 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 2 /* 3 字符缓冲输出流使用步骤: 4 1:创建FileWrite对象,指定输出文件 5 2:创建BufferedWrite对象,对FileWrite进行“包装”,使其效率提高 6 3:使用BufferedWrite对象调用write方法,将数据写入内部缓冲区中 7 4:使用BufferedWrite对象调用flush方法,将内部缓冲区的数据刷新到文件中 8 5:释放资源(若释放资源,第4步flush可省略,因为在调用close时会先进行flush再释放资源) 9 */ 10 BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("c.txt")); 11 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { 12 bw.write("相信美好的事情即将发生..."); 13 bw.newLine(); 14 } 15 bw.flush(); 16 bw.close(); 17 }
2、字符缓冲输入流(BufferedReader)
1 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 2 /* 3 字符缓冲输入流使用步骤: 4 1:创建FileReader对象,指定输出文件 5 2:创建BufferedReader对象,对FileReader进行“包装”,使其效率提高 6 3:使用BufferedReader对象调用read/readLine方法,将数据读入内部缓冲区中 7 4:释放资源 8 */ 9 10 // 方式一 11 /* 12 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("c.txt")); 13 String s = ""; 14 while ((s = br.readLine()) != null) { 15 System.out.println(s); 16 } 17 br.close(); 18 */ 19 20 // 方式二 21 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("c.txt")); 22 int len = 0; 23 while ((len = br.read()) != -1) { 24 System.out.print((char) len); 25 } 26 br.close(); 27 }
分类:
[编程语言] Java
标签:
Java 缓冲流




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· Manus的开源复刻OpenManus初探
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· 从HTTP原因短语缺失研究HTTP/2和HTTP/3的设计差异
· 三行代码完成国际化适配,妙~啊~