C4.5算法总结
C4.5是一系列用在机器学习和数据挖掘的分类问题中的算法。它的目标是监督学习:给定一个数据集,其中的每一个元组都能用一组属性值来描述,每一个元组属于一个互斥的类别中的某一类。C4.5的目标是通过学习,找到一个从属性值到类别的映射关系,并且这个映射能用于对新的类别未知的实体进行分类。
C4.5由J.Ross Quinlan在ID3的基础上提出的。ID3算法用来构造决策树。决策树是一种类似流程图的树结构,其中每个内部节点(非树叶节点)表示在一个属性上的测试,每个分枝代表一个测试输出,而每个树叶节点存放一个类标号。一旦建立好了决策树,对于一个未给定类标号的元组,跟踪一条有根节点到叶节点的路径,该叶节点就存放着该元组的预测。决策树的优势在于不需要任何领域知识或参数设置,适合于探测性的知识发现。
从ID3算法中衍生出了C4.5和CART两种算法,这两种算法在数据挖掘中都非常重要。下图就是一棵典型的C4.5算法对数据集产生的决策树。
比如我们判断一个人能不能结婚,那么每个人就可以作为一个具体的对象,该对象有着很多属性,比如年龄,性别,帅不帅,工作NB不,有没有女朋友,是不是富二代6个属性,而结婚也作为该对象的一个属性,而”结婚”属性就可以作为我们的预测属性!然后根据其他属性来预测我们的目标属性--结婚属性,比如说,年龄:30,性别:男,长的帅,工作不错,又女朋友,还是富二代!根据这些属性我们就可以得出该人今年可以结婚!当然这是预测出来的!这时,我们肯定有个疑问了,这是如何预测的呢?这实质上是根据我们的统计数据得出的,比如我们统计10000个人,根据这一万个人的6个属性以及目标属性(结婚)最终得出一组数据,我们用这组数据做成一个决策树!而其中这10000个人的样本我们则称为训练样本!
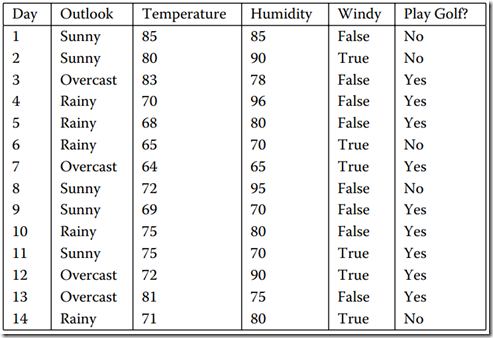
我们还是拿”打高尔夫球”这个经典的例子来作具体研究吧!该例其实就是通过一些列的属性来决定是否适合打高尔夫!刚刚说了训练样本,我们就来看看训练样本吧!图1是我用WPF做了一个简单的CRUD界面,用来把我们的样本显示的展现出来。具体看图1。。
图1 数据集
我们从图中可以看出,该表中共有6列,而每一列中的列名对应一个属性,而我们以实践经验知道,“Day”即日期这个属性并不能帮我们预测今天是否适合去打Golf.故该属性我们就应该选择摒弃!再看该系统中的其他5给属性。很显然,图1中我用红笔画出来的属性“Play Golf”该属性就是我们的预测属性。而其他4个属性“Outlook”(天气)”、Temperature”(温度) 、“Humdity”(湿度)、“Windy”(是否刮风)这四个属性进行判断今天去 Play Golf。
那我们接下来的工作自然就是根据属性1-4得出我们的决策树了!那么我们来想想该决策树的算法,实质上其遵循一种统一的递归模式:即,首先用根节点表示一个给定的数据集(比如在这,就是我们的14个样本);然后,从根节点开始在每个节点上测试一个特定的属性,把节点数据集划分成更小的子集(这一步,比如根据属性Outlook划分,可以划分出三个子集出来,即属于Sunny的一个子集样本,属于Overcast的子集样本,属于Rainy的子集样本),该子集并用子树进行表示;该过程就开始一直进行,直到子集称为“纯的”,也就是说直到子集中的所有实例都属于同一个类别,树才停止生长。
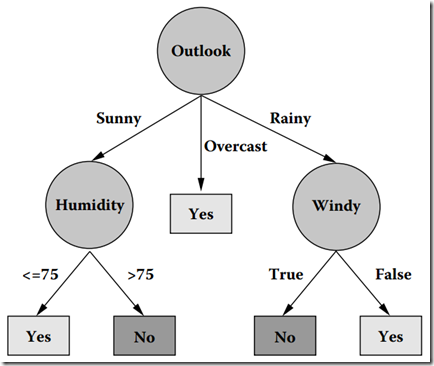
根据算法产生的决策树:
图2 在数据集上通过C4.5生成的决策树
看图2,首先是根据Outlook属性进行划分,根据Outlook的三个属性值(Sunny、Overcast、Rainy)划分出了三个组合,而其中Overcast划分中的集合是“纯”的了。故此子树就停止生长了。而根据Sunny属性值划分中的样例集合1,2,8,9,11显然还不是“纯”的(该组样例中有的PlayGolf是Yes,而有的是No),故需要再次对其进行划分,直到分组中的所有样例都是“纯”的位置,才停止生长。
算法描述
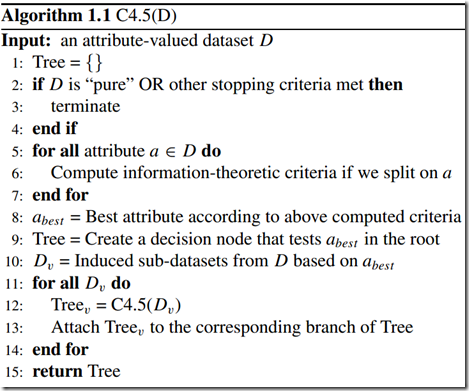
C4.5并不一个算法,而是一组算法—C4.5,非剪枝C4.5和C4.5规则。下图中的算法将给出C4.5的基本工作流程:
图3 C4.5算法流程
我们可能有疑问,一个元组本身有很多属性,我们怎么知道首先要对哪个属性进行判断,接下来要对哪个属性进行判断?换句话说,在图2中,我们怎么知道第一个要测试的属性是Outlook,而不是Windy?其实,能回答这些问题的一个概念就是属性选择度量。
属性选择度量
属性选择度量又称分裂规则,因为它们决定给定节点上的元组如何分裂。属性选择度量提供了每个属性描述给定训练元组的秩评定,具有最好度量得分的属性被选作给定元组的分裂属性。目前比较流行的属性选择度量有--信息增益、增益率和Gini指标。
先做一些假设,设D是类标记元组训练集,类标号属性具有m个不同值,m个不同类Ci(i=1,2,…,m),CiD是D中Ci类的元组的集合,|D|和|CiD|分别是D和CiD中的元组个数。
(1)信息增益
信息增益实际上是ID3算法中用来进行属性选择度量的。它选择具有最高信息增益的属性来作为节点N的分裂属性。该属性使结果划分中的元组分类所需信息量最小。对D中的元组分类所需的期望信息为下式:
Info(D)又称为熵。
现在假定按照属性A划分D中的元组,且属性A将D划分成v个不同的类。在该划分之后,为了得到准确的分类还需要的信息由下面的式子度量:
信息增益定义为原来的信息需求(即仅基于类比例)与新需求(即对A划分之后得到的)之间的差,即
我想很多人看到这个地方都觉得不是很好理解,所以我自己的研究了文献中关于这一块的描述,也对比了上面的三个公式,下面说说我自己的理解。
一般说来,对于一个具有多个属性的元组,用一个属性就将它们完全分开几乎不可能,否则的话,决策树的深度就只能是2了。从这里可以看出,一旦我们选择一个属性A,假设将元组分成了两个部分A1和A2,由于A1和A2还可以用其它属性接着再分,所以又引出一个新的问题:接下来我们要选择哪个属性来分类?对D中元组分类所需的期望信息是Info(D) ,那么同理,当我们通过A将D划分成v个子集Dj(j=1,2,…,v)之后,我们要对Dj的元组进行分类,需要的期望信息就是Info(Dj),而一共有v个类,所以对v个集合再分类,需要的信息就是公式(2)了。由此可知,如果公式(2)越小,是不是意味着我们接下来对A分出来的几个集合再进行分类所需要的信息就越小?而对于给定的训练集,实际上Info(D)已经固定了,所以选择信息增益最大的属性作为分裂点。
但是,使用信息增益的话其实是有一个缺点,那就是它偏向于具有大量值的属性。什么意思呢?就是说在训练集中,某个属性所取的不同值的个数越多,那么越有可能拿它来作为分裂属性。例如一个训练集中有10个元组,对于某一个属相A,它分别取1-10这十个数,如果对A进行分裂将会分成10个类,那么对于每一个类Info(Dj)=0,从而式(2)为0,该属性划分所得到的信息增益(3)最大,但是很显然,这种划分没有意义。
(2)信息增益率
正是基于此,ID3后面的C4.5采用了信息增益率这样一个概念。信息增益率使用“分裂信息”值将信息增益规范化。分类信息类似于Info(D),定义如下:
这个值表示通过将训练数据集D划分成对应于属性A测试的v个输出的v个划分产生的信息。信息增益率定义:
选择具有最大增益率的属性作为分裂属性。
(3)Gini指标
Gini指标在CART中使用。Gini指标度量数据划分或训练元组集D的不纯度,定义为:
C#实现代码如下:
计算信息增益率:
1 using System; 2 using System.Collections; 3 using System.Collections.Generic; 4 using System.Data; 5 using System.Linq; 6 using System.Text; 7 using System.Threading.Tasks; 8 9 namespace C4._5.BLL 10 { 11 public class Entropy 12 { 13 public int[] statNum = new int[2];//训练统计结果:0->No 1->Yes 14 public double EntropyValue = 0; 15 private int mTotal = 0; 16 private string mTargetAttribute = "PlayGolf"; 17 18 public void getEntropy(DataTable samples) 19 { 20 CountTotalClass(samples,out statNum[0],out statNum[1]); 21 EntropyValue = CalcEntropy(statNum[0],statNum[1]); 22 } 23 /// <summary> 24 /// 统计各个样本集合中所包含的目标属性Yes或者No的数目 25 /// </summary> 26 public void CountTotalClass(DataTable samples,out int no,out int yes) 27 { 28 yes = no = 0; 29 foreach (DataRow aRow in samples.Rows) 30 { 31 if ((string)aRow[mTargetAttribute] == "Yes") 32 yes++; 33 else if ((string)aRow[mTargetAttribute] == "No") 34 no++; 35 else 36 throw new Exception("出错!"); 37 } 38 } 39 /// <summary> 40 /// 计算熵值 41 /// </summary> 42 /// <returns></returns> 43 public double CalcEntropy(int no,int yes) 44 { 45 double entropy = 0; 46 double total = (double)(yes + no); 47 double p = 0; 48 if (no != 0) 49 { 50 p = no / total; 51 entropy += -p * Math.Log(p,2); 52 } 53 if (yes != 0) 54 { 55 p = yes / total; 56 entropy += -p * Math.Log(p, 2); 57 } 58 return entropy; 59 } 60 /// <summary> 61 /// 该注释可能有问题,从属性中的样本集合中得到yes或者no的数目 62 /// </summary> 63 /// <param name="samples"></param> 64 /// <param name="attribute"></param> 65 /// <param name="value"></param> 66 /// <param name="no"></param> 67 /// <param name="yes"></param> 68 public void GetValuesToAttribute(DataTable samples, Attribute attribute, string value, out int no, out int yes) 69 { 70 no = yes = 0; 71 foreach (DataRow row in samples.Rows) 72 { 73 if ((string)row[attribute.AttributeName] == value) 74 { 75 if ((string)row[mTargetAttribute] == "No") 76 { 77 no++; 78 } 79 else if ((string)row[mTargetAttribute] == "Yes") 80 { 81 yes++; 82 } 83 else 84 { 85 throw new Exception("出错"); 86 } 87 } 88 } 89 } 90 /// <summary> 91 /// 计算信息收益 92 /// </summary> 93 /// <param name="samples"></param> 94 /// <param name="attribute"></param> 95 /// <returns></returns> 96 public double Gain(DataTable samples, Attribute attribute) 97 { 98 mTotal = samples.Rows.Count; 99 string[] values=attribute.values; 100 double sum=0.0; 101 for (int i = 0; i < values.Length; i++) 102 { 103 int no, yes; 104 no = yes = 0; 105 GetValuesToAttribute(samples,attribute,values[i],out no,out yes); 106 if (yes == (yes + no) || no == (yes + no)) 107 { 108 sum += 0; 109 } 110 else 111 { 112 sum += (double)(yes + no) / (double)mTotal * (-(double)yes / (double)(yes + no) * Math.Log(((double)yes / (double)(yes + no)), 2) - (double)no / (double)(yes + no) * Math.Log(((double)no / (double)(yes + no)), 2)); 113 } 114 } 115 return SplitInfo(samples,mTargetAttribute)- sum; 116 } 117 /// <summary> 118 /// 获得targetAttribute属性下的所有属性值 119 /// </summary> 120 /// <param name="samples"></param> 121 /// <param name="targetAttribute"></param> 122 /// <returns></returns> 123 private ArrayList GetDistinctValues(DataTable samples, string targetAttribute) 124 { 125 ArrayList distinctValues = new ArrayList(samples.Rows.Count); 126 foreach (DataRow row in samples.Rows) 127 { 128 if (distinctValues.IndexOf(row[targetAttribute]) == -1) 129 distinctValues.Add(row[targetAttribute]); 130 } 131 return distinctValues; 132 } 133 /// <summary> 134 /// 按某个属性值计算该属性的熵值 135 /// </summary> 136 /// <param name="samples"></param> 137 /// <param name="attribute"></param> 138 /// <returns></returns> 139 public double SplitInfo(DataTable samples, string attribute) 140 { 141 ArrayList values = GetDistinctValues(samples,attribute); 142 for (int i = 0; i < values.Count; i++) 143 { 144 if (values[i] == null || (string)values[i] == "") 145 { 146 values.RemoveAt(i); 147 } 148 } 149 int[] count=new int[values.Count]; 150 for (int i = 0; i < values.Count; i++) 151 { 152 foreach (DataRow aRow in samples.Rows) 153 { 154 if ((string)aRow[attribute] == (string)values[i]) 155 count[i]++; 156 } 157 } 158 double entropy = 0; 159 double total = samples.Rows.Count; 160 double p = 0; 161 for (int i = 0; i < values.Count; i++) 162 { 163 if (count[i] != 0) 164 { 165 p = count[i] / total; 166 entropy += -p * Math.Log(p,2); 167 } 168 } 169 return entropy; 170 } 171 /// <summary> 172 /// 获得指定属性的信息增益率 173 /// </summary> 174 /// <param name="samples">样本集合</param> 175 /// <param name="attribute"></param> 176 /// <returns></returns> 177 public double GainRatio(DataTable samples, Attribute attribute) 178 { 179 double splitInfoA = this.SplitInfo(samples,attribute.AttributeName);//计算各个属性的熵值 180 double gainA = Gain(samples,attribute);//信息增益 181 double gainRatioA = gainA / splitInfoA; 182 return gainRatioA; 183 } 184 } 185 }
构造决策树:
public class DTree_ID3 { private string mTargetAttribute = "result"; public Entropy en = new Entropy(); public TreeNode roots; /// <summary> /// 获得信息增益率最大的属性 /// </summary> /// <param name="samples"></param> /// <param name="attributes"></param> /// <returns></returns> private Attribute getBestAttribute(DataTable samples,Attribute[] attributes) { double maxGain = 0.0; Attribute bestAttribute = null; foreach (Attribute attribute in attributes) { double aux = en.GainRatio(samples,attribute); if (aux > maxGain) { maxGain = aux; bestAttribute = attribute; } } return bestAttribute; } /// <summary> /// 判断样例集是否属于同一类,即该样例集是否是"纯"的,是则返回此属性值,否则返回Null /// </summary> /// <param name="samples"></param> /// <param name="targetAttribute"></param> /// <returns></returns> public string AllSamplesSameClass(DataTable samples, string targetAttribute) { DataRow row = samples.Rows[0]; string targetValue = (string)row[targetAttribute]; for (int i = 1; i < samples.Rows.Count; i++) { if (targetValue!=samples.Rows[i][targetAttribute].ToString()) { return null; } } return targetValue; } /// <summary> /// 获得属性的目标属性的值(解释有可能错误) /// </summary> /// <param name="samples"></param> /// <param name="targetAttribute"></param> /// <returns></returns> private ArrayList GetDistinctValues(DataTable samples, string targetAttribute) { ArrayList distinctValues = new ArrayList(samples.Rows.Count); foreach (DataRow row in samples.Rows) { if (distinctValues.IndexOf(row[targetAttribute]) == -1) distinctValues.Add(row[targetAttribute]); } return distinctValues; } /// <summary> /// /// </summary> /// <param name="samples"></param> /// <param name="targetAttribute"></param> /// <returns></returns> private object GetMostCommonValue(DataTable samples, string targetAttribute) { ArrayList distinctValues = GetDistinctValues(samples,targetAttribute); int[] count=new int[distinctValues.Count]; foreach (DataRow row in samples.Rows) { int index = distinctValues.IndexOf(row[targetAttribute]); count[index]++; } int MaxIndex = 0; int MaxCount = 0; for (int i = 0; i < count.Length; i++) { if (count[i] > MaxCount) { MaxCount = count[i]; MaxIndex = i; } } return distinctValues[MaxIndex]; } /// <summary> /// 构造决策树 /// </summary> /// <param name="samples">样本集合</param> /// <param name="targetAttribute">目标属性</param> /// <param name="attributes">该样本所含的属性集合</param> /// <returns></returns> private TreeNode BuildTree(DataTable samples, string targetAttribute, Attribute[] attributes) { TreeNode temp = new TreeNode(); //如果samples中的元祖是同一类C string c = AllSamplesSameClass(samples,targetAttribute); if (c != null) //返回N作为叶节点,以类C标记 return new TreeNode(new Attribute(c).AttributeName + c); //if attributes为空,then if (attributes.Length == 0)//返回N作为叶子节点,标记为D中的多数类,多数表决 { return new TreeNode(new Attribute(GetMostCommonValue(samples,targetAttribute)).AttributeName); } //计算目标属性的熵值,即PlayGolf的熵值 mTargetAttribute = targetAttribute; en.getEntropy(samples); //找出最好的分类属性,即信息熵最大的 Attribute bestAttribute = getBestAttribute(samples,attributes); //标记为节点root DTreeNode root = new DTreeNode(bestAttribute); temp.Text = bestAttribute.AttributeName; DataTable aSample = samples.Clone(); //为bestAttribute的每个输出value划分元祖并产生子树 foreach (string value in bestAttribute.values) { aSample.Rows.Clear(); //aSamples为满足输出value的集合,即一个划分(分支) DataRow[] rows = samples.Select(bestAttribute.AttributeName+"="+"'"+value+"'"); foreach (DataRow row in rows) { aSample.Rows.Add(row.ItemArray); } //删除划分属性 ArrayList aArributes = new ArrayList(attributes.Length-1); for (int i = 0; i < attributes.Length; i++) { if (attributes[i].AttributeName != bestAttribute.AttributeName) { aArributes.Add(attributes[i]); } } //如果aSample为空,加一个树叶到节点N,标记为aSample中的多数类 if (aSample.Rows.Count == 0) { TreeNode leaf = new TreeNode(); leaf.Text = GetMostCommonValue(samples, targetAttribute).ToString() + "(" + value + ")"; temp.Nodes.Add(leaf); } else //加一个由BulidTree(samples,targetAttribute,attributes)返回的节点到节点N { DTree_ID3 dc3 = new DTree_ID3(); TreeNode ChildNode = dc3.BuildTree(aSample,targetAttribute,(Attribute[])aArributes.ToArray(typeof(Attribute))); ChildNode.Text += "(" + value + ")"; temp.Nodes.Add(ChildNode); } } roots = temp; return temp; } public TreeNode MountTree(DataTable samples, string targetAttribute, Attribute[] attributes) { return BuildTree(samples, targetAttribute, attributes); } }



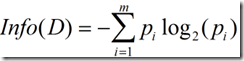
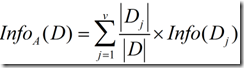
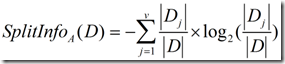
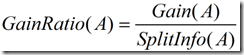
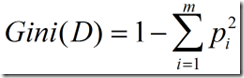

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号