Typescript学习概括
1. 常用类型注解
let age: number = 20;
JS已有:
- 原始类型:number、string、boolean、null、undefined、symbol
- 对象类型:object (包括:数组、对象、函数等对象)
TS新增:
- 联合类型、自定义类型(类型别名)、接口、元组、字面量类型、枚举、void、any 等
注:类型别名和接口的区别:
- 类型别名可以指定约束任意类型
- 接口只能指定约束对象类型
数组类型两种写法: let num: number[] = [1,2,3] // 推荐 let str: Array<string> = ['a','b','c'] 联合类型: let arr: number|string = 'abc' let arr: number|string[] = 1 // number 或 字符串类型的数组 let arr: (number|string)[] = [1,'a'] // 数组中既有number类型,又有string类型 类型别名: type CustomArray = (number|string)[] // 起别名 let arr: CustomArray = [1,'a'] 函数类型: function fn(num: number):number { return num } function fn(num?: number):void { // 函数参数可选 console.log(num) } 对象类型: let per:{ name: string; age: number; say():void } = { name: 'zzz', ahe: 20, say(){ } } 接口: interface Person { name: string age: number } let per: Person = {...} 接口继承: interface P1 = { x:number; y:number; } interface P2 extends = { z:number } 元组类型: let position: [number, number] = [1,2] 类型推论: let num = 2 // 这时候num已经是number类型了 //下面则没有定 lat num num = 2 字面量类型: const name = "abc" // 此时,因为const声明的是常量,因此 name 的类型就已经确定了,是字面量“abc” let name: ( "a" | "b" | "c" ) = "a" // 不会报错 枚举: enum Name { a, b, c } let name: Name = b // 不会报错 console.log(Name.a+Name.b+Name.c) // 1 2 3 枚举成员是有值的,默认从0递增 enum P { a=2, b, c } // P.a=2 , P.b=3 , P.c=4 => 数字枚举 enum P { a="a",b="b",c="c" } // 字符串枚举没有自增行为,因此 必修 要赋初值 any类型: let obj:any = { x=0 } obj() // 不会报错 obj.a=1 // 不报错 等等 TS中的typeof操作符: let P = { x:1,y:2 } function fn(point:P){ } // 相当于function fn(point:{ x:number;y:number }) {}
2. 高级注解类型
- class 类
- 类型兼容性
- 交叉类型
- 泛型 和 keyof
- 索引签名类型、索引查询类型
- 映射类型
2.1 class类
class Person { age = 20 } const p = new Person() // 鼠标放上p显示 p:Person p.age // number 类型
class Person { age: number gender: string // ① constructor(age: number, gender: string) { // ② this.age = age this.gender = gender // this.gender 指上面①的gender,gender 指②的 } ageAdd(n: number) { this.age += n } } const p = new Person(20,'男') p.ageAdd(10) // p.age=30
2.2 类的继承和实现接口
- 类的继承 extends
class Animal { move() { console.log('Moving along!') } } class Dog extends Animal { bark() { console.log('汪') } } const dog = new Dog()
- 实现接口 implements
// 1. 定义接口 interface Singable { sing(): void } // 2. 实现接口 class Person implements Singable { // 必须实现sing() sing() { console.log('wowowowo') } }
2.3 public protected private
- public 均可访问
- protected 类内和子类可以访问,但实例不可
- private 仅类内可访问
2.4 readonly 只读类型
class Person { readonly age: number = 20 // 必须有类型约束,没有number约束的话,age 的类型变成字面量‘20’ constructor(age: number) { this.age = age // 可以 } } let p = new Person(18) console.log(p.age)// 可以 p.age = 22 // 报错
2.5 类型兼容性




2.6 交叉类型
interface Person { name: string } interface Contact { phone: string } type PersonDetail = Person & Contact
2.7 泛型
- 泛型函数
// 泛型函数 function fn<Type>(n: Type):Type { return n } // <Type> 占位 const f1 = fn<number>(20) // 因为有类型推断机制,所以<number>一般可省略 const f2 = fn<string>('abc')
- 泛型约束
function fn<Type>(n: Type[]):Type[] { // 用 [] 来约束是它一个泛型数组, 不然 n.length 报错 console.log( n.length ) } // 使用 extends 添加泛型约束 interface Length { length: number } function fn<Type extends Length>(n: Type):Type { console.log(n.length) // 由于要实现接口Length,而接口要求其有length属性,因此不会报错 }
- keyof
function getProp<Type, Key extends keyof Type>(objL Type, key: Key) { return obj[key] } getProp({ name: 'zrh', age: 20 }, 'age') getProp({ name: 'zrh', age: 20 }, 'name')
- 泛型接口
// 泛型接口 interface IdFn<Type> { id:(value: Type) => Type ids:() => Type[] } // 接口实现 let obj: IdFn<number> = { id(value) { return value } ids() { return [1,2,3] } }
2.8 泛型工具类
- Partial<Type>

- Readonly<Type>

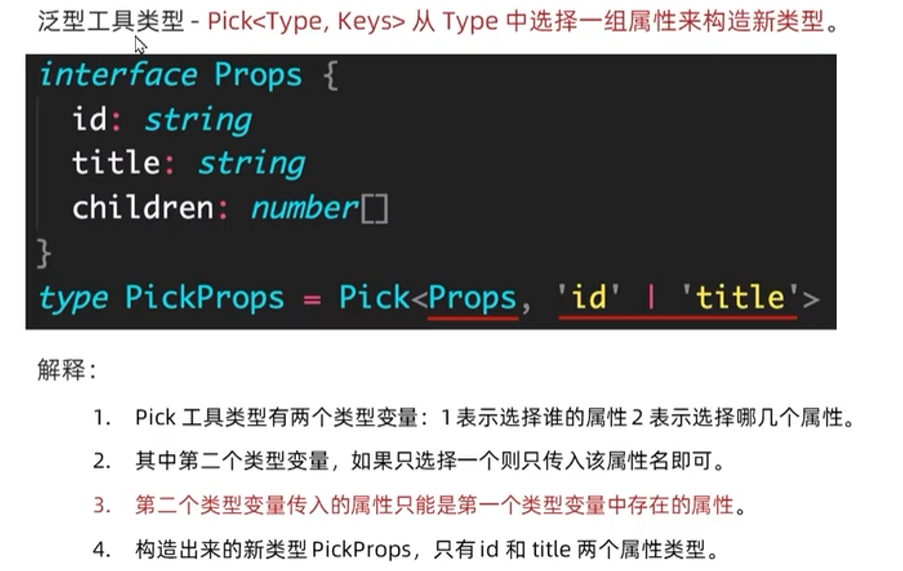
- Pick<Type>
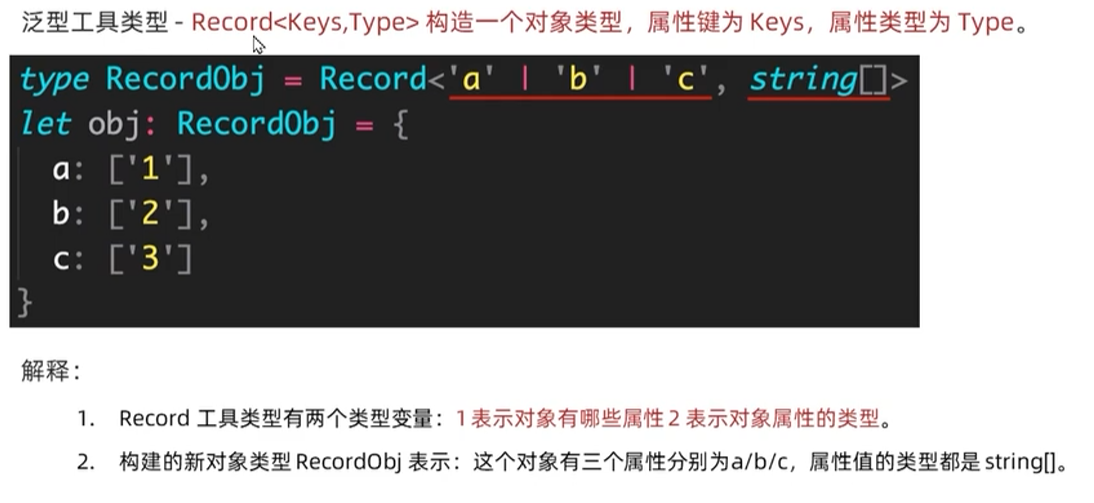
- Record<Keys,Type>
本文来自博客园,作者:RHCHIK,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/suihung/p/16455654.html





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)