计算机组成原理
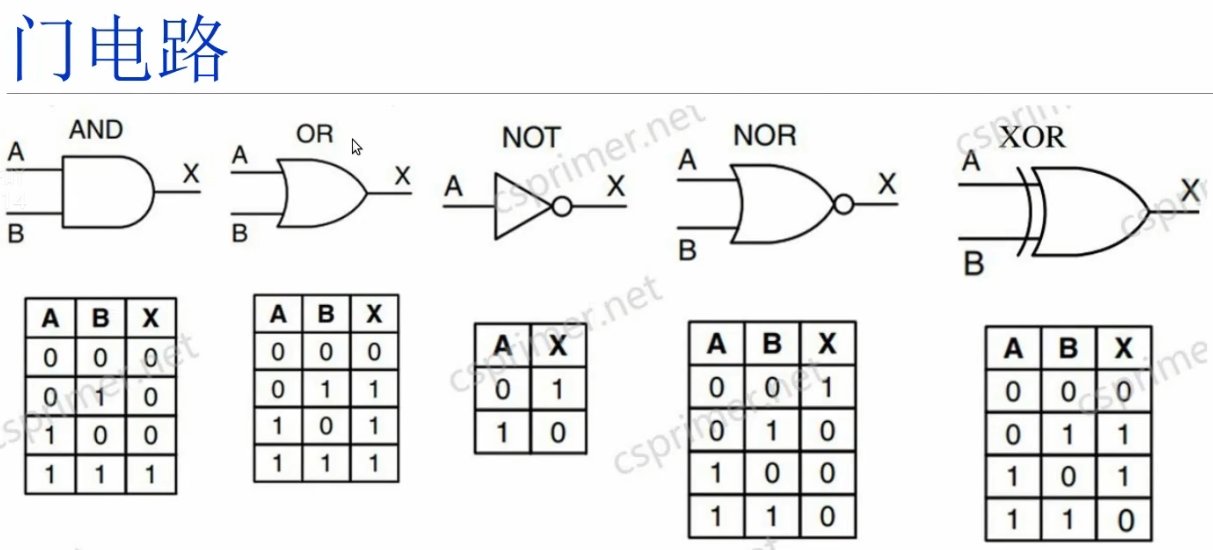
门电路实现#
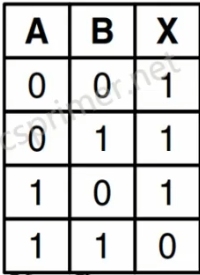
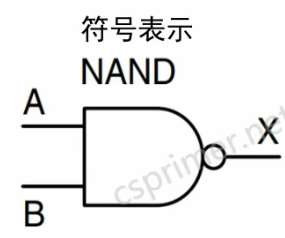
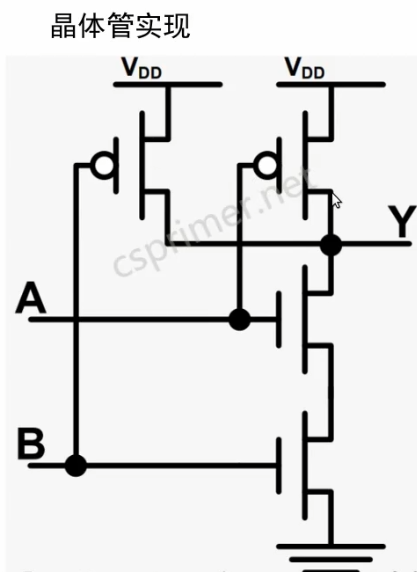
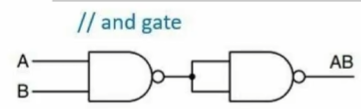
与非门
可以使用两个NMOS管串联跟两个PMOS管并联构成:
NMOS管是当gate输入高电压导通,PMOS管是当gate输入低电压的时候导通。
等价电路:交换律、结合律、分配律、德摩根律、幂等律、双重否定律
与非门Verilog HDL表示
module Nand(input a, b, output out);
nmos n1(o1, 0, b);
nmos n2(out, o1, a);
pmos p1(out, 1, b);
pmos p2(out, 1, a);
endmodule
与门实现(用两个与非门连接)
module And(input a, b, output out);
Nand g1(a, b, AnandB);
Nand g2(AnandB, AnandB, out);
endmodule
非门实现(两个输入一样的与非门)
module Not(input in, output out);
// your code here
Nand g1(in,in,out);
endmodule
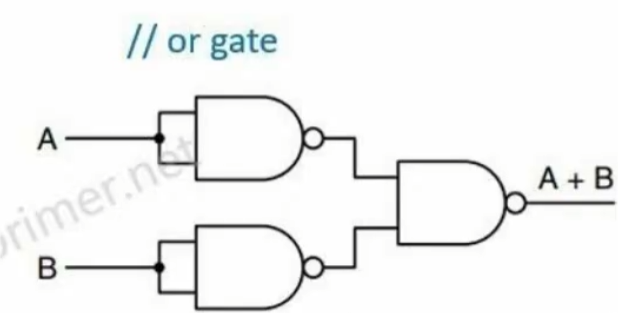
或门实现(三个与非门)
module Or(input a, b, output out);
// your code here
wire nand_a, nand_b;
// 第一个NAND门,模拟 NAND(A, A)
Nand nand1(a, a, nand_a);
// 第二个NAND门,模拟 NAND(B, B)
Nand nand2(b, b, nand_b);
// 最后一个NAND门,模拟 NAND(nand_a, nand_b),得到 OR 结果
Nand nand3(nand_a, nand_b, out);
endmodule
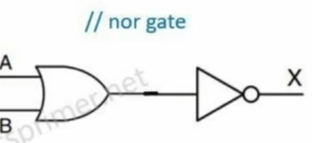
或非门(一个或门和一个非门)
module Nor(input a, b, output out);
// your code here
wire out1;
Or g1(a,b,out1);
Nand g2(out1,out1,out);
endmodule
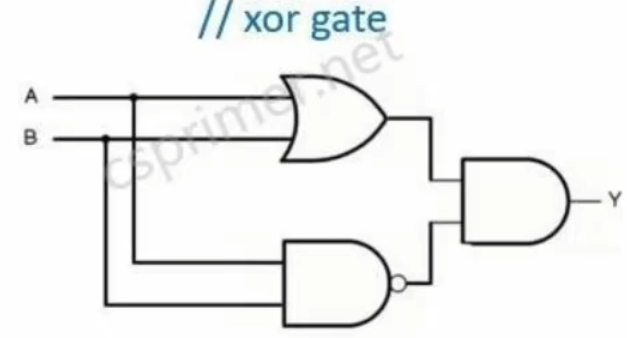
异或门(一个或门和一个与非门并联,再接一个与门)
module Xor(input a, b, output out);
// your code here
wire out1,out2;
Or g1(a,b,out1);
Nand g2(a,b,out2);
And g3(out1,out2,out);
endmodule
加法器实现#
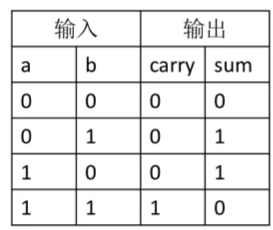
先看半加器
通过一位的加法的真值表:
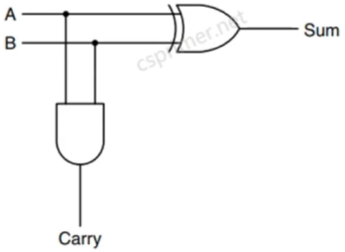
sum符合异或门特性,carry符合与门特性,得到:
module HalfAdder(input a,b, output sum, carry);
// your code here
Xor g1(a,b,sum);
And g2(a,b,carry);
endmodule
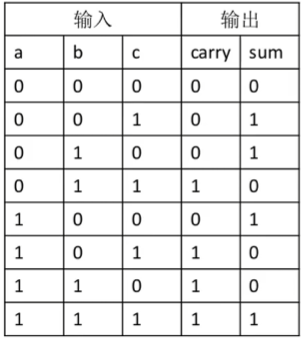
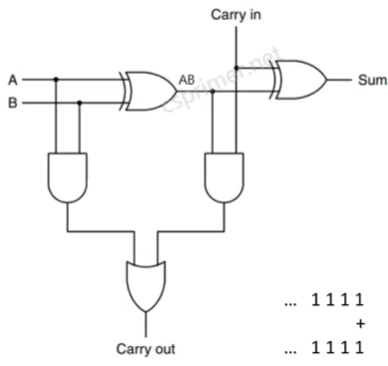
全加器(考虑进位)
module FullAdder(input a,b,c, output sum, carry);
// your code here
wire AB,carry1,carry2;
HalfAdder g1(a,b,AB,carry1);
HalfAdder g2(AB,c,sum,carry2);
Or g3(carry1,carry2,carry);
endmodule
16位加法器
module Add16(input[15:0] a,b, output[15:0] out);
// your code here
wire [15:0] c;
FullAdder g01(a[0],b[0],1'b0,out[0],c[0]);
FullAdder g02(a[1],b[1],c[0],out[1],c[1]);
FullAdder g03(a[2],b[2],c[1],out[2],c[2]);
FullAdder g04(a[3],b[3],c[2],out[3],c[3]);
FullAdder g05(a[4],b[4],c[3],out[4],c[4]);
FullAdder g06(a[5],b[5],c[4],out[5],c[5]);
FullAdder g07(a[6],b[6],c[5],out[6],c[6]);
FullAdder g08(a[7],b[7],c[6],out[7],c[7]);
FullAdder g09(a[8],b[8],c[7],out[8],c[8]);
FullAdder g10(a[9],b[9],c[8],out[9],c[9]);
FullAdder g11(a[10],b[10],c[9],out[10],c[10]);
FullAdder g12(a[11],b[11],c[10],out[11],c[11]);
FullAdder g13(a[12],b[12],c[11],out[12],c[12]);
FullAdder g14(a[13],b[13],c[12],out[13],c[13]);
FullAdder g15(a[14],b[14],c[13],out[14],c[14]);
FullAdder g16(a[15],b[15],c[14],out[15],c[15]);
endmodule
减法
负数的补码由他的正数按位取反再加1
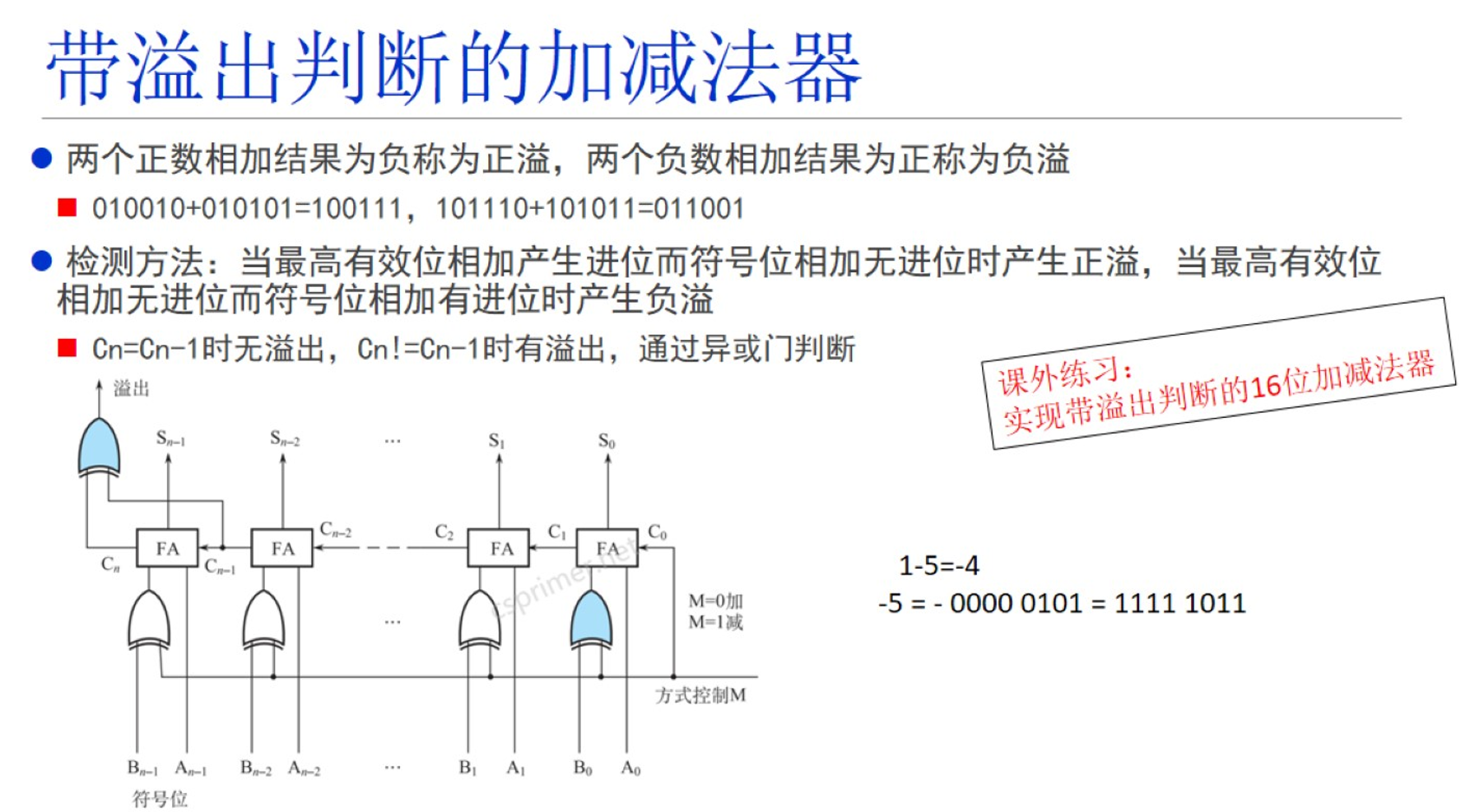
带溢出判断的加法器
两正数相加结果为负数=正溢
两负数相加结果为正=负溢
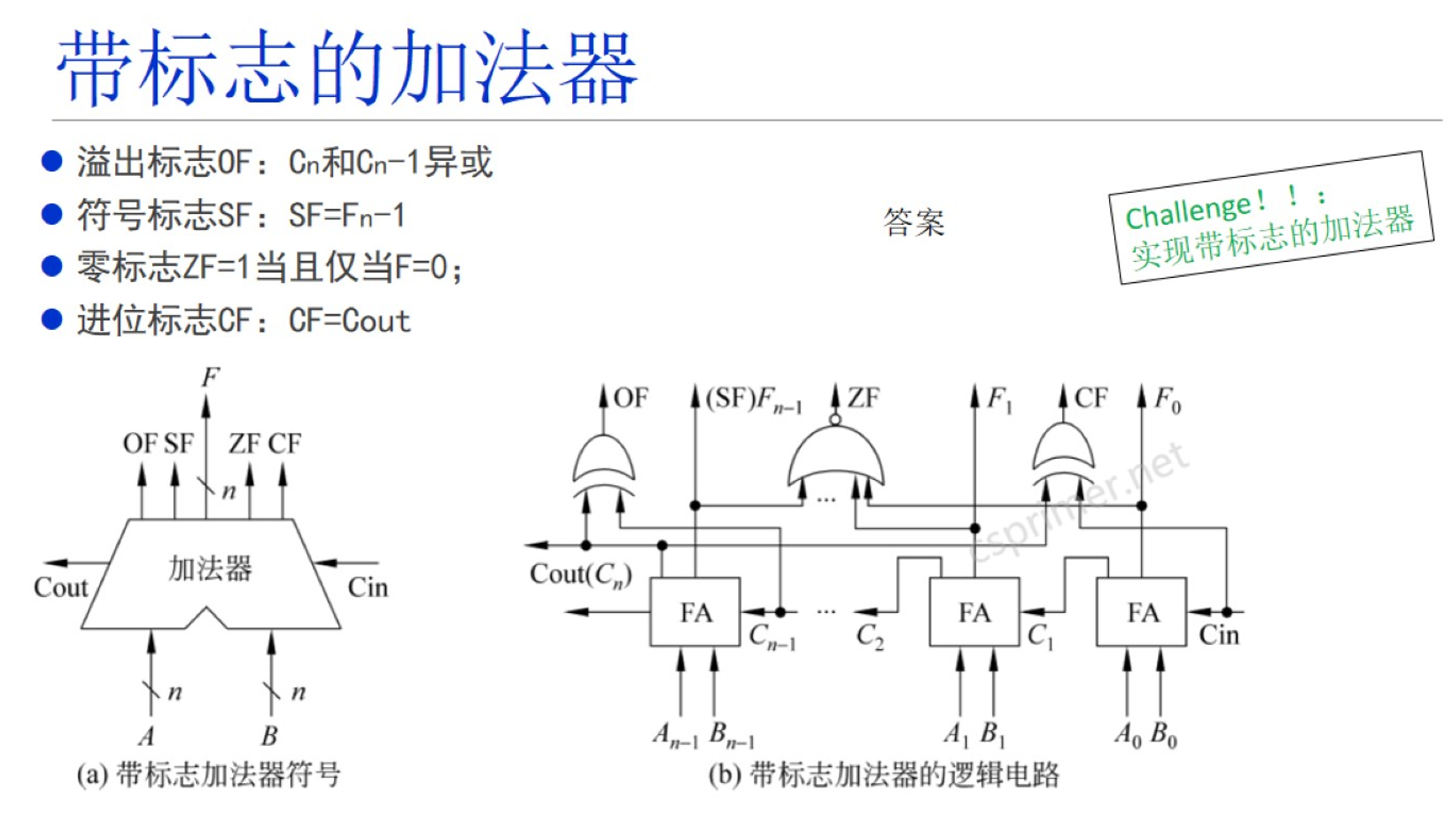
寄存器存储器的实现#
时钟
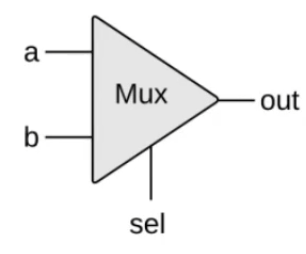
多路选择器(multiplexor)
sel = 0,选择a作为输出
sel =1,选择b作为输出
/**
* Multiplexor:
* if (sel == 0) out = a
* else out = b
*/
module Mux(input a, b, sel, output out);
Not g1(sel, nsel);
And g2(a, nsel, o1);
And g3(b, sel, o2);
Or g4(o1, o2, out);
endmodule
16位的多路选择器
/**
* 16-bit multiplexor:
* for i = 0..15 out[i] = a[i] if sel == 0
* b[i] if sel == 1
*/
module Mux16(input[15:0] a, b, input sel, output[15:0] out);
Mux g15(a[15], b[15], sel, out[15]);
Mux g14(a[14], b[14], sel, out[14]);
Mux g13(a[13], b[13], sel, out[13]);
Mux g12(a[12], b[12], sel, out[12]);
Mux g11(a[11], b[11], sel, out[11]);
Mux g10(a[10], b[10], sel, out[10]);
Mux g09(a[9], b[9], sel, out[9]);
Mux g08(a[8], b[8], sel, out[8]);
Mux g07(a[7], b[7], sel, out[7]);
Mux g06(a[6], b[6], sel, out[6]);
Mux g05(a[5], b[5], sel, out[5]);
Mux g04(a[4], b[4], sel, out[4]);
Mux g03(a[3], b[3], sel, out[3]);
Mux g02(a[2], b[2], sel, out[2]);
Mux g01(a[1], b[1], sel, out[1]);
Mux g00(a[0], b[0], sel, out[0]);
endmodule
4way/8way 多路选择器
即输入4个情况/输入8个情况
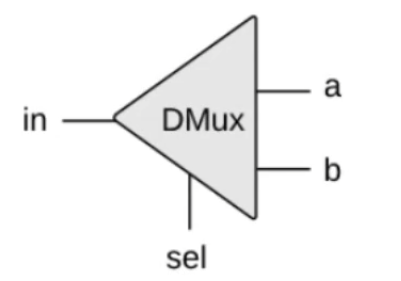
多路复用器(Demultiplexor)
/**
* Demultiplexor:
* if sel == 0, a= in, b = 0;
* if sel == 1, a= 0, b = in;
*/
module DMux(input in, sel, output a, b);
Not g1(sel, nsel);
And g2(nsel, in, a);
And g3(sel, in, b);
endmodule
4way/8way 多路复用器
即输出4个情况/输出8个情况
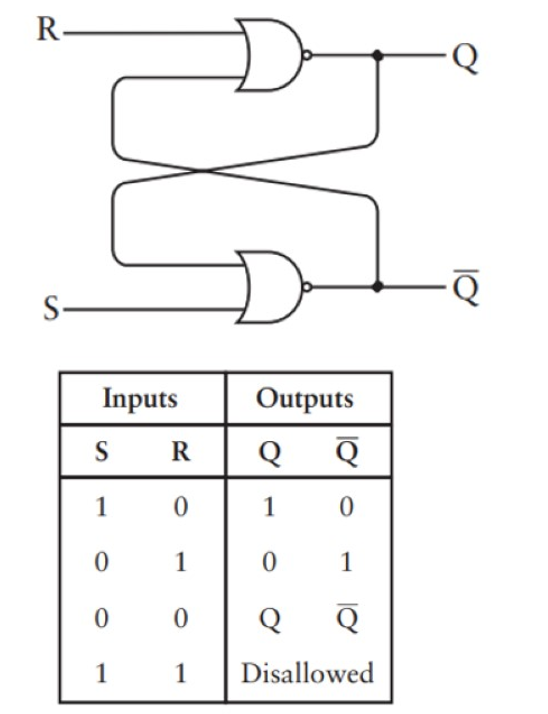
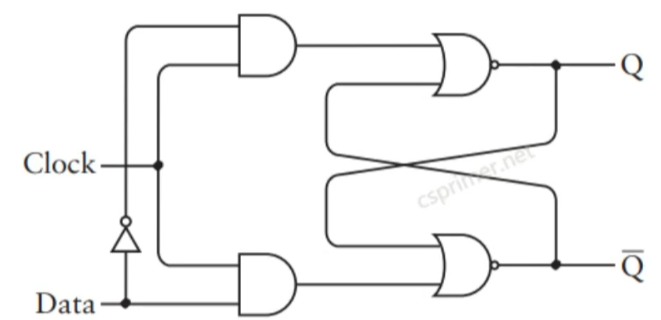
SR锁存器
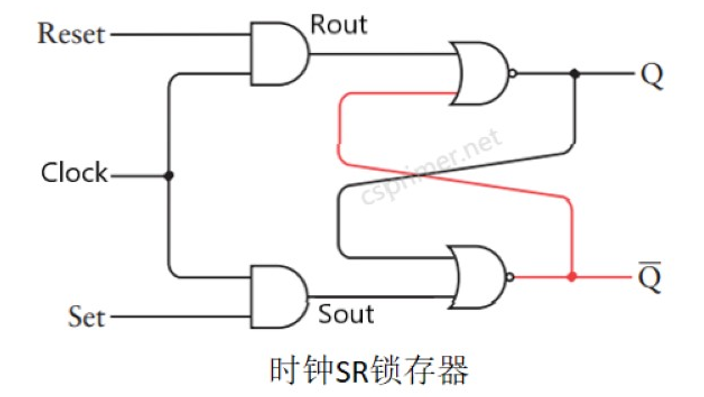
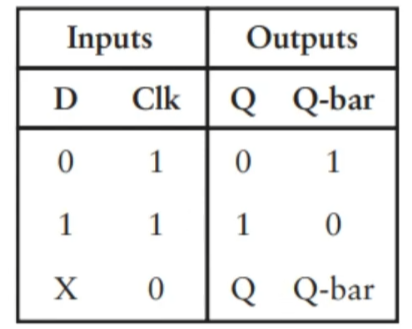
时钟SR锁存器(当时钟=1时候,输出才受r 和s 影响,当时钟=0,输出保持之前的值)
module SRFF (input R, clock, S, output Q, Q_dot);
// your code here
wire Rout,Sout;
And g1(R,clock,Rout);
And g2(S,clock,Sout);
Nor g3(Rout,Q_dot,Q);
Nor g4(Sout,Q,Q_dot);
endmodule
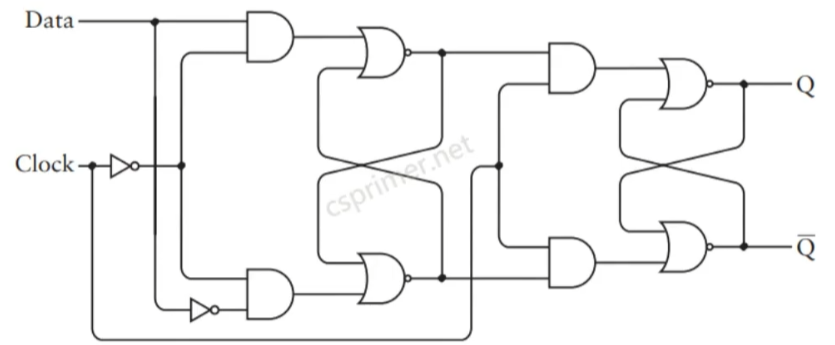
D锁存器(就是把SR锁存器两个输入变成一个输入)也叫电平触发
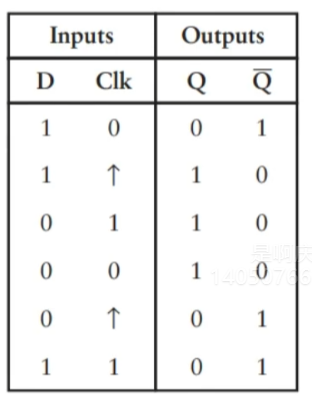
D触发器(两个时钟SR锁存器构成),属于边沿触发,只有当时钟从0->1时才是输出等于输入,其他情况保持之前的值。
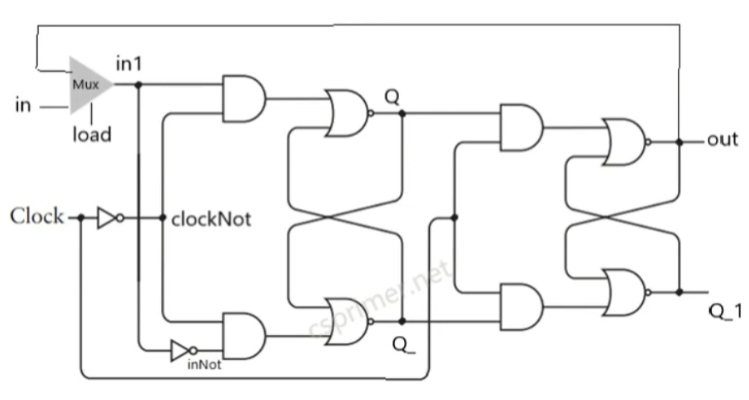
D触发器的实现
module DFF(input in, clock, load, output out);
// your code here
wire in1,inNot,clockNot,Q,Q_,Q_dot;
Mux g1(out,in,load,in1);
Not g3(in1,inNot);
Not g4(clock,clockNot);
SRFF g2(in1,clockNot,inNot,Q, Q_);
SRFF g5(Q,clock,Q_,out, Q_dot);
endmodule
16位的寄存器(16个D触发器),当load=1,时钟从0->1的时候,输出等于输入。当load=0,就保持之前的值。
/**
* 16-bit register:
* If clk[t] == 1 then out[t+1] = in[t]
* else out does not change
*/
module Register(input[15:0] in, input clock, load, output[15:0] out);
DFF g01(in[15], clock, load, out[15]);
DFF g02(in[14], clock, load, out[14]);
DFF g03(in[13], clock, load, out[13]);
DFF g04(in[12], clock, load, out[12]);
DFF g05(in[11], clock, load, out[11]);
DFF g06(in[10], clock, load, out[10]);
DFF g07(in[9], clock, load, out[9]);
DFF g08(in[8], clock, load, out[8]);
DFF g09(in[7], clock, load, out[7]);
DFF g10(in[6], clock, load, out[6]);
DFF g11(in[5], clock, load, out[5]);
DFF g12(in[4], clock, load, out[4]);
DFF g13(in[3], clock, load, out[3]);
DFF g14(in[2], clock, load, out[2]);
DFF g15(in[1], clock, load, out[1]);
DFF g16(in[0], clock, load, out[0]);
endmodule
8个寄存器组合成一个RAM8的存储器,input[2:0] address有3位也就是八个地址,分别对应八个寄存器
通过多路复用器,当load=1时,选择把输入存储到哪个寄存器里,比如load=1,address=1,就把loadB设为1,当时钟0->1时候,o1=in(输出等于输入)
然后再使用多路选择器,通过地址选择哪个寄存器作为输出。
module RAM8(input[15:0] in, input clk, load, input[2:0] address, output[15:0] out);
wire[15:0] o0,o1,o2,o3,o4,o5,o6,o7;
DMux8Way g0(load, address, loadA, loadB, loadC, loadD, loadE, loadF, loadG, loadH);
Register r0(in, clk, loadA, o0);
Register r1(in, clk, loadB, o1);
Register r2(in, clk, loadC, o2);
Register r3(in, clk, loadD, o3);
Register r4(in, clk, loadE, o4);
Register r5(in, clk, loadF, o5);
Register r6(in, clk, loadG, o6);
Register r7(in, clk, loadH, o7);
Mux8Way16 g1(o0, o1, o2, o3, o4, o5, o6, o7, address, out);
endmodule
8个RAM8存储器组合成RAM64,地址范围0-5,即2的6次方64个地址
address[5:3] 前三位八个地址,作为8个RAM8的选择
address[2:0] 后三位8个地址,作为8个寄存器的选择
module RAM64(input [15:0] in, input clk,load, input [5:0] address, output [15:0] out);
wire[15:0] o1, o2, o3, o4, o5, o6, o7, o8;
DMux8Way d1(load, address[5:3], loadA, loadB, loadC, loadD, loadE, loadF, loadG, loadH);
RAM8 r1(in, clk, loadA, address[2:0], o1);
RAM8 r2(in, clk, loadB, address[2:0], o2);
RAM8 r3(in, clk, loadC, address[2:0], o3);
RAM8 r4(in, clk, loadD, address[2:0], o4);
RAM8 r5(in, clk, loadE, address[2:0], o5);
RAM8 r6(in, clk, loadF, address[2:0], o6);
RAM8 r7(in, clk, loadG, address[2:0], o7);
RAM8 r8(in, clk, loadH, address[2:0], o8);
Mux8Way16 m1(o1, o2, o3, o4, o5, o6, o7, o8, address[5:3], out);
endmodule
8个RAM64存储器组合成RAM512,地址范围0-8,即2的9次方512个地址
module RAM512(input [15:0] in, input clk,load, input [8:0] address, output [15:0] out);
// your code here
wire[15:0] o1, o2, o3, o4, o5, o6, o7, o8;
DMux8Way d1(load, address[8:6], loadA, loadB, loadC, loadD, loadE, loadF, loadG, loadH);
RAM64 r1(in, clk, loadA, address[5:0], o1);
RAM64 r2(in, clk, loadB, address[5:0], o2);
RAM64 r3(in, clk, loadC, address[5:0], o3);
RAM64 r4(in, clk, loadD, address[5:0], o4);
RAM64 r5(in, clk, loadE, address[5:0], o5);
RAM64 r6(in, clk, loadF, address[5:0], o6);
RAM64 r7(in, clk, loadG, address[5:0], o7);
RAM64 r8(in, clk, loadH, address[5:0], o8);
Mux8Way16 m1(o1, o2, o3, o4, o5, o6, o7, o8, address[8:6], out);
endmodule
执行会很慢。需要verilog高级语法。
16位CPU指令设计#
指令设计
D寄存器:仅用来存储数据值
A寄存器:存储地址或数据
A指令:用来为A寄存器设置15位的值
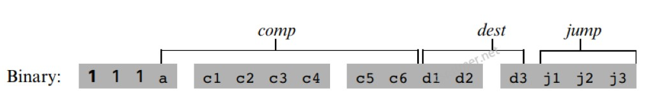
C指令:完成算术逻辑操作,存储器读写操作,控制流跳转操作
介绍C指令的comp域,a=0,按照左边计算。a=1,按照右边计算。
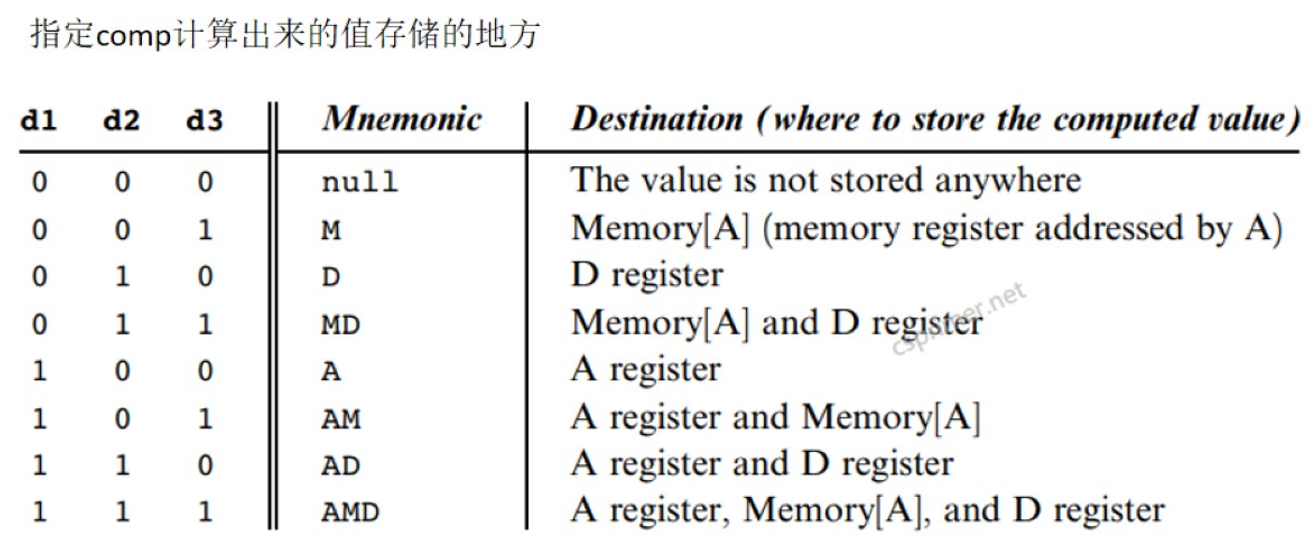
介绍C指令的dest域,他是用来指定comp计算出来的值存储的地方。
d1对应A寄存器,1,0,0表示把结果存储在A寄存器
d2对应D寄存器,0,1,0表示把结果存储在D寄存器
d3对应Memory[A],0,0,1表示把结果存住在Memory[A]
三个都为0表示不存储值。三个都为1表示这三个地方都存储。
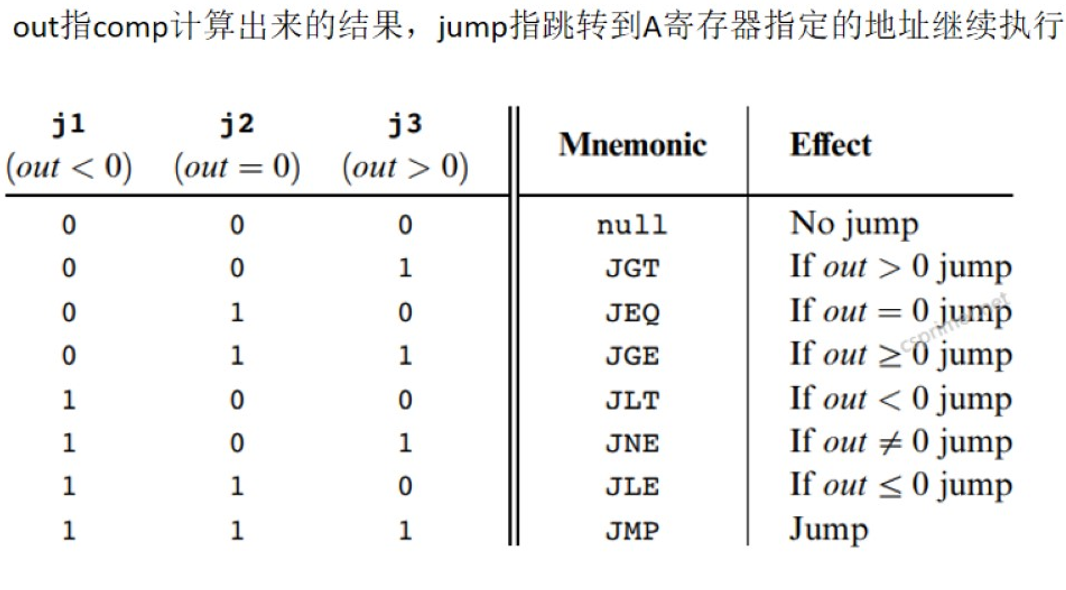
介绍C指令的jump域
0 0 0 不跳转
1 1 1无条件跳转
其他情况,根据comp计算出来的结果判断,如:0 1 0,out=0,跳转
ALU实现#
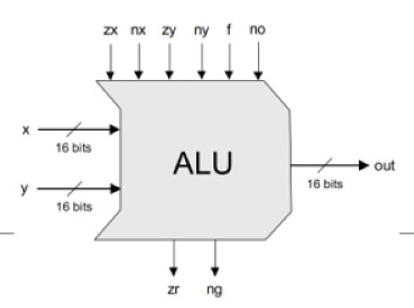
ALU主要实现C指令comp域描述的计算,他有两个16位的输入系x,y,一个16位的输出 out,6个控制输入zx,nx,zy,ny,f,no,2个控制输出zr,ng
ALU在六个控制输入不同的组合下可以实现不同的个功能:comp域六位对应zx,nx,zy,ny,f,no
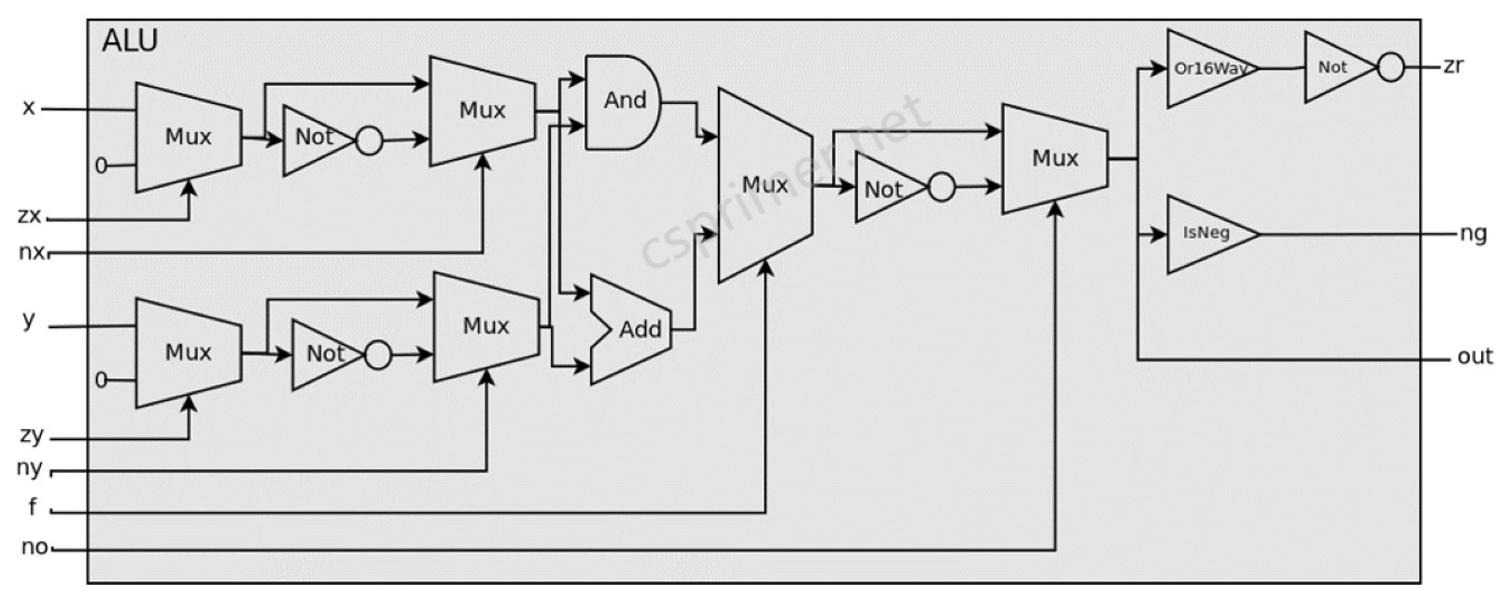
if可以使用多路选择器来进行判断,ALU数据通路图:
Or16way
/**
* 16-way Or:
* out = (in[0] or in[1] or ... or in[15])
*/
module Or16Way(input[15:0] in,output out);
// your code here
wire out1,out2,out3,out4,out5,out6,out7,out8,out9,out10,out11,out12,out13,out14;
Or g1(in[0],in[1],out1);
Or g2(out1,in[2],out2);
Or g3(out2,in[3],out3);
Or g4(out3,in[4],out4);
Or g5(out4,in[5],out5);
Or g6(out5,in[6],out6);
Or g7(out6,in[7],out7);
Or g8(out7,in[8],out8);
Or g9(out8,in[9],out9);
Or g10(out9,in[10],out10);
Or g11(out10,in[11],out11);
Or g12(out11,in[12],out12);
Or g13(out12,in[13],out13);
Or g14(out13,in[14],out14);
Or g15(out14,in[15],out);
endmodule
IsNeg
module IsNeg(input[15:0] in, output out);
// your code here
Or g1(in[15],1'b0,out);
endmodule
ALU
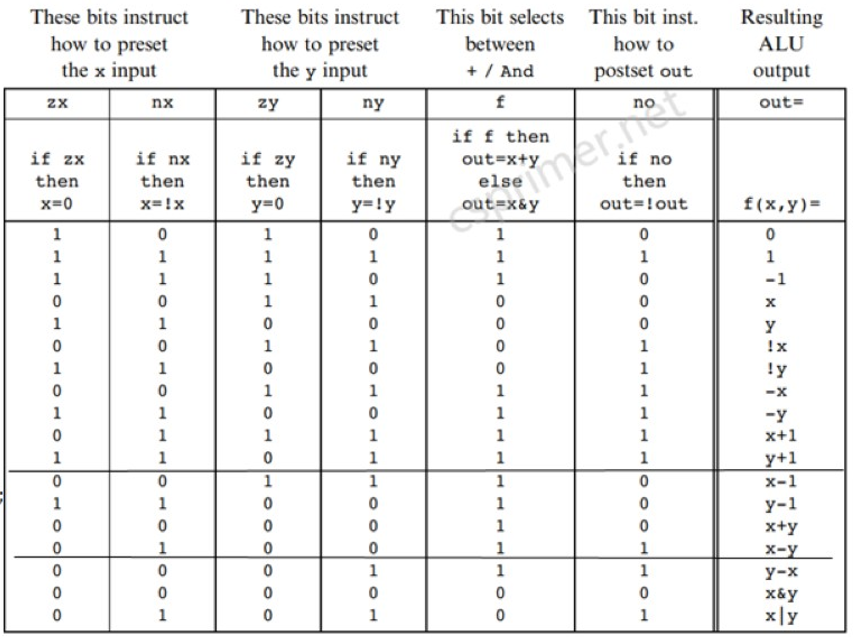
/**
* The ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit).
* Computes one of the following functions:
* x+y, x-y, y-x, 0, 1, -1, x, y, -x, -y, !x, !y,
* x+1, y+1, x-1, y-1, x&y, x|y on two 16-bit inputs,
* according to 6 input bits denoted zx,nx,zy,ny,f,no.
* In addition, the ALU computes two 1-bit outputs:
* if the ALU output == 0, zr is set to 1; otherwise zr is set to 0;
* if the ALU output < 0, ng is set to 1; otherwise ng is set to 0.
*/
// Implementation: the ALU logic manipulates the x and y inputs
// and operates on the resulting values, as follows:
// if (zx == 1) set x = 0 // 16-bit constant
// if (nx == 1) set x = !x // bitwise not
// if (zy == 1) set y = 0 // 16-bit constant
// if (ny == 1) set y = !y // bitwise not
// if (f == 1) set out = x + y // integer 2's complement addition
// if (f == 0) set out = x & y // bitwise and
// if (no == 1) set out = !out // bitwise not
// if (out == 0) set zr = 1
// if (out < 0) set ng = 1
module ALU(input[15:0] x, y, input zx,nx,zy,ny,f,no, output[15:0] out, output zr, ng);
wire[15:0] x1, notx1, x2, y1, noty1, y2, andxy, addxy, o1, noto1, o2;
wire notzr;
// your code here, use Mux16,Not16,Add16,And16,Or16Way,IsNeg to implement
// if (zx == 1) set x = 0
Mux16 g1(x,16'h0,zx,x1);
// if (nx == 1) set x = !x
Not16 g2(x1,notx1);
Mux16 g3(x1,notx1,nx,x2);
// if (zy == 1) set y = 0
Mux16 g4(y,16'h0,zy,y1);
// if (ny == 1) set y = !y
Not16 g5(y1,noty1);
Mux16 g6(y1,noty1,ny,y2);
// addxy = x + y
Add16 g7(x2,y2,addxy);
// andxy = x & y
And16 g8(x2,y2,andxy);
// if (f == 1) set out = x + y else set out = x & y
Mux16 g9(andxy,addxy,f,o1);
// if (no == 1) set out = !out
Not16 g10(o1,noto1);
Mux16 g11(o1,noto1,no,out);
// zr
Or16Way g12(out,notzr);
Not g13(notzr,zr);
// ng
IsNeg g14(out,ng);
endmodule





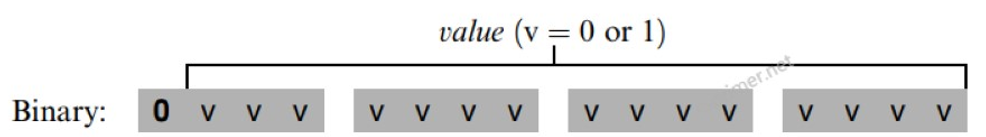



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 阿里最新开源QwQ-32B,效果媲美deepseek-r1满血版,部署成本又又又降低了!
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 开源Multi-agent AI智能体框架aevatar.ai,欢迎大家贡献代码
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· AI技术革命,工作效率10个最佳AI工具