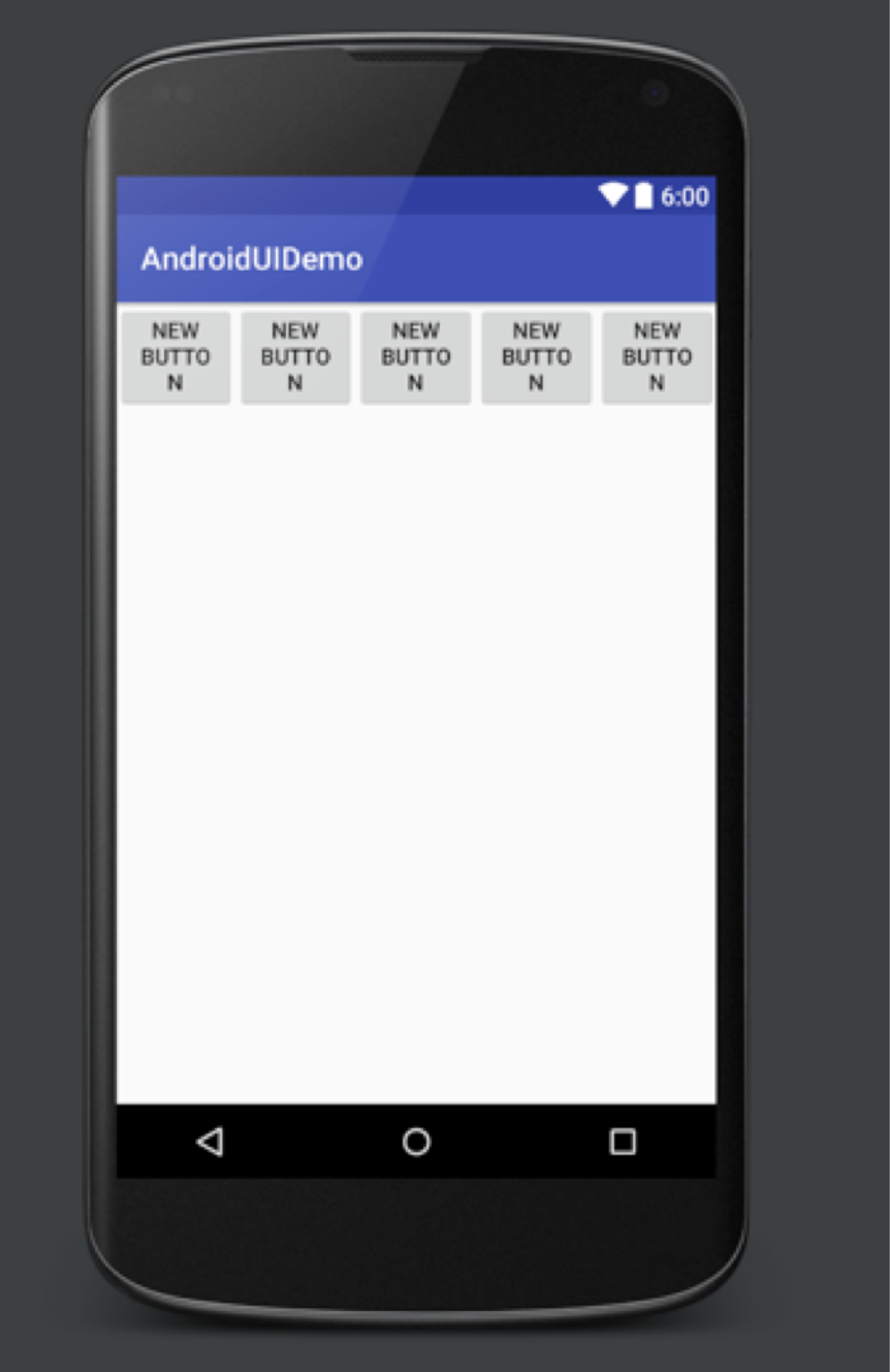
一、线性布局
线性布局的关键字为 Linerlayout 就是一排一排的排列,按照水平(vertical)和垂直(horizontal)的方式来排列,线性布局控制其中各个组件的大小可以通过控制权重(weight)来分配
< ?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
< LinearLayout
xmlns:android="https://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
< Button
android:id="@+id/button"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="New Button"/>
< Button
android:id="@+id/button3"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="New Button"/>
< Button
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1" android:text="New Button"/>
< Button
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="New Button"/>
< Button
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="New Button"/>
< /LinearLayout>
二、相对布局
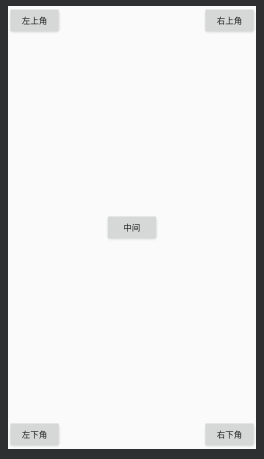
相对布局的关键字为Relativelayout,可以是块与块之间的关系,也可以是元素与元素之间的关系。类似于html里面的div标签,一般是相对应parent或者是相对于某个id。
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<!--相对布局练习-->
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:text="中间"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
android:text="右上角"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
android:text="右下角"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="左上角"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:text="左下角"/>
</RelativeLayout>
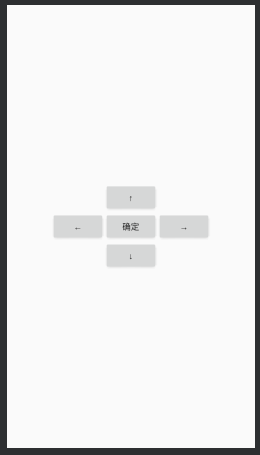
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<!--相对布局相对于同级控件练习-->
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:text="确定"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:id="@+id/centerbutton"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:text="←"
android:layout_centerVertical="true"
android:layout_toLeftOf="@id/centerbutton"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:text="→"
android:layout_centerVertical="true"
android:layout_toRightOf="@id/centerbutton"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:text="↑"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_above="@id/centerbutton"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:text="↓"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_below="@id/centerbutton"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
</RelativeLayout>
三、其他布局
(1)绝对布局关键字absolutelayout,直接规定空间的实际大小,一般针对手表等对像素有规定的开发
(2)表格布局关键字tablelayout、tablerow,类似于html里面的table标签
(3)帧布局framelayout
这三种布局的效果都可以通过线性布局和相对布局通过嵌套组合来实现~
四、常用单位
字体常用单位sp、布局常用单位dp、像素单位px不常用






