[实验7]流类库与输入输出
一、实验目的
- 理解流的概念
- 熟悉流类库中常用的类及成员函数用法
- 熟悉 I/O 格式控制方法,掌握常用格式控制
- 了解文件 I/O,掌握文件 I/O 基本用法
二、实验准备
结合第 11 章教材、课件,复习/学习如下内容:
1.基础知识
(1)流是什么?如何理解?
(2)C++中 I/O 是通过什么来实现的?
(3)常用 I/O 流类的继承/派生层次关系
(4)预定义标准流对象 cin, cout, cerr, clog
2.C++中格式化 I/O 方法
3.文件 I/O 方法及常用成员函数
三、实验内容
1.基础练习
(1)教材习题 11-7
(2)教材习题 11-3
(3)教材习题 11-4
2.应用练习
(1)已知有班级名单文件list.txt(见实验 7 附件包)。编写一个应用程序实现随机抽点
5 位同学,在屏幕上显示结果,同时,也将结果写入文件 roll.txt。
① 编写程序实现题目基本功能要求。(必做)
② ******选做******)
对①中实现的基本功能进行完善、扩充,使得这个点名应用程序更灵活、更方便。比如:
a) 从键盘输入班级文件名,支持对不同班级的点名操作;
b) 从键盘输入用于保存点名结果的文件名。更灵活地,自动获取当前系统日期作为文件名,比如 20180612.txt。(如果希望更细粒度,文件名可以到小时和分钟这一层级);
c) 随机抽点人数不固定,通过键盘按键控制何时抽点结束;
d) 通过菜单及程序的函数模块划分,或类的设计与实现,做成一个更完善的应用,等等。
(2)统计英文文本文件字符数、单词数、行数,文件名由键盘输入。
① 编写 C++程序实现题目基本功能要求。(必做)
② ******选做******
a) 提供菜单,由用户选择统计内容;
b) 思考当文本内容数量级偏大,①处已实现的程序能否胜任,实现快速统计?在算法和处理逻辑上是否存在进一步改进的部分?
四、实验结论
1.基础练习
(1)教材习题 11-7
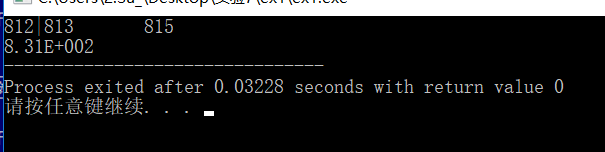
① 源码及运行结果截图;
② 以注释方式标注格式控制部分的作用;
#include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { ios_base::fmtflags original_flags = cout.flags(); //1保存现在的格参数设置 cout<< 812<<'|'; cout.setf(ios_base::left,ios_base::adjustfield); //2把对齐方式改为左对齐 cout.width(10); //3输出的宽度改为10 cout<< 813 << 815 << '\n'; cout.unsetf(ios_base::adjustfield); //4取消对齐方式的设置 cout.precision(2); cout.setf(ios_base::uppercase|ios_base::scientific); //5设置 浮点数的显示 cout << 831.0 ; cout.flags(original_flags); //6恢复原来的设置 return 0; }
(2)教材习题 11-3
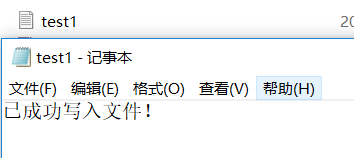
① 源码及程序运行结果截图。
② 截图显示磁盘上是否生成指定文件,并且正确写入数据。
#include<fstream> using namespace std; int main() { ofstream file("test1.txt"); file<<"已成功写入文件!"; file.close(); return 0; }
(3)教材习题 11-4
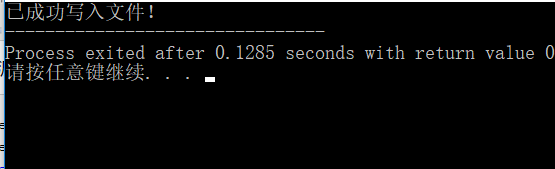
① 源码及程序运行结果截图。
② 截图显示磁盘上源文件内容,与屏幕显示结果对照,是否正确读入。
#include <fstream> #include<iostream> using namespace std; int main(){ string s; ifstream file("test1.txt"); getline(file,s); cout<<s; file.close(); return 0; }
2.应用练习
(1)
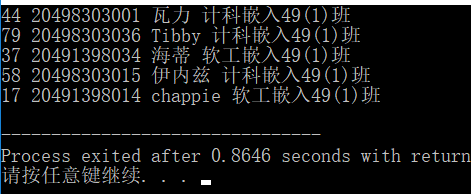
① 源码及程序运行结果截图;磁盘文件 roll.txt 及内容截图;
#include<iostream> #include<fstream> #include<string> #include<stdlib.h> using namespace std; int m; struct student { string num; string id,name,clas; }stu[100]; int main(){ ifstream fin("list.txt"); int i=0; while(fin>>stu[i].num>>stu[i].id>>stu[i].name>>stu[i].clas) { i++; } fin.close(); int a,j=5; ofstream fout("roll.txt"); while(j--) { a=rand()%i+1; cout<<stu[a].num<<" "<<stu[a].id<<" "<<stu[a].name<<" "<<stu[a].clas<<endl; fout<<stu[a].num<<" "<<stu[a].id<<" "<<stu[a].name<<" "<<stu[a].clas<<endl; } fout.close(); return 0; }

(2)借鉴了大佬的算法思路!!!
①
a) 简洁陈述统计字符数、单词数、行数的算法思路;
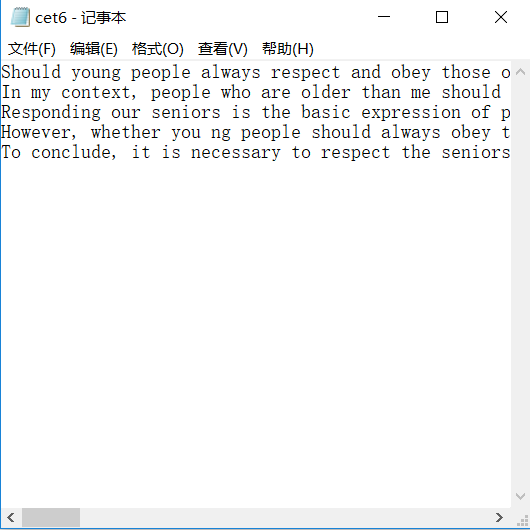
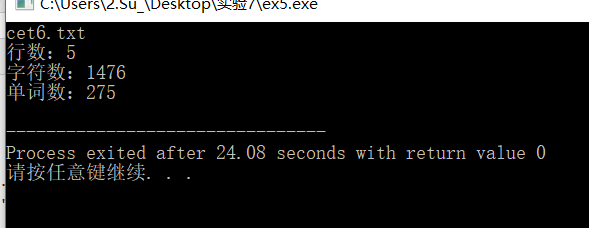
b) 源码及程序运行结果截图;用于测试统计的文本文件内容截图;
#include<string.h> #include<fstream> using namespace std; int main(){ string filename; cin>>filename; ifstream fin(filename.c_str()); long line=0,ch=0,word=0; char str[1000]; while(fin.getline(str,1000)) { for(int i=0;i<strlen(str);i++) { ch++; if(str[i]=='?'||str[i]==','||str[i]=='.'||str[i]=='!'||str[i]=='('||str[i]==')'||str[i]==' ' ||str[i]=='"'||str[i]=='-'||str[i]=='#'||str[i]=='/'||str[i]==':') word++; } line++; } cout<<"行数:"<<line<<endl<<"字符数:"<<ch<<endl<<"单词数:"<<word<<endl; return 0; }
注:
① 源代码中,必要的部分,请添加注释,增加代码的可读性
② 博客园中请采用平台支持的插入代码方式,以方便其它同学评阅和测试运行。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号