使用 JVM 进程缓存 Caffeine
使用 JVM 进程缓存的优点就是没有网络开销,性能速度最快;缺点就是容量有限,无法共享;比较适合性能要求高,缓存数据量小的场景。如果我们自己实现 JVM 进程缓存的话,会使用到 Map 数据类型,相关的过期移除策略以及容量控制都得自己实现,比较麻烦。Caffeine 是一个基于 Java8 开发的提供了近乎最佳命中率的高性能的 JVM 进程缓存库,使用起来非常方便省心。
由于 Caffeine 的使用非常简单,这里就直接列出 Demo 代码进行演示,在博客最后会提供源代码下载。
Caffeine 的官网地址为:https://github.com/ben-manes/caffeine
一、搭建工程
新建一个 SpringBoot 工程 springboot_caffeine,结构如下:
首先看一下 pom 文件,主要是引入 caffeine 的依赖包:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.jobs</groupId> <artifactId>springboot_caffeine</artifactId> <version>1.0</version> <properties> <maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source> <maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target> </properties> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>2.4.5</version> </parent> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> </dependency> <!--引入 Caffeine 缓存依赖--> <dependency> <groupId>com.github.ben-manes.caffeine</groupId> <artifactId>caffeine</artifactId> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> <version>2.4.5</version> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project>
二、测试代码展示
在 CaffeineTest 类中,编写了使用 Caffeine 的用法,非常简单,具体内容如下:
package com.jobs; import com.github.benmanes.caffeine.cache.Cache; import com.github.benmanes.caffeine.cache.Caffeine; import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test; import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest; import java.time.Duration; @SpringBootTest public class CaffeineTest { @Test void test1() { // 构建 cache 对象,由于是泛型,因此可以声明出你想要的类型 Cache<String, String> cache = Caffeine.newBuilder().build(); // 存数据 或 更新数据 cache.put("user", "侯胖胖"); // 取数据 String user = cache.getIfPresent("user"); System.out.println("user = " + user); // 取数据,如果未取到,可以执行方法,比如查询数据库,然后把结果自动存储到缓存中 String fatUser = cache.get("fatUser", key -> { return "任肥肥"; }); System.out.println("fatUser = " + fatUser); } //设置最大容量,超过容量的话,清除之前添加的缓存 @Test void test2() throws InterruptedException { // 创建缓存对象 Cache<String, String> cache = Caffeine.newBuilder() // 设置缓存最大容量上限为 1 .maximumSize(1).build(); cache.put("user1", "侯胖胖"); cache.put("user2", "任肥肥"); cache.put("user3", "乔豆豆"); // 延迟10ms,给清理线程一点时间 Thread.sleep(10L); // 获取数据 System.out.println("user1: " + cache.getIfPresent("user1")); System.out.println("user2: " + cache.getIfPresent("user2")); System.out.println("user3: " + cache.getIfPresent("user3")); } //设置缓存的有效期,超时后,将获取不到 @Test void test3() throws InterruptedException { // 创建缓存对象 Cache<String, String> cache = Caffeine.newBuilder() // 设置缓存有效期为 1 秒 .expireAfterWrite(Duration.ofSeconds(1)) .build(); // 存数据 cache.put("user", "乔豆豆"); // 获取数据 System.out.println("user: " + cache.getIfPresent("user")); // 休眠一会儿 Thread.sleep(1300L); // 再获取数据 System.out.println("user: " + cache.getIfPresent("user")); } }
可以看出:我们在构建 Caffeine 缓存实例时,可以设置最大容量,以及缓存的有效期。
三、依赖注入示例
在 CaffeineConfig 类中,我们只需要构建实例并加上 @Bean 注解,即可全局使用:
package com.jobs.config; import com.github.benmanes.caffeine.cache.Cache; import com.github.benmanes.caffeine.cache.Caffeine; import com.jobs.pojo.Employee; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; @Configuration public class CaffeineConfig { @Bean public Cache<String, Employee> itemCache() { return Caffeine.newBuilder() //初始容量为100 .initialCapacity(100) //最大容量为10000 .maximumSize(10000) //写入后60秒过期 .expireAfterWrite(60, TimeUnit.SECONDS) .build(); } }
当然你也可以把初始容量、最大容量、缓存有效期等参数,配置到 application.yml 文件中。
下面我们在 EmpolyeeController 类中,注入 Caffeine 缓存实例并使用:
package com.jobs.controller; import com.github.benmanes.caffeine.cache.Cache; import com.jobs.pojo.Employee; import com.jobs.pojo.Result; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*; import java.util.Random; @RequestMapping("/emp") @RestController public class EmployeeController { @Autowired private Cache<String, Employee> employeeCache; @PostMapping("/add") public Result<Boolean> addEmployee(Employee emp) { employeeCache.put(emp.getName(), emp); return Result.success(true); } @PostMapping("/update") public Result<Boolean> updateEmployee(Employee emp) { employeeCache.put(emp.getName(), emp); return Result.success(true); } @GetMapping("/get/{name}") public Result<Employee> getEmployee(@PathVariable("name") String name) { //如果能够取到,则返回获取的内容 //如果取不到,则执行方法(比如去数据库中获取),然后存储到缓存中 Employee employee = employeeCache.get(name, key -> new Employee(key, new Random().nextInt(50))); return Result.success(employee); } @DeleteMapping("/delete") public Result<Boolean> deleteEmployee(String name) { employeeCache.invalidate(name); return Result.success(true); } }
下面列出 Employee 类的内容:
package com.jobs.pojo; import lombok.AllArgsConstructor; import lombok.Data; import lombok.NoArgsConstructor; @Data @NoArgsConstructor @AllArgsConstructor public class Employee { //姓名 private String name; //年龄 private Integer age; }
为了能够统一返回值,一般我们都会定义一个返回类,这里定义了 Result 类:
package com.jobs.pojo; import lombok.Data; @Data public class Result<T> { //状态 private Integer status; //消息 private String msg; //数据 private T data; public static <T> Result<T> success(T object) { Result<T> r = new Result<T>(); r.status = 0; r.msg = "success"; r.data = object; return r; } public static <T> Result<T> fail(Integer status, String msg) { Result r = new Result(); r.status = status; r.msg = msg; return r; } public static <T> Result<T> error(String msg) { Result r = new Result(); r.status = 500; r.msg = msg; return r; } }
以上就是使用 Caffeine 的代码示例,非常简单。Caffeine 也提供了异步调用的方法,这里就不演示了,可以参考官网。
官网也列出了 Caffeine 与其它相关的 JVM 进程缓存的性能对比,如下图所示:
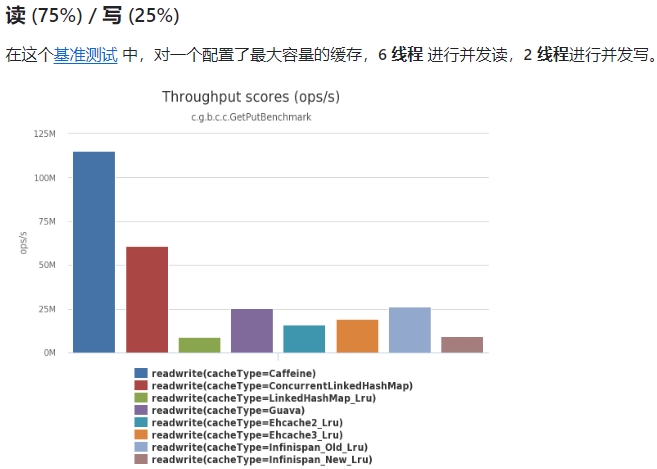
官网性能基准测试的结果访问地址为:https://github.com/ben-manes/caffeine/wiki/Benchmarks-zh-CN
本篇博客的Demo源代码下载地址为:https://files.cnblogs.com/files/blogs/699532/springboot_caffeine.zip



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(五):向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理