一、MyBatis 使用 XML 配置 SQL 总结
MyBatis 是一款优秀的基于 Java 的持久层框架,它内部封装了 JDBC 操作数据库的繁琐细节,使开发者只需要关注 SQL 语句本身,后期再结合 Spring 框架的依赖注入,大大减少了操作数据库的代码量,从而提高开发效率。
MyBatis 可以通过 XML 方式配置 SQL 语句,也可以通过注解的方式编写 SQL 语句,具体采用哪种方式取决于公司的开发规定,建议两种开发方式都要掌握,其实两种方式都很容易。
MyBatis 的官网地址为:https://mybatis.org/mybatis-3/zh/sqlmap-xml.html
本篇博客主要介绍 MyBatis 使用 XML 配置 SQL 语句的方式实现对数据库操作的具体细节,在博客的最后面会提供源代码。
一、导入 jar 包
新建一个 Maven 项目,在 pom.xml 文件中导入 4 个 jar 包:
mysql 的 jar 包:https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/mysql/mysql-connector-java
mybatis 的 jar 包:https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.mybatis/mybatis
log4j 的 jar 包:https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/log4j/log4j
junit 的 jar 包:https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/junit/junit
我在 pom.xml 配置的都是当前最新版本的 jar 包,如下所示:
<!--导入 mysql 的 jar 包--> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <version>8.0.28</version> </dependency> <!--导入 mybatis 的 jar 包--> <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis</artifactId> <version>3.5.9</version> </dependency> <!--导入 log4j 的 jar 包--> <!--主要是为了查看 mybatis 生成的最终 sql 语句--> <dependency> <groupId>log4j</groupId> <artifactId>log4j</artifactId> <version>1.2.17</version> </dependency> <!--导入 junit 的 jar 包--> <!--方便编写测试方法,对 mybatis 操作数据库进行测试--> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.13.2</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency>
配置好引用的 jar 包后,打开右侧的 Maven 窗口,刷新一下,这样 Maven 会自动下载所需的 jar 包文件。
二、搭建整个项目工程
整个项目工程的结构和整体内容,如下图所示,
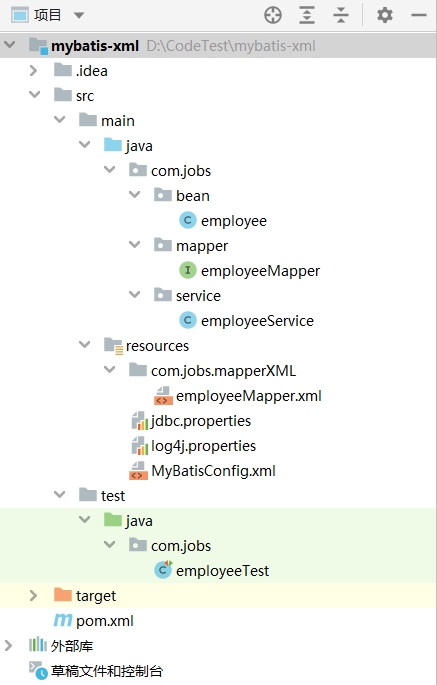
项目工程结构简单介绍:
com.jobs.bean 包下存放的是实体类
com.jobs.mapper 包下存放的是 Mybatis 操作数据库的接口
com.jobs.service 包下存放的是使用 Mybatis 的类库操作数据的业务方法
resources 目录下的配置文件介绍:
com.jobs.mapperXML 下的 employeeMapper.xml 是对应 com.jobs.mapper 包下接口的 sql 语句配置文件
jdbc.properties 是数据库连接参数的文件
log4j.properties 是配置 log4j 日志输出参数的文件
MyBatisConfig.xml 是 MyBatis 的核心配置文件
test 目录下的文件介绍:
com.jobs.employeeTest 类是专门用来编写 junit 单元测试方法的,用来测试 MyBatis 是否搭建成功
三、编写配置文件内容
jdbc.properties 文件配置数据库连接信息,内容如下:
driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/testdb username=root password=123456
log4j.properties 文件配置控制台日志输出的信息,内容如下:
# 输出 debug 以上的所有类型的日志信息(DEBUG INFO WARN ERROR FATAL) # stdout 配置项的名称(表明使用下面的 log4j.appender.stdout 对应的配置) log4j.rootLogger=DEBUG, stdout # log4j.appender.stdout 配置的是控制台输出 log4j.appender.stdout=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender # 该项配置表示要自定义日志显示的格式 log4j.appender.stdout.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout # 自定义日志显示格式: # %p 表示输出每条日志的级别信息(DEBUG INFO WARN ERROR FATAL) # %t 表示输出产生日志的线程的名称 # %m 表示输出具体的日志信息 # %n 表示根据当前操作系统类型,输出一个回车换行 log4j.appender.stdout.layout.ConversionPattern=%p [%t] - %m%n
MyBatisConfig.xml 文件是 MyBatis 的核心配置文件,配置内容如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!--引入MyBatis 的 DTD 约束--> <!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"> <configuration> <!--引入数据库连接的配置文件--> <properties resource="jdbc.properties"/> <!--引入 log4j 日志,方便查看运行过程中所生成的 sql 语句--> <settings> <setting name="logImpl" value="log4j"/> </settings> <!--为实体类 bean 起别名,这样就可以在 SQL 配置文件中直接使用 bean 的类名代替全限定类名--> <typeAliases> <!--如果实体类 bean 比较少的话,可以采用 typeAlias 逐个配置--> <!--<typeAlias type="com.jobs.bean.employee" alias="employee"/>--> <!--绝大多数情况下,都是直接配置实体类 bean 所在的包,这样包下所有的实体类都自动配置--> <package name="com.jobs.bean"/> </typeAliases> <!--environments 配置数据库环境,环境可以有多个。default 属性指定使用的是哪个--> <environments default="mysql"> <!--environment配置数据库环境,id属性唯一标识--> <environment id="mysql"> <!--transactionManager 事务管理,这里采用 JDBC 默认的事务--> <transactionManager type="JDBC"></transactionManager> <!--dataSource 数据源信息,这里采用连接池--> <dataSource type="POOLED"> <!--通过引入的 jdbc.properties 文件中的 key 获取数据库连接的配置信息--> <property name="driver" value="${driver}" /> <property name="url" value="${url}" /> <property name="username" value="${username}" /> <property name="password" value="${password}" /> </dataSource> </environment> </environments> <!-- mappers 引入操作数据库的接口映射配置文件 --> <mappers> <!-- 如果有多个接口映射配置文件,可以添加多个 mapper 配置--> <mapper resource="com/jobs/mapperXML/employeeMapper.xml"/> </mappers> </configuration>
四、数据库表和实体类
MySQL 数据库下创建了 testdb 数据库,里面创建了一张 employee 表,具体 SQL 语句如下:
-- 创建数据库 CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS `testdb`; USE `testdb`; -- 创建表 CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `employee` ( `e_id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `e_name` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL, `e_age` int(11) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`e_id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=7 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; -- 向表中添加数据 INSERT INTO `employee` (`e_id`, `e_name`, `e_age`) VALUES(1, '侯胖胖', 25),(2, '杨磅磅', 23), (3, '李吨吨', 33),(4, '任肥肥', 35),(5, '乔豆豆', 32);
com.jobs.bean.employee 实体类的内容如下:(这里故意让【实体类的字段】与【数据库的字段】名称不一样)
package com.jobs.bean; public class employee { //主键id private Integer id; //姓名 private String name; //年龄 private Integer age; public employee() { } public employee(Integer id, String name, Integer age) { this.id = id; this.name = name; this.age = age; } public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Integer getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age; } //方便将员工信息在控制台打印出来查看 @Override public String toString() { return "employee{" + "id=" + id + ", name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + '}'; } }
五、Mapper 接口和 SQL 配置
这里采用 Mybatis 的动态代理开发方式实现持久层的开发,这种方式是市场上各个企业普遍采用的方式。
Mapper 接口:操作数据库的接口文件
Mapper.xml:该文件为 Mapper 接口 中的每个方法,配置连接数据库后具体要执行的 SQL 语句
Mapper 接口 和 Mapper.xml 必须遵守以下开发规范:
-
Mapper.xml 文件中的 namespace 与 Mapper接口 的全限定名相同
-
Mapper 接口方法名和 Mapper.xml 中定义的每个 statement 的 id 相同
-
Mapper 接口方法的输入参数类型和 Mapper.xml 中定义的每个 sql 的 parameterType 的类型相同
-
Mapper 接口方法的输出参数类型和 mapper.xml 中定义的每个 sql 的 resultType 的类型相同
-
如果 sql 语句返回的字段名称与实体类的字段名称不一致,可以通过 resultMap 提前两者之间的字段对应关系
下面列出 com.jobs.mapper.employeeMapper 这个 Mapper 接口 的内容:
package com.jobs.mapper; import com.jobs.bean.employee; import java.util.List; public interface employeeMapper { //查询全部 List<employee> selectAll(); //根据id查询 employee selectById(Integer id); //新增数据 Integer insert(employee ele); //修改数据 Integer update(employee ele); //删除数据 Integer delete(Integer id); //根据条件查询 List<employee> selectCondition(employee ele); //根据多个id查询 List<employee> selectByIds(List<Integer> ids); }
然后列出 resources 目录下 com/jobs/mapperXML/employeeMapper.xml 这个 Mapper.xml 文件的内容:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!--MyBatis的DTD约束--> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <!--namespace 名称空间,必须配置为 Mapper 接口的全限定名--> <mapper namespace="com.jobs.mapper.employeeMapper"> <!--由于【数据库字段】与【bean实体类字段】不一致, 因此这里需要配置【数据库字段】和【bean实体类字段】的对应关系--> <resultMap id="employee_map" type="employee"> <id column="e_id" property="id" /> <result column="e_name" property="name" /> <result column="e_age" property="age" /> </resultMap> <!--配置公用的 SQL 语句,方面下面进行引用--> <sql id="select" >SELECT e_id,e_name,e_age FROM employee</sql> <!--查询全部,这里的 id 必须与 Mapper 接口中的对应的方法名称完全相同--> <!--resultMap 表示将查询结构中每条记录,封装成 employee_map 所对应的 employee 实体对象--> <select id="selectAll" resultMap="employee_map"> <!--引用上面配置的公用 SQL 语句--> <include refid="select"/> order by e_id; </select> <!--根据id查询,parameterType 表示传入的参数类型--> <select id="selectById" resultMap="employee_map" parameterType="int"> <include refid="select"/> WHERE e_id = #{id} </select> <!--新增数据,由于在 Mybatis 的核心配置文件,已经配置了 bean 的别名即为类名 因此这里可以直接使用 bean 的类名作为参数类型--> <insert id="insert" parameterType="employee"> insert into employee(e_id,e_name,e_age) VALUES (#{id},#{name},#{age}) </insert> <!--修改数据--> <update id="update" parameterType="employee"> UPDATE employee SET e_name = #{name},e_age = #{age} WHERE e_id = #{id} </update> <!--删除数据--> <delete id="delete" parameterType="int"> DELETE FROM employee WHERE e_id = #{id} </delete> <!--根据条件查询--> <select id="selectCondition" resultMap="employee_map" parameterType="employee"> <include refid="select"/> <where> <!--根据条件,动态拼接SQL语句--> <if test="id != null"> e_id = #{id} </if> <if test="name != null"> AND e_name like CONCAT('%',#{name},'%') </if> <if test="age != null"> AND e_age = #{age} </if> </where> order by e_id desc </select> <!--根据多个id查询--> <select id="selectByIds" resultMap="employee_map" parameterType="list"> <include refid="select"/> <where> <!--通过循环拼接 SQL 语句--> <foreach collection="list" open="e_id IN (" close=")" item="id" separator=","> #{id} </foreach> </where> </select> </mapper>
六、编写 Service 方法访问数据库
Service 里面的方法定义可以与 Mapper 接口中的方法不一样,这里为了方便,就保持一致了。
com.jobs.service.employeeService 的内容如下所示:
package com.jobs.service; import com.jobs.bean.employee; import com.jobs.mapper.employeeMapper; import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.util.List; public class employeeService { //查询所有 public List<employee> selectAll() { List<employee> list = null; SqlSession sqlSession = null; InputStream is = null; try { //加载核心配置文件 is = Resources.getResourceAsStream("MyBatisConfig.xml"); //获取SqlSession工厂对象 SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(is); //通过工厂对象获取SqlSession对象,openSession 的参数为 true 表示自动提交事务 //对于增删改操作,如果 openSession 为 false, //在程序代码最后需要通过 sqlSession.commit() 提交事务,才能使写操作生效 sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true); //通过动态代理获取StudentMapper接口的实现类对象 employeeMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(employeeMapper.class); //调用接口方法 list = mapper.selectAll(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (sqlSession != null) { sqlSession.close(); } if (is != null) { try { is.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } return list; } //根据id查询单个员工 public employee selectById(Integer id) { employee ele = null; SqlSession sqlSession = null; InputStream is = null; try { is = Resources.getResourceAsStream("MyBatisConfig.xml"); SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(is); sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true); employeeMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(employeeMapper.class); ele = mapper.selectById(id); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (sqlSession != null) { sqlSession.close(); } if (is != null) { try { is.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } return ele; } //新增 public Integer insert(employee ele) { Integer result = null; SqlSession sqlSession = null; InputStream is = null; try { is = Resources.getResourceAsStream("MyBatisConfig.xml"); SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(is); sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true); employeeMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(employeeMapper.class); result = mapper.insert(ele); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (sqlSession != null) { sqlSession.close(); } if (is != null) { try { is.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } return result; } //修改 public Integer update(employee ele) { Integer result = null; SqlSession sqlSession = null; InputStream is = null; try { is = Resources.getResourceAsStream("MyBatisConfig.xml"); SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(is); sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true); employeeMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(employeeMapper.class); result = mapper.update(ele); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { //6.释放资源 if (sqlSession != null) { sqlSession.close(); } if (is != null) { try { is.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } return result; } //删除 public Integer delete(Integer id) { Integer result = null; SqlSession sqlSession = null; InputStream is = null; try { is = Resources.getResourceAsStream("MyBatisConfig.xml"); SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(is); sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true); employeeMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(employeeMapper.class); result = mapper.delete(id); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (sqlSession != null) { sqlSession.close(); } if (is != null) { try { is.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } return result; } //根据条件查询 public List<employee> selectCondition(employee ele) { List<employee> list = null; SqlSession sqlSession = null; InputStream is = null; try { is = Resources.getResourceAsStream("MyBatisConfig.xml"); SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(is); sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true); employeeMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(employeeMapper.class); list = mapper.selectCondition(ele); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (sqlSession != null) { sqlSession.close(); } if (is != null) { try { is.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } return list; } //根据多个id查询 public List<employee> selectByIds(List<Integer> ids) { List<employee> list = null; SqlSession sqlSession = null; InputStream is = null; try { is = Resources.getResourceAsStream("MyBatisConfig.xml"); SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(is); sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true); employeeMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(employeeMapper.class); list = mapper.selectByIds(ids); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (sqlSession != null) { sqlSession.close(); } if (is != null) { try { is.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } return list; } }
上面有很多重复代码,有兴趣的话,可以自己进行一下封装。实际上也没有封装的必要,因为后面使用 Spring 框架集成了 MyBatis 后,上面的很多代码根本就不需要写了。
七、使用 junit 测试验证
com.jobs.employeeTest 类编写的测试方法内容如下所示:
package com.jobs; import com.jobs.bean.employee; import com.jobs.service.employeeService; import org.junit.Test; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; public class employeeTest { private employeeService service = new employeeService(); //查询全部测试 @Test public void selectAll() { List<employee> elist = service.selectAll(); for (employee ele : elist) { System.out.println(ele); } } //根据id查询测试 @Test public void selectById() { employee ele = service.selectById(3); System.out.println(ele); } //新增测试 @Test public void insert() { employee ele = new employee(6, "任天蓬", 26); Integer result = service.insert(ele); System.out.println(result); } //修改测试 @Test public void update() { employee ele = new employee(6, "任天蓬", 16); Integer result = service.update(ele); System.out.println(result); } //根据条件动态生成SQL语句查询测试 @Test public void selectCondition() { //可以同时启用多个条件,根据条件动态拼接 SQL 语句 employee ele = new employee(); //ele.setId(4); //通过 id 查询 ele.setName("任"); //通过姓名模糊查询 //ele.setAge(35); //通过年龄查询 List<employee> elelist = service.selectCondition(ele); for (employee empl : elelist) { System.out.println(empl); } } //根据多个 id 查询测试 @Test public void selectByIds() { ArrayList<Integer> ids = new ArrayList<>(List.of(1,2,3)); List<employee> elelist = service.selectByIds(ids); for (employee empl : elelist) { System.out.println(empl); } } //删除测试 @Test public void delete() { Integer result = service.delete(6); System.out.println(result); } }
OK,到此为止,已经快速介绍完毕,希望对大家有用,源代码下载地址如下:
https://files.cnblogs.com/files/blogs/699532/MybatisXmlCode.zip



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(五):向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理