java并发:线程同步机制之ThreadLocal
一、初识ThreadLocal
ThreadLocal实例通常作为静态的私有的(private static)字段出现在一个类中,这个类用来关联线程。
A、当使用ThreadLocal维护变量时,ThreadLocal为每个使用该变量的线程提供了一个独立初始化的变量副本,所以每一个线程都可以独立地改变自己的副本,而不会影响其他线程所对应的副本。
B、从线程的角度看,目标变量就像是线程的本地变量,这也是类名中Local所要表达的意思。
严格来说,ThreadLocal 并不属于多线程间的通信机制,⽽是让每个线程有⾃⼰“独⽴”的变量,线程之间互不影响。
下图展示了实际工作机制:
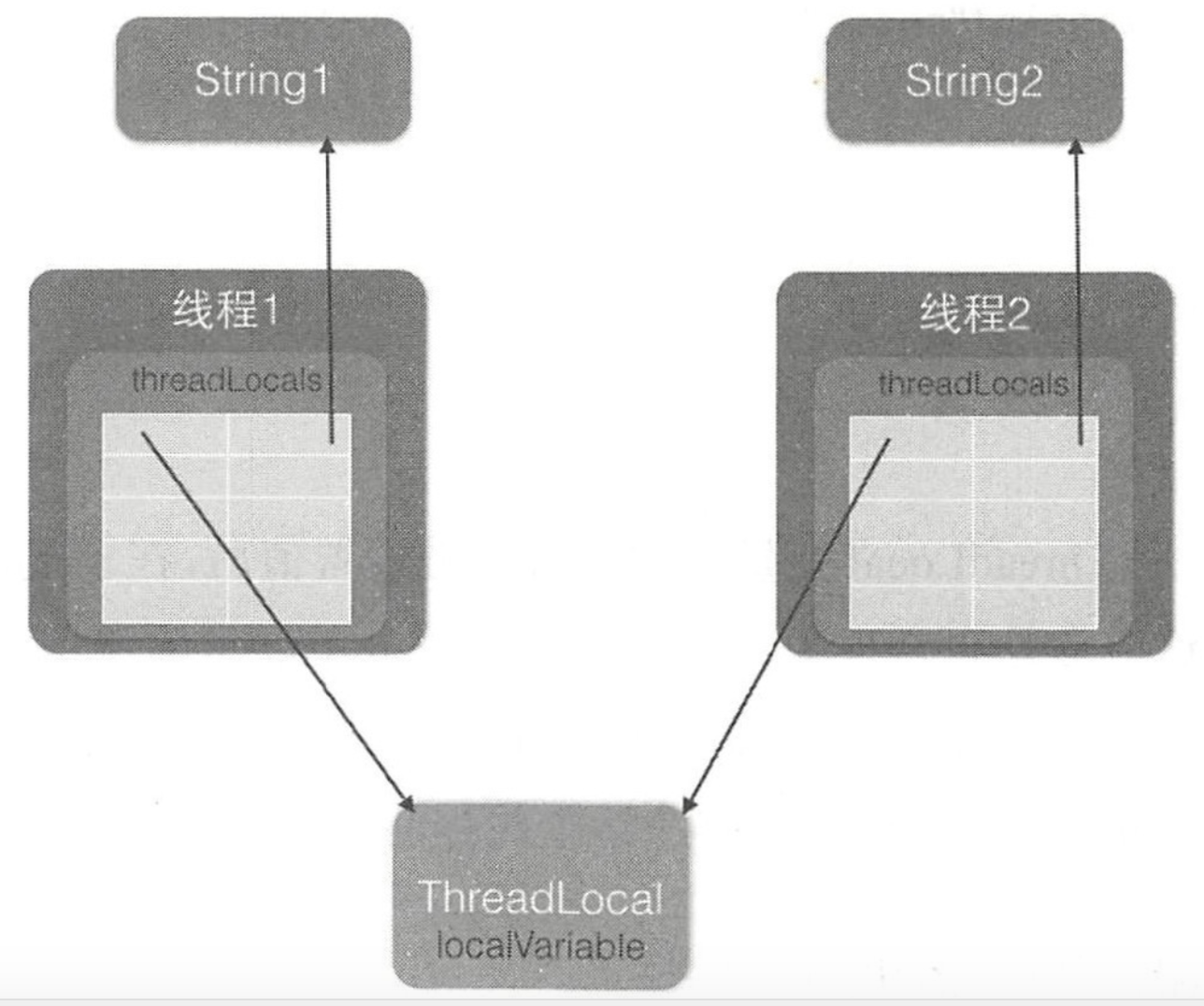
解释:
- 在每个线程内部都有一个名为 threadLocals 的成员变量
- 该变量的类型为HashMap
- 其中 key为ThreadLocal变量的this引用
- value为 set方法设置的值
ThreadLocal 内存结构
graph TB Thread1[线程1] --> ThreadLocalMap1[ThreadLocalMap] ThreadLocalMap1 --> Entry1["Entry<WeakReference, Value>"] Thread2[线程2] --> ThreadLocalMap2[ThreadLocalMap] ThreadLocalMap2 --> Entry2["Entry<WeakReference, Value>"] ThreadLocal实例 -->|弱引用| Entry1 ThreadLocal实例 -->|弱引用| Entry2
Thread定义 —— threadLocals变量

简而言之:每个线程的本地变量存放在线程自己的内存变量 threadLocals中
二、详述Threadlocal
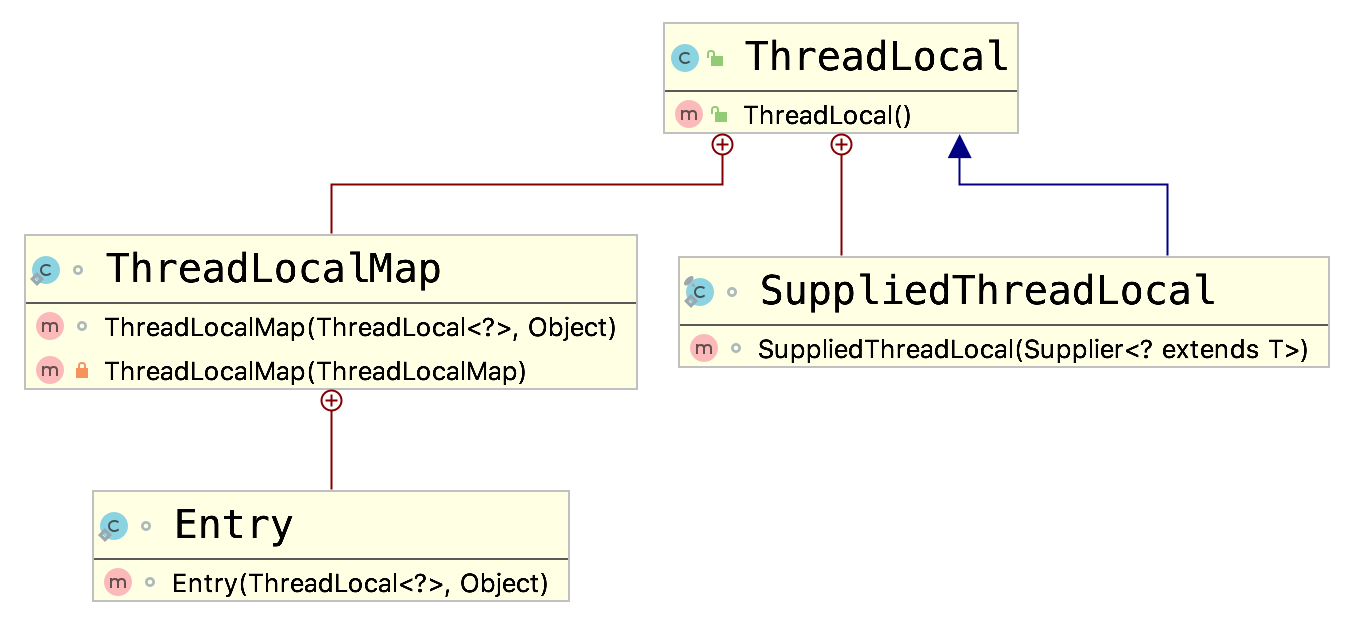
其类图如下:
ThreadLocal中的方法以及内部类如下图所示:
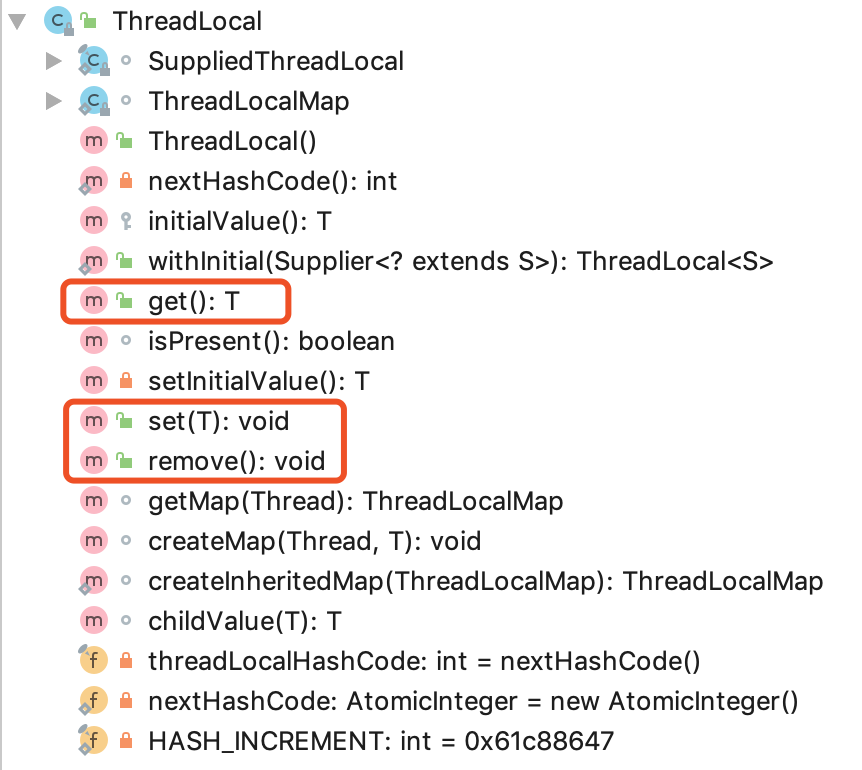
其主要方法如下:
- void set(T value)
该方法用来设置当前线程中变量的副本
- public T get()
该方法用来获取当前线程中变量的副本
- public void remove()
该方法用来移除当前线程中变量的副本,目的是为了减少内存的占用,该方法是JDK 5.0新增的方法。
需要指出的是,当线程结束以后,对应线程的局部变量将自动被垃圾回收,所以显式调用该方法清除线程的局部变量并不是必须的操作,但它可以加快内存回收的速度。
- protected T initialValue()
该方法是一个protected方法,ThreadLocal中的缺省实现直接返回一个null,一般用来重写。
ThreadLocal<SimpleDateFormat> oldWay = new ThreadLocal<>() { @Override protected SimpleDateFormat initialValue() { return new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd"); } };
Java 8+ 使用 withInitial 更简洁:
ThreadLocal<SimpleDateFormat> newWay = ThreadLocal.withInitial(() -> new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd"));
三、示例
生成线程序列号
public class ThreadId { private static final AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(0); private static final ThreadLocal<Integer> threadId = new ThreadLocal<Integer>() { @Override protected Integer initialValue() { return atomicInteger.getAndIncrement(); } }; // Returns the current thread's unique ID, assigning it if necessary public static int get() { return threadId.get(); } }
四、实现机制
(1)get()方法源码

(2)set()方法源码

(3)remove()方法源码

(4)getMap()、createMap

解读:
从源码可以看出,ThreadLocal的get、set、remove方法都是操作当前线程。
当一个线程调用 ThreadLocal 的 set 方法设置变量时,当前线程的 ThreadLocalMap 里会存放一条记录,这条记录的key为ThreadLocal的弱引用,value则为设置的值。
(5)withInitial(Supplier<? extends S> supplier)

ThreadLocal.withInitial(Supplier<? extends S> supplier) 是 Java 8 引入的静态工厂方法,用于创建带有延迟初始化功能的 ThreadLocal 变量。它通过 Supplier 函数式接口提供初始值生成逻辑,解决了传统 ThreadLocal 需要子类重写 initialValue() 的问题,代码更简洁且符合函数式编程风格。
延迟初始化(Lazy Initialization)
每个线程首次调用 get() 方法时,才会执行 supplier 生成初始值,避免提前初始化造成的资源浪费
示例:线程安全的日期格式化
private static final ThreadLocal<SimpleDateFormat> dateFormat = ThreadLocal.withInitial(() -> new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")); // 多线程环境下安全使用 String formattedDate = dateFormat.get().format(new Date());
解读:
Supplier 每次调用生成新对象(如 new SimpleDateFormat())
示例:数据库连接隔离
public class ConnectionManager { private static ThreadLocal<Connection> connectionHolder = ThreadLocal.withInitial(() -> DriverManager.getConnection(DB_URL)); public static Connection getConnection() { return connectionHolder.get(); } }
五、典型应用场景
1. 上下文信息传递(Web 框架核心)
public class UserContextHolder { private static final ThreadLocal<User> holder = new ThreadLocal<>(); public static void set(User user) { holder.set(user); } public static User get() { return holder.get(); } public static void clear() { holder.remove(); } } // 拦截器中设置 public class AuthInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor { @Override public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse res, Object handler) { User user = authenticate(req); UserContextHolder.set(user); // 绑定到当前线程 return true; } @Override public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse res, Object handler, Exception ex) { UserContextHolder.clear(); // 请求结束清理 } } // 业务层直接获取 @Service public class OrderService { public void createOrder(Order order) { User currentUser = UserContextHolder.get(); // 无需参数传递 // ... } }
解读:
在 Web 请求处理链中传递用户会话信息 —— 解决问题:多层方法调用需频繁传递上下文参数,天然支持线程安全
2. 数据库连接管理(ORM 框架基础)
场景:确保同一事务中使用相同连接
public class ConnectionManager { private static final ThreadLocal<Connection> connHolder = new ThreadLocal<>(); public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException { Connection conn = connHolder.get(); if (conn == null || conn.isClosed()) { conn = DataSource.getConnection(); connHolder.set(conn); } return conn; } public static void closeConnection() throws SQLException { Connection conn = connHolder.get(); if (conn != null) { conn.close(); connHolder.remove(); } } } // 事务管理器 public void beginTransaction() { Connection conn = ConnectionManager.getConnection(); conn.setAutoCommit(false); }
Hibernate 实际应用:
// SessionFactoryImpl.java private static final ThreadLocal<Session> threadSession = new ThreadLocal<>(); public Session getCurrentSession() { return threadSession.get(); }
3. 分布式跟踪(全链路追踪)
场景:微服务调用链传递 TraceID等
public class TraceContext { private static final ThreadLocal<String> traceIdHolder = new ThreadLocal<>(); public static void startTrace() { traceIdHolder.set(UUID.randomUUID().toString()); } public static String getTraceId() { return traceIdHolder.get(); } } // HTTP 过滤器 public class TraceFilter implements Filter { @Override public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain) { TraceContext.startTrace(); chain.doFilter(req, res); TraceContext.clear(); } } // 日志增强 @Aspect public class LogAspect { @Before("execution(* com.service..*(..))") public void log(JoinPoint jp) { MDC.put("traceId", TraceContext.getTraceId()); // 传递到日志系统 } }
4. 性能监控(线程级指标)
场景:记录单个请求的处理时间
public class PerformanceMonitor { private static final ThreadLocal<Long> startTime = new ThreadLocal<>(); public static void start() { startTime.set(System.nanoTime()); } public static void end() { long duration = System.nanoTime() - startTime.get(); log.info("Process time: {} ns", duration); startTime.remove(); } } // AOP 监控 @Aspect public class PerfAspect { @Around("execution(* com.controller..*(..))") public Object monitor(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable { PerformanceMonitor.start(); Object result = pjp.proceed(); PerformanceMonitor.end(); return result; } }
六、ThreadLocalMap
ThreadLocalMap 里面的 key 是弱依赖,在 GC 的时候被回收,但是对应的 value还是会造成内存泄漏(即 ThreadLocalMap里面存在 key为 null但 value不为 null 的Entry项)。
触发清理的时机

ThreadLocalMap 的 set、get方法可以在一些时机下对这些Entry项进行清理,但这是不及时的,也不是每次都会执行,所以在一些情况下还是会发生内存漏,因此建议在使用完毕后及时调用 remove方法。
try { threadLocal.set(resource); // 使用资源... } finally { threadLocal.remove(); // 必须手动移除! }
其他注意事项
避免存储大对象

其类图如下:
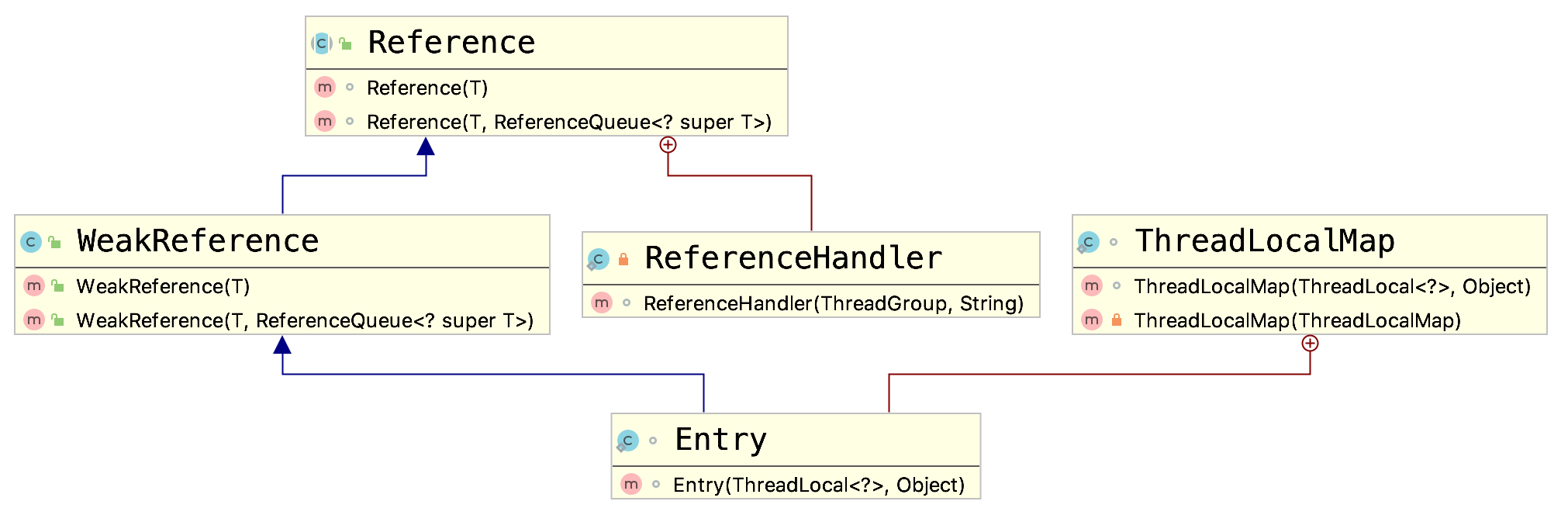
ThreadLocalMap的部分源码如下:
/** * ThreadLocalMap is a customized hash map suitable only for * maintaining thread local values. No operations are exported * outside of the ThreadLocal class. The class is package private to * allow declaration of fields in class Thread. To help deal with * very large and long-lived usages, the hash table entries use * WeakReferences for keys. However, since reference queues are not * used, stale entries are guaranteed to be removed only when * the table starts running out of space. */ static class ThreadLocalMap { /** * The entries in this hash map extend WeakReference, using * its main ref field as the key (which is always a * ThreadLocal object). Note that null keys (i.e. entry.get() * == null) mean that the key is no longer referenced, so the * entry can be expunged from table. Such entries are referred to * as "stale entries" in the code that follows. */ static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> { /** The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */ Object value; Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v) { super(k); value = v; } } /** * The initial capacity -- MUST be a power of two. */ private static final int INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16; /** * The table, resized as necessary. * table.length MUST always be a power of two. */ private Entry[] table; /** * The number of entries in the table. */ private int size = 0; /** * The next size value at which to resize. */ private int threshold; // Default to 0 /** * Set the resize threshold to maintain at worst a 2/3 load factor. */ private void setThreshold(int len) { threshold = len * 2 / 3; } /** * Increment i modulo len. */ private static int nextIndex(int i, int len) { return ((i + 1 < len) ? i + 1 : 0); } /** * Decrement i modulo len. */ private static int prevIndex(int i, int len) { return ((i - 1 >= 0) ? i - 1 : len - 1); } /** * Construct a new map initially containing (firstKey, firstValue). * ThreadLocalMaps are constructed lazily, so we only create * one when we have at least one entry to put in it. */ ThreadLocalMap(ThreadLocal<?> firstKey, Object firstValue) { table = new Entry[INITIAL_CAPACITY]; int i = firstKey.threadLocalHashCode & (INITIAL_CAPACITY - 1); table[i] = new Entry(firstKey, firstValue); size = 1; setThreshold(INITIAL_CAPACITY); } /** * Construct a new map including all Inheritable ThreadLocals * from given parent map. Called only by createInheritedMap. * * @param parentMap the map associated with parent thread. */ private ThreadLocalMap(ThreadLocalMap parentMap) { Entry[] parentTable = parentMap.table; int len = parentTable.length; setThreshold(len); table = new Entry[len]; for (int j = 0; j < len; j++) { Entry e = parentTable[j]; if (e != null) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") ThreadLocal<Object> key = (ThreadLocal<Object>) e.get(); if (key != null) { Object value = key.childValue(e.value); Entry c = new Entry(key, value); int h = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len - 1); while (table[h] != null) h = nextIndex(h, len); table[h] = c; size++; } } } }
弱引用
将key设置为弱引用

内存关系图:
graph TB Thread[线程实例] --> ThreadLocalMap ThreadLocalMap --> Entry1[Entry] ThreadLocalMap --> Entry2[Entry] Entry1 -.弱引用.-> ThreadLocalA[ThreadLocal对象] Entry1 --> ValueA[强引用:存储的值] Entry2 -.弱引用.-> ThreadLocalB[ThreadLocal对象] Entry2 --> ValueB[强引用:存储的值]
补充:强引用、弱引用的核心特性
强引用:只要存在强引用,对象永不回收(常见对象引用方式)
弱引用:当 JVM 执行垃圾回收时,无论内存是否充足,被弱引用指向的对象都会被回收
当外部强引用消失时:
ThreadLocal 实例仅被弱引用持有
GC 发生时,ThreadLocal 对象被回收
Entry 的 key 变为 null
后续 ThreadLocalMap 操作(set/get/remove)会清理 key 为 null 的 Entry
其他
此处重点关注一下ThreadLocalMap中的几个成员变量及方法
(1)private Entry[] table;
table是一个Entry类型的数组,该变量在ThreadLocalMap的构造函数中初始化
Entry是ThreadLocalMap的一个内部类
(2)set()方法
/** * Set the value associated with key. * * @param key the thread local object * @param value the value to be set */ private void set(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value) { // We don't use a fast path as with get() because it is at // least as common to use set() to create new entries as // it is to replace existing ones, in which case, a fast // path would fail more often than not. Entry[] tab = table; int len = tab.length; int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1); for (Entry e = tab[i]; e != null; e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) { ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get(); if (k == key) { e.value = value; return; } if (k == null) { replaceStaleEntry(key, value, i); return; } } tab[i] = new Entry(key, value); int sz = ++size; if (!cleanSomeSlots(i, sz) && sz >= threshold) rehash(); }
(3)getEntry()方法
/** * Get the entry associated with key. This method * itself handles only the fast path: a direct hit of existing * key. It otherwise relays to getEntryAfterMiss. This is * designed to maximize performance for direct hits, in part * by making this method readily inlinable. * * @param key the thread local object * @return the entry associated with key, or null if no such */ private Entry getEntry(ThreadLocal<?> key) { int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (table.length - 1); Entry e = table[i]; if (e != null && e.get() == key) return e; else return getEntryAfterMiss(key, i, e); } /** * Version of getEntry method for use when key is not found in * its direct hash slot. * * @param key the thread local object * @param i the table index for key's hash code * @param e the entry at table[i] * @return the entry associated with key, or null if no such */ private Entry getEntryAfterMiss(ThreadLocal<?> key, int i, Entry e) { Entry[] tab = table; int len = tab.length; while (e != null) { ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get(); if (k == key) return e; if (k == null) expungeStaleEntry(i); else i = nextIndex(i, len); e = tab[i]; } return null; }
(4)remove()方法
/** * Remove the entry for key. */ private void remove(ThreadLocal<?> key) { Entry[] tab = table; int len = tab.length; int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1); for (Entry e = tab[i]; e != null; e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) { if (e.get() == key) { e.clear(); expungeStaleEntry(i); return; } } }
七、总结
ThreadLocal 是构建高并发系统的关键基础设施,合理应用可大幅提升代码质量和性能。
ThreadLocal 一般都是声明在静态变量中,如果不断地创建ThreadLocal而没有调用其remove方法,将导致内存泄露,特别是在高并发的Web容器当中。
// 静态保证只有一个ThreadLocal引用 private static final ThreadLocal<DateFormat> formatHolder = ThreadLocal.withInitial(SimpleDateFormat::new);
ThreadLocal在处理线程的局部变量时比synchronized同步机制更简单,更方便,且拥有更高的并发性。
性能优势:
(1)无竞争访问:线程直接操作专属存储区
(2)线性扩展:线程增长时吞吐量近线性提升
ThreadLocal 在线程隔离数据场景下比 synchronized 更简单、更高效,但需明确其适用边界;当需要维护跨线程共享状态的一致性时,synchronized 或 CAS 操作仍是必要选择。
现代 Java 开发中,应根据场景组合使用:
线程隔离:优先考虑 ThreadLocal 或 ScopedValue
共享修改:采用 synchronized 或 VarHandle
高并发计数:使用 LongAdder



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号