AQS总结
java并发编程核心JUC,JUC的核心是AQS,而AQS的核心是Unsafe使用的CAS(compare and swap)。
AQS全称:AbstractQuenedSynchronizer抽象的队列式同步器。
AQS定义了一套多线程访问共享资源的同步器框架,许多同步类实现都依赖于它。如:ReentrantLock/Semaphore/CountDownLatch...。
大白话,AQS就是基于CLH队列,用volatile修饰共享变量state,线程通过CAS去改变状态符,成功则获取锁成功,失败则进入等待队列,等待被唤醒。
深入理解,多线程访问共享资源涉及步骤(ReentrantLock为例):
抢锁
// 尝试获取锁 成功返回true,失败返回false
// 失败则进行入队操作
public final void acquire(int arg) {
if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))
selfInterrupt();
}
// 公平锁与非公平锁实现不同 公平锁
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
// 判断是否已锁
if (c == 0) {
// 是否有队列有队列直接返回false 抢锁失败
// cas抢锁,抢锁成功设置当前线程
if (!hasQueuedPredecessors() &&
compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
// 重入锁
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 非公平锁直接强锁
final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
// 判断是否已锁
if (c == 0) {
if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
// 重入锁
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0) // overflow
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
入队
// 入队前先创建节点
if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))
selfInterrupt();
// 创建节点
private Node addWaiter(Node mode) {
Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode);
// Try the fast path of enq; backup to full enq on failure
Node pred = tail;
// 尾节点存在 证明队列存在 直接放入队列尾部
if (pred != null) {
node.prev = pred;
if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) {
pred.next = node;
return node;
}
}
//
enq(node);
return node;
}
// 队列不存在情况 创建两个节点,头结点作为 当前持有锁的节点
private Node enq(final Node node) {
for (;;) {
Node t = tail;
if (t == null) { // Must initialize
if (compareAndSetHead(new Node()))
tail = head;
} else {
node.prev = t;
if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) {
t.next = node;
return t;
}
}
}
}
// 入队操作:总结就是我是下一个头结点就跳出循环 否则一直循环等待我是下一个头结点
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
boolean failed = true; // 入队失败标记
try {
boolean interrupted = false;// 中断标记
// 自旋
for (;;) {
// 当前节点的前节点是头结点证明直接下一个就能轮到他 进行获取锁,点尝试获取锁,获取成功把自己设置为头节点,之前的头结点需要GC回收
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return interrupted;
}
// 不是下一个要处理的节点,就通过park()进入等待状态。直到被唤醒
// 如果自己可以休息了,就通过park()进入waiting状态,直到被unpark()。如果不可中断的情况下被中断了,那么会从park()中醒过来,发现拿不到资源,从而继续进入park()等待。
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
// 设置自己等待waiting 如果
private static boolean shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(Node pred, Node node) {
int ws = pred.waitStatus; // 等待标记
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL) // 前节点 正处于等待标记(停止休息)
/*
* This node has already set status asking a release
* to signal it, so it can safely park.
*/
return true;
if (ws > 0) { // 标识前节点取消或者放弃获取锁
/*
* Predecessor was cancelled. Skip over predecessors and indicate retry.
* 如果前节点放弃了,那就一直往前找,直到找到最近一个正常等待的状态,并排在它的后边。
* 注意:那些放弃的结点,由于被自己“加塞”到它们前边,它们相当于形成一个无引用链,稍后就会被保安大叔赶走了(GC回收)!
*/
do {
node.prev = pred = pred.prev;
} while (pred.waitStatus > 0);
pred.next = node;
} else {
/*
* waitStatus must be 0 or PROPAGATE. Indicate that we
* need a signal, but don't park yet. Caller will need to
* retry to make sure it cannot acquire before parking.
* 如果前节点正常,那就把前节点的状态设置成SIGNAL,告诉它拿完号后通知自己一下。有可能失败,人家说不定刚刚释放完呢!
*/
compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL);
}
return false;
}
// 真正处于等待状态
private final boolean parkAndCheckInterrupt() {
LockSupport.park(this); // 调用park()使线程进入waiting状态
return Thread.interrupted();
}

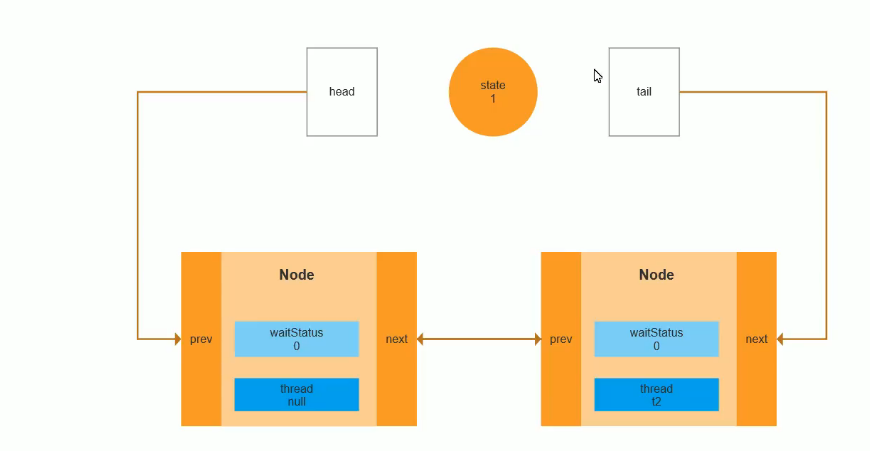
释放锁
// 释放锁
public void unlock() {
sync.release(1);
}
// 先进行状态修改再进行头节点的下一个节点唤醒操作
public final boolean release(int arg) {
if (tryRelease(arg)) {
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0)
unparkSuccessor(h);
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 锁状态设置为 状态 - 1(重入锁多次释放)
protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) {
int c = getState() - releases;
if (Thread.currentThread() != getExclusiveOwnerThread())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
boolean free = false;
if (c == 0) {
free = true;
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
}
setState(c);
return free;
}
// waitStatus头结点等待设置为0 头节点的下一个节点unpark 被唤醒。
private void unparkSuccessor(Node node) {
/*
* If status is negative (i.e., possibly needing signal) try
* to clear in anticipation of signalling. It is OK if this
* fails or if status is changed by waiting thread.
*/
int ws = node.waitStatus;
if (ws < 0)
compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, ws, 0);
/*
* Thread to unpark is held in successor, which is normally
* just the next node. But if cancelled or apparently null,
* traverse backwards from tail to find the actual
* non-cancelled successor.
*/
Node s = node.next;
if (s == null || s.waitStatus > 0) {
s = null;
for (Node t = tail; t != null && t != node; t = t.prev)
if (t.waitStatus <= 0)
s = t;
}
if (s != null)
LockSupport.unpark(s.thread);
}
出队
// 出队在 入队操作时 发现当前节点的头结点 并能成功抢锁 则头结点出队。p.next = null; // help GC
唤醒
// 锁释放头结点的下一个节点被唤醒。





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本
· C#/.NET/.NET Core优秀项目和框架2025年2月简报
· Manus爆火,是硬核还是营销?
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下
· 【杭电多校比赛记录】2025“钉耙编程”中国大学生算法设计春季联赛(1)