XML 5—— Schema
- 理解Schema的数据类型
- 理解Schema的元素类型
- 理解验证与约束
-
Schema(模式),其作用与dtd一样,也是用于验证XML文档的有效性,只不过它提供了比dtd更强大的功能和更细粒度的数据类型,另外Schema还可以自定义数据类型。此外,Schema是一个XML文件,而dtd不是。
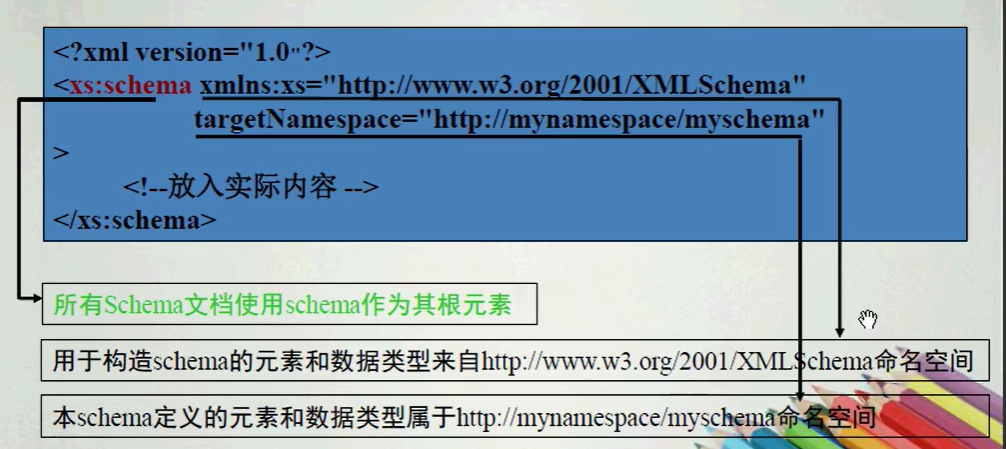
- 所有的Schema文档其根元素必须叫做Schema。
- SimpleType 与 ComplexType的区别
- SimpleType类型的元素没有子元素,也没有属性。
- 当需要定义的元素包含了子元素或者属性时,必须要使用ComplexType。
- SimpleContent,用于 ComplexType元素上,用于限定该ComplexType的内容类型,表示该ComplexType没有子元素,同时该ComplexType需要有属性,否则它就成为SimpleType了。
- 通过DOCTYPE 可以明确指定文档的根元素,因为DOCTYPE后面跟的元素就是文档的根元素;通过Schema是没法明确指定目标XML文档的根元素,XmlSpy是通过推断哪个元素包含了其他元素来选择包含其他元素最多的那个元素作为文档的根,但我们可以明确指定文档的根元素而不必按照XmlSpy的生成来做。
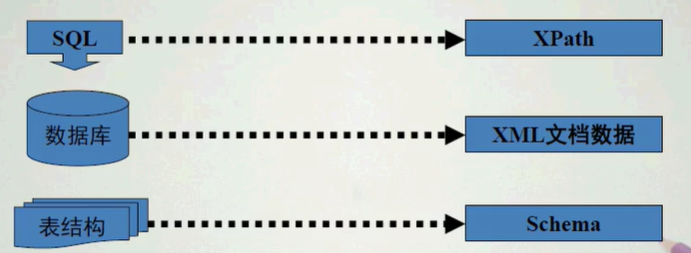
- XML Schema是用一套预先规定的XML元素和属性创建的,这些元素和属性定义了XML文档的结构和内容模式。
- XML Schema规定XML文档实例的结构和每个元素/属性的数据类型。

DTD vs Schema
- DTD的局限性
- DTD不遵守XML语法(写XML文档实例时候用一种语法,写DTD的时候用另外一种语法)
- DTD数据类型有限(与数据库数据类型不一致)
- DTD不可扩展
- DTD不支持命名空间(命名冲突)
- Schema的新特性
- Schema基于XML语法
- Schema可以用能处理XML文档的工具处理
- Schema大大扩充了数据类型,可以自定义数据类型
- Schema支持元素的继承——Object-Oriented'
- Schema支持属性组
Schema的数据类型
- 简单类型
- 内置的数据类型(built-in datatypes)
- 基本的数据类型
-
数据类型 描述 string 表示字符串 boolean 布尔型 decimal 代表特定精度的数字 float 代表单精度32位浮点数 double 代表双精度64为浮点数 duration 代表持续时间 dateTime 代表特定时间 time 代表特定时间,但是是每天重复的 date 代表日期 hexBinary 代表十六进制数 anyURI 代表一个URI,用来定位文件 NOTATION 代表NOTATION类型
-
- 扩展的数据类型
-
数据类型 描述 ID 用于唯一标识元素 IDREF 参考ID类型的元素或属性 ENTITY 实体类型 NMTOKEN NMTOKEN类型 NMTOKENS NMTOKEN类型集 long 表示整型数,大小介于-9223372036854775808和9223372036854775807之间 int 表示整型数,大小介于-2147483648和2147483647之间 short 表示整型数,大小介于-32768和32767之间 byte 表示整型数,大小介于-128和127之间
-
- 基本的数据类型
- 用户自定义数据类型(通过simpleType定义)
- 内置的数据类型(built-in datatypes)
- 复杂类型(通过complexType定义)
Schema的数据类型的特性
| 特性 | 描述 |
| enumeration | 在制定的数据集中选择,限定用户的选值 |
| fractionDigits | 限定最大的小数位,用于控制精度 |
| length | 指定数据的长度 |
| maxExclusive | 指定数据的最大值(小于) |
| maxInclusive | 指定数据的最大值(小于等于) |
| maxLength | 指定长度的最大值 |
| minExclusive | 指定最小值(大于) |
| minInclusive | 指定最小值(大于等于) |
| minLength | 指定最小长度 |
| Pattern | 指定数据的显示规范 |
Schema的元素类型
- schema
- 作用:包含已经定义的schema
- 用法:<xs:schema>
- 属性:
- xmlns
- targetNamespace
- element
- 作用:声明一个元素
- 属性
- name
- type
- tef
- minOccurs
- maxOccurs
- substitutionGroup
- fixed
- default
- 示例
-
<xs:element name="cat" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:element name="dog" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:element name="pets"> <xs:complexType> <xs:sequence minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded"> <xs:element ref="cat"/> <xs:element ref="dog"/> </xs:sequence> </xs:complexType> </xs:element>
-
- attribute
- 作用:声明一个属性
- 属性:name/type/ref/use
- 示例:
-
<xs:complexType name="myComplexType"> <xs:attribute name="mnybaseattribute" type="xs:string" use="required"/> </xs:complexType>
-
- group
- 作用:把一组元素声明组合在一起,以便他们能够一起被复合类型应用
- 属性:name/ref
- 示例
-
<xs:element name="thing1" type="xs:string"/> <xs:element name="thing2" type="xs:string"/> <xs:attribute name="myAttribute" type="xs:decimal"/> <xs:group name="myGroupOfThings> <xs:sequence> <xs:element ref="thing1"/> <xs:element ref="thing2"> </xs:sequence> </xs:group> <xs:complexType name="myComplexType"> <xs:group ref="myGroupbfThings"/> <xs:attribute ref="myAttribute"/> </xs:complexType>
-
- attributeGroup
- 作用:把一组属性声明组合在一起,以便可以被复合类型应用
- 属性:name/ref
- 示例
-
<xs:attributeGroup name="myAttributeGroup"> <xs:attribute name="someatfributel" type="xs:integer"/> <xs:attribute name="someattribute2" type="xs:string"/> </xs:aftribnteGroup> <xs:complexType name="myElementType"> <xs:attributeGroup ref="myAttributeGroup"/> </xs:complexType>
-
- simpleType
- 作用:定义 一个简单类型,它决定了元素和属性值的约束和相关信息
- 属性:name
- 内容:应用已经存在的简单类型,三种方式
- restriction,限定一个范围,定义一个约束条件
-
<xs:simpleType name="freezeboilrangeInteger"> <xs:restriction base="xs:integer"> <xs:minEnclusive value="0"/> <xs:maxInclusive value="100"/> </xs:restriction> </xs:simpleType>
-
- list,从一个特定数据类型的集合中选择定义一个简单类型元素
-
<xs:simpleType name="listOfDates"> <xs:list itemType="xs:date"/> </xs:simpleType>
-
- union,从一个特定数据类型的集合中选择定义一个简单类型元素
-
<xs:schema xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"> <xs:attribute name="allframesize"> <xs:simpleType> <xs:union> <xs:simpleType> <xs:restriction base="roadbikesize"/> </xs:simpleType> <xs:simpleType> <xs:restriction base="mountainbikesize/> </ xs:simpleType> </xs:union> </xs:simpleType> </xs:attribute> </xs:schema>
-
- restriction,限定一个范围,定义一个约束条件
- simpleContent
- 作用:应用于complexType,对它的内容进行约束和扩展
- 示例
-
<xs:element name="shoeSize"> <xs:complexType> <xs:simpleContent>(元素下不包括子元素) <xs:extension base="xs:decimal"> <xs:attribute name="sizing"> <xs:simpleType> <xs:restriction base="xs:string"> <xs:enumeration value="US"/> <xs:enumeration value="European"/> <xs:enumeration value="UK"/> </xs:restriction> </xs:simpleType> </xs:attribute> </xs:extension> </xs:simpleContent> </xs:complexType> </xs:element>
-
- complexType
- 作用:定义一个复合类型,它决定了一组元素和属性值的约束和相关信息
- 属性:name
- 示例
-
<xs:complexType name="internationalShoeSize"> <xs:simpleContent> <xs:extension base="xs:decimal"> <xs:attribute name="sizing" type="xs:string"/> </xs:extension> </xs:simpleContent> </xs:complexType> <xs:element name="myShoeSize" type="internatiomalShoeSize"/>
-
-
complexType与simpleType区别
-
simpleType类型的元素中不能包含元素或者属性。
-
当需要声明一个元素的子元素和/或属性时,用complexType。
-
当需要基于内置的基本数据类型定义一个新的数据类型时,用simpleType。
-
- choice
- 允许唯一的一个元素从一个组中被选择
- 属性:minOccurs/maxOccurs
- 示例:
-
<xs:complexType name="chadState"> <xs:choice minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="1"> <xs:element ref="selected"/> <xs:element ref="unselected"/> <xs:element ref="dimpled"/> <xs:element ref="perforated"/> </xs:choice> <xs:attribute name="candidate" type='candidatelype"/> </xs:complexType>
-
- unique
- sequence
- 作用:给一组元素一个特定的序列
- 示例
-
<xs:element name="zooAnimals"> <xs:complexType> <xs:sequence minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded"> <xs:element name="elephant"/> <xs:element name="bear"/> <xs:element name="giraffe"/> </xs:sequence> </xs:complexType> </xs:element>
-
转载请注明出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/stu-jyj3621


