HTTPD之二---HTTPD服务详解——httpd的配置文件常见设置
HTTP服务器应用
http服务器程序
httpd apache nginx lighttpd
应用程序服务器
IIS .asp tomcat .jsp jetty 开源的servlet容器,基于Java的web容器 Resin CAUCHO公司,支持servlets和jsp的引擎 webshpere(IBM), weblogic(BEA), jboss,oc4j(Oracle)
市场占有率统计
www.netcraft.com
Httpd介绍
特性:
高度模块化:core + modules DSO: Dynamic Shared Object 动态加/卸载 MPM:multi-processing module多路处理模块
MPM工作模式
prefork:多进程I/O模型,每个进程响应一个请求,默认模型
一个主进程:生成和回收n个子进程,创建套接字,不响应请求 多个子进程:工作work进程,每个子进程处理一个请求;系统初始时,预先生成多个空闲进程,等待请求,最大不超过1024个
worker:复用的多进程I/O模型,多进程多线程,IIS使用此模型
一个主进程:生成m个子进程,每个子进程负责生个n个线程,每个线程响应一个请求,并发响应请求:m*n
event:事件驱动模型(worker模型的变种)
一个主进程:生成m个子进程,每个进程直接响应n个请求,并发响应请求:m*n,有专门的线程来管理这些keep-alive类型的线程,当有真实请求时,将请求传递给服务线程,执行完毕后,又允许释放。这样增强了高并发场景下的请求处理能力
httpd-2.2:event 测试版,centos6默认
httpd-2.4:event 稳定版,centos7默认
prefork MPM

worker MPM

event MPM

进程角色

httpd功能特性
1> 虚拟主机
IP、Port、FQDN
2> CGI:Common Gateway Interface,通用网关接口
3> 反向代理
4> 负载均衡
5> 路径别名
6> 丰富的用户认证机制
basic
digest
7> 支持第三方模块
httpd-2.4新特性
MPM支持运行为DSO机制;以模块形式按需加载 event MPM生产环境可用 异步读写机制 支持每模块及每目录的单独日志级别定义 每请求相关的专用配置 增强版的表达式分析式 毫秒级持久连接时长定义 基于FQDN的虚拟主机不需要NameVirutalHost指令 新指令,AllowOverrideList 支持用户自定义变量 更低的内存消耗
Httpd 安装
安装方式:
rpm:centos发行版,稳定,建议使用 编译:定制或特殊需求
安装httpd并启动服务:
yum install httpd -y systemctl start httpd
CentOS 7程序环境:httpd-2.4
配置文件:
/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf /etc/httpd/conf.d/*.conf
检查配置语法:
httpd –t
服务单元文件: /usr/lib/systemd/system/httpd.service
配置文件:/etc/sysconfig/httpd
服务控制和启动:
systemctl enable|disable httpd.service
systemctl {start|stop|restart|status} httpd.service
站点网页文档根目录:
/var/www/html
模块文件路径:
/etc/httpd/modules /usr/lib64/httpd/modules
主程序文件:
/usr/sbin/httpd
主进程文件:
/etc/httpd/run/httpd.pid
日志文件目录:
/var/log/httpd access_log: 访问日志 error_log:错误日志
安装帮助文档包:
yum isntall httpd-manual -y
注意:安装完帮助手册之后,重启httpd服务,没有网络也可以在网上输入指定的IP地址加manual手册就可以查看帮助手册。
示例:192.168.34.100/manual

Httpd 常见配置
httpd配置文件的组成:
主要组成
Global Environment Main server configuration virtual host
配置格式:directive value
directive 不区分字符大小写 value 为路径时,是否区分大小写,取决于文件系统
官方帮助
http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.4/
(2)httpd 配置文件的组成:修改前先备份,养成好习惯
vim /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
为了避免配置文件比较混乱,可以新建一个测试文件单独存放写入的配置文件信息即可
vim /etc/httpd/conf.d/testconf ServerTokens Prod systemcl relaod httpd 重新加载httpd服务
测试显示信息结果
[root@centos7html]#curl -I http://192.168.34.100/ HTTP/1.1 403 Forbidden Date: Wed, 27 Nov 2019 13:04:46 GMT Server: Apache 可以看到此时只是显示apache头部 Last-Modified: Thu, 16 Oct 2014 13:20:58 GMT ETag: "1321-5058a1e728280" Accept-Ranges: bytes Content-Length: 4897 Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8

配置文件在的设置 首部显示的信息
ServerTokens Major|Minor|Min[imal]|Prod[uctOnly]|OS|Full
ServerTokens Prod[uctOnly] : Server: Apache
ServerTokens Major: Server: Apache/2
ServerTokens Minor: Server: Apache/2.0
ServerTokens Min[imal]: Server: Apache/2.0.41
ServerTokens OS: Server: Apache/2.0.41 (Unix)
ServerTokens Full (or not specified): Server: Apache/2.0.41 (Unix) PHP/4.2.2 MyMod/1.2
This setting applies to the entire server and cannot be enabled or disabled on a virtualhost-by-virtualhost basis.
After version 2.0.44, this directive also controls the information presented by the ServerSignature directive.
建议使用:ServerTokens Prod 越详细越不安全

修改监听的IP和Port
Listen [IP:]PORT
(1) 省略IP表示为本机所有IP
(2) Listen指令至少一个,可重复出现多次
Listen 80 Listen 8080
示例:
Listen 192.168.1.100:8080 Lsten 80
指定固定的IP地址和监听端口固定绑定
vim /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf Listen 192.168.34.100:9527 监听指定的IP地址和端口号

在/var/www/html目录下创建一个index.html文件
![]()
在另外一个终端监听,此时就必须指定IP地址和端口号才能监听到具体的内容

持久连接
Persistent Connection:连接建立,每个资源获取完成后不会断开连接,而是继续等待其它的请求完成,默认关闭持久连接 断开条件:时间限制:以秒为单位, 默认5s,httpd-2.4 支持毫秒级 副作用:对并发访问量大的服务器,持久连接会使有些请求得不到响应 折衷:使用较短的持久连接时间
设置:KeepAlive On|Off 默认支持长久连接
KeepAliveTimeout 15 默认是以s为单位,断开时长
测试:telnet WEB_SERVER_IP PORT
GET /URL HTTP/1.1 Host: WEB_SERVER_IP
开始验证断开时长情况:
vim /etc/httpd/conf.d/test.conf KeepAliveTimeout 15 设置断开时长为15s systemctl reload httpd 重新加载httpd

此时在另一个主机上连接配置好的连接超时时长机器,连接超过15s之后就会自定断开
[root@centos777~]#telnet 192.168.34.100 80 Trying 192.168.34.100... Connected to 192.168.34.100. Escape character is '^]'. GET /index.html HTTP/1.1 HOST: 1.1.1.1
MPM( Multi-Processing Module)多路处理模块
prefork, worker, event
切换使用的MPM,默认使用prefork模块较多
vim /etc/httpd/conf.modules.d/00-mpm.conf
启用要启用的MPM相关的LoadModule指令即可
查看静态编译的模块
httpd -l
查看静态编译及动态装载的模块
httpd –M
动态模块加载:不需重启即生效
动态模块路径
/usr/lib64/httpd/modules/
修改模块配置,只需要将前面的注释去掉,重启httpd服务,就可以使用当前的模块:
vim /etc/httpd/conf.modules.d/00-mpm.conf

prefork的配置:
StartServers 8 # 一开始启动服务时有8个进程 MinSpareServers 5 # 最小空闲进程 MaxSpareServers 20 # 最大空闲进程 ServerLimit 256 # 最多进程数,最大20000 MaxRequestsPerChild 4000 # 子进程最多能处理的请求数量。在处理MaxRequestsPerChild 个请求之后,子进程将会被父进程终止,这时候子进程占用的内存就会释放(为0时永远不释放) MaxClients 256 # 最大并发数
修改httpd的include包含的以*.conf结尾的配置文件,防止与主配置文件混乱,限制进程数与并发数,设置情况需要根据生产环境进行设置,设置完之后重启httpd服务:systemctl restart httpd
[root@centos7 ~]# vim /etc/httpd/conf.d/test.conf StartServers 8 MinSpareServers 5 MaxSpareServers 20 ServerLimit 256 MaxClients 256 MaxRequestsPerChild 4000
worker的配置:
ServerLimit 16 最多线程数 StartServers 2 一开始准备2个线程 MaxRequestWorkers 150 最大处理请求数量 MinSpareThreads 25 最小空闲进程 MaxSpareThreads 75 最大空闲进程 ThreadsPerChild 25 每个子线程的25个最大线程
与上面的prefork配置同理,需要开启work模块,并设置work模块的最大线程与进程,限制大小可以根据实际生产环境进行设置。
[root@centos7 ~]# vim /etc/httpd/conf.d/test.conf ServerLimit 16 StartServers 2 MaxRequestWorkers 150 MinSpareThreads 25 MaxSpareThreads 75 ThreadsPerChild 25
DSO: Dynamic Shared Object
加载动态模块配置
/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf Include conf.modules.d/*.conf
配置指定实现模块加载格式:
LoadModule <mod_name> <mod_path>
模块文件路径可使用相对路径:相对于ServerRoot(默认/etc/httpd)
示例:
LoadModule auth_basic_module modules/mod_auth_basic.so
演示:
如果不想让此LoadModule auth_basic_module模块不再生效,直接在配置文件中注释掉此模块即可
[root@centos7~]#cd /etc/httpd/conf.modules.d [root@centos7conf.modules.d]#ls 00-base.conf 00-dav.conf 00-lua.conf 00-mpm.conf 00-proxy.conf 00-systemd.conf 01-cgi.conf [root@centos7conf.modules.d]#vim 00-base.conf 在此配置文件中修改配置文件
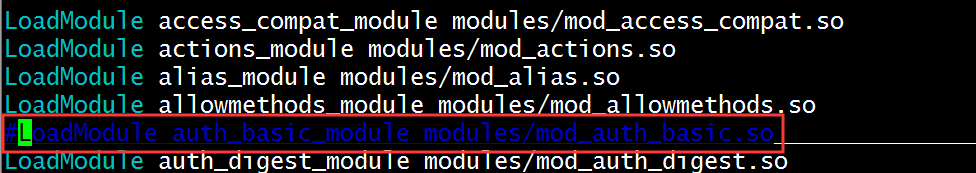
由于已经被注释掉,此时已经搜不到此模块信息:
httpd -M |grep basic

再将配置文件中的模块再修改回去,此时再验证结果
vim /etc/httpd/conf.modules.d/00-base.conf,将要启用的模块的#去掉即可,此时已经能查看到当前的模块

定义'Main' server的文档页面路径
DocumentRoot “/path”
文档路径映射:
DocumentRoot指向的路径为URL路径的起始位置
示例:
DocumentRoot "/app/data“ http://HOST:PORT/test/index.html --> /app/data/test/index.html
注意:SELinux和iptables的状态
练习:
新建一个/data/www目录,将访问的网站页面是此目录,我们怎么去修改呢?
[root@centos7data]#mkdir /data/www [root@centos7data]#cp /var/www/html/index.html /data/www/ [root@centos7 ~]# echo welcome to beijing > /data/www/index.html
修改定义文件格式,将文件格式可以写入到临时的文件中,在include包含的*.conf配置文件中指定新的访问网页路径,不需要注释掉httpd默认的主配置文件的/var/www/html/目录,默认会优先访问新创建的目录路径
[root@centos7conf.modules.d]#vim /etc/httpd/conf.d/test.conf DocumentRoot "/data/www" <Directory "/data/www"> Require all granted </Directory>

修改完之后重新启动httpd服务
systemctl restart httpd
此时可以通过/data/html访问页面。

定义站点主页面
搜索:/DirectoryIndex
格式:DirectoryIndex index.html index.html.var
分析:
查询http://192.168.30.106/ 及其子目录时,不指定文件,可以默认打开目录下的index.html文件
在配置文件中默认的模块语句,优先使用index.html文件
vim /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
<IfModule dir_module>
DirectoryIndex index.html
</IfModule>

如果将baidu.html写在index.html上面,此时的优先级高于index.html文件,优先访问的就是baidu.html

子配置文件 /etc/httpd/conf.d/welcome.conf 的welcome.conf不是以conf结尾的文件,且将/var/www/html/目录下的index.html文件移动到别的目录下,此时访问页面时就会报错

[root@centos7conf.d]#mv welcome.conf welcome.conf.bak 将配置文件改名 [root@centos7conf.d]#systemctl restart httpd [root@centos7data]#mv /var/www/html/index.html /data/ 将index.html文件移动到data目录下
重启httpd服务:systemctl restart httpd
报错页面,此时被拒绝访问:

站点访问控制常见机制
可基于两种机制指明对哪些资源进行何种访问控制访问控制机制有两种:客户端来源地址,用户账号
文件系统路径:
<Directory “/path"> ... </Directory> <File “/path/file”> ... </File> <FileMatch "PATTERN"> ... </FileMatch>
URL路径:支持正则,通配符
<Location ""> ... </Location> <LocationMatch ""> ... </LocationMatch>
示例:
<FilesMatch "\.(gif|jpe?g|png)$"> <Files “?at.*”> 通配符 <Location /status> <LocationMatch "/(extra|special)/data">
<Directory>中“基于源地址”实现访问控制
(1) Options:后跟1个或多个以空白字符分隔的选项列表,可在总配置文件中修改,也可从创建一个自配置文件中修改设置
在选项前的+,- 表示增加或删除指定选项
常见选项:
Indexes:指明的URL路径下不存在与定义的主页面资源相符的资源文件时,返回索引列表给用户 FollowSymLinks:允许访问符号链接文件所指向的源文件 None:全部禁用 All: 全部允许
在新建的文件夹中进行设置/etc/httpd/conf.d/test.conf
vim /etc/httpd/conf.d/test.conf
<directory /data/www> options indexes 指明URL路径下部存在于定义的主页面资源相符的资源文件时,返回列表给用户 Require all granted </directory>

配置文件中指明要访问的文件路径:vim /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf

将/etc/httpd/conf.d/welcome.conf的配置文件进行修改并重启httpd服务,然后再网页访问,此时就可以显示文件列表信息:
[root@centos7html]#cd /etc/httpd/conf.d [root@centos7conf.d]#ls autoindex.conf manual.conf README test.conf userdir.conf welcome.conf [root@centos7conf.d]#mv welcome.conf welcome.conf.bak [root@centos7conf.d]#systemctl restart httpd
显示效果:

(2)FollowSymLinks:允许访问符号链接文件所指向的源文件
[root@centos7conf.d]#cd /data/www [root@centos7www]#ls baidu.html index.html.bak shenzhen.html [root@centos7www]#ln -s /etc etcdir 将etc创建一个软连接,软连接名为etcdir
在新建的文件中修改配置文件,允许访问软连接的源文件
vim /etc/httpd/conf.d/test.conf <directory /data/www> options indexes FollowSymLinks 允许访问软连接的源文件 Require all granted </directory>
重启httpd服务
systemctl restart httpd
在网页上查看效果,此时可以看到etcdir软链接到etc下的文件:


示例一:
<Directory /web/docs> Options Indexes FollowSymLinks </Directory> <Directory /web/docs/spec> Options FollowSymLinks </Directory>
示例二:
<Directory /web/docs> Options Indexes FollowSymLinks </Directory> <Directory /web/docs/spec> Options +Includes -Indexes </Directory>
(3)AllowOverride
与访问控制相关的哪些指令可以放在指定目录下的.htaccess(由AccessFileName指定)文件中,覆盖之前的配置指令
只对<directory>语句有效
AllowOverride All: .htaccess中所有指令都有效 AllowOverride None: .htaccess 文件无效,默认不写就是文件无效 AllowOverride AuthConfig Indexes 除了AuthConfig 和Indexes的其它指令都无法覆盖
在/data/www/目录下新建一个.htaccess文件,并将指定的指令添加到该文件中
cd /data/www 切换到www目录下 vim .htaccesss 新建一个.htaccess文件 options indexes FollowSymLinks 允许使用的指令
然后在/etc/httpd/conf.d/test.conf配置文件中修改相关配置文件,允许所有指令有效:
vim /etc/htttpd/conf.d/test.conf
<directory /data/www> allowoverride all #options indexes FollowSymLinks Require all granted </directory>

重启httpd服务:
systemctl restart httpd
查看网页效果,可以访问结果:

(4)基于IP的访问控制:
1> 无明确授权的目录,默认拒绝
2> 允许所有主机访问:Require all granted
3> 拒绝所有主机访问:Require all denied
4> 控制特定的IP访问:
Require ip IPADDR:授权指定来源的IP访问
Require not ip IPADDR:拒绝特定的IP访问
5> 控制特定的主机访问:
Require host HOSTNAME:授权特定主机访问
Require not host HOSTNAME:拒绝 HOSTNAME:
6> FQDN:特定主机
domin.tld:指定域名下的所有主机
不能有失败,至少有一个成功匹配才成功,即失败优先
<RequireAll> Require all granted Require not ip 172.16.1.1 拒绝特定IP </RequireAll>
多个语句有一个成功,则成功,即成功优先
<RequireAny> Require all denied 所有都不可以访问 require ip 172.16.1.1 允许特定IP </RequireAny>
演示:
先将/etc/httpd/conf.d目录下的welcome.conf.bak恢复为welcome.conf
cd /etc/httpd/conf.d mv welcome.conf.bak welcome.conf
在配置文件中/etc/httpd/conf.d/test.conf修改内容,不允许192.168.34.101访问
<directory /data/www> <requireall> 此配置需要嵌套在directory中 Require all granted require not ip 192.168.34.101 拒绝192.168.34.101进行访问 </requireall> </directory>
检查语法:httpd -t 并重启httpd服务。

用192.168.34.101主机进行远程登录尝试,此时访问拒绝:
curl -I 192.168.34.100

192.168.34.102访问100的主机正常:

演示:
在配置文件中/etc/httpd/conf.d/test.conf修改内容,只允许192.168.34.101IP地址访问
<directory /data/www> <requireany> Require all denied require ip 192.168.34.101 </requireany> </directory>

httpd -t 检查语法,重启httpd服务。

192.168.34.101主机访问正常

192.168.34.102访问被拒绝:

演示:也可以针对特定的文件夹进行访问控制
[root@centos7conf.d]#cd /data/www/ [root@centos7www]#mkdir news [root@centos7data]#echo /data/www/index.html > www/news/index.html
修改新建test.conf配置文件信息
vim /etc/httpd/conf.d/test.conf <directory /data/www> 允许访问/data/www目录下的文件 Require all granted </directory> <directory /data/www/news> 不允许访问/data/www/news目录下的信息 Require all denied </directory>
查看结果,此时可以访问到/data/www目录下的index.html文件,不能访问到news目录下的文件

日志设定
日志类型:
访问日志 错误日志
错误日志:
ErrorLog logs/error_log LogLevel warn LogLevel 可选值: debug, info, notice, warn,error, crit, alert, emergmo
httpd服务器默认的错误日志路径:/etc/httpd/logs/error_log
用户访问网页的日志默认存放路径在 /var/log/httpd/目录下:

访问日志:
定义日志格式:LogFormat format strings
LogFormat "%h %l %u %{%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S}t \"%r\" %>s %b \"%{Referer}i\" \"%{User-Agent}i\"" testlog
使用日志格式:
CustomLog logs/access_log testlog
参考帮助:http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.2/mod/mod_log_config.html#formats
%h 客户端IP地址
%l 远程用户,启用mod_ident才有效,通常为减号“-”
%u 验证(basic,digest)远程用户,非登录访问时,为一个减号“-”
%t 服务器收到请求时的时间
%r First line of request,即表示请求报文的首行;记录了此次请求的“方法”,“URL”以及协议版本
%>s 响应状态码
%b 响应报文的大小,单位是字节;不包括响应报文http首部
%{Referer}i 请求报文中首部“referer”的值;即从哪个页面中的超链接跳转至当前页面的
%{User-Agent}i 请求报文中首部“User-Agent”的值;即发出请求的应用程序
在配置文件中/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf搜索/combined能具体看到日志格式和定义,如下图:
可以在此配置文件中定义名称和格式:
LogFormat "%h %l %u %t \"%r\" %>s %b \"%{Referer}i\" \"%{User-Agent}i\"" combined # 两个combined需要对应才能使用
CustomLog "logs/access_log" combined

查询成功与错误日志:

帮助文档中可以查询具体含义:

设定默认字符集
AddDefaultCharset UTF-8 此为默认值 中文字符集:GBK, GB2312, GB18030
可以新建一个配置文件/etc/httpd/conf.d/test.conf中修改字符集:
![]()
定义路径别名
格式:Alias /URL/ "/PATH/" 有没有都无所谓,虚拟的目录
DocumentRoot "/www/htdocs"
http://www.magedu.com/download/bash.rpm
==>/www/htdocs/download/bash.rpm
Alias /download/ "/rpms/pub/"
http://www.magedu.com/download/bash.rpm
==>/rpms/pub/bash.rpm
http://www.magedu.com/images/logo.png
==>/www/htdocs/images/logo.png
演示:
新建一个sports目录,将index.html文件放到sports目录下
[root@centos7data]#mkdir sports [root@centos7data]#ls sports www [root@centos7data]#cp www/index.html sports/
在新建的配置文件中/etc/httpd/conf.d/test.conf中添加别名配置文件,定义别名为sports
vim /etc/httpd/conf.conf/test.conf

重启httpd服务:systemctl restart httpd
查看网页显示结果:

基于用户的访问控制
1)认证质询:WWW-Authenticate:响应码为401,拒绝客户端请求,并说明要求客户端提供账号和密码
2)认证:Authorization:客户端用户填入账号和密码后再次发送请求报文;认证通过时,则服务器发送响应的资源
3)认证方式两种:
basic:明文 digest:消息摘要认证,兼容性差
4)安全域:需要用户认证后方能访问的路径;应该通过名称对其进行标识,以便于告知用户认证的原因
5)用户的账号和密码
虚拟账号:仅用于访问某服务时用到的认证标识 存储:文本文件,SQL数据库,ldap目录存储,nis等
basic认证配置示例:
(1) 定义安全域
<Directory “/path"> Options None AllowOverride None AuthType Basic AuthName "String“ AuthUserFile "/PATH/HTTPD_USER_PASSWD_FILE" Require user username1 username2 ... </Directory>
允许账号文件中的所有用户登录访问:
Require valid-user
提供账号和密码存储(文本文件)
使用专用命令完成此类文件的创建及用户管理
需要安装httpd-tools包:
[root@centos7 httpd]# yum install httpd-tools -y
htpasswd [options] /PATH/HTTPD_PASSWD_FILE username
-c 自动创建文件,仅应该在文件不存在时使用 -p 明文密码 -d CRYPT格式加密,默认 -m md5格式加密 -s sha格式加密 -D 删除指定用户
指定特定的用户进行访问网页
新建一个admin目录,并将文件的路径指向admin目录下的index.html下:
[root@centos7www]#pwd /data/www [root@centos7www]#mkdir admin [root@centos7www]#echo /data/www/admin/index.html > /data/www/admin/index.html 将文件指向admin目录下的index.html文件中
创建一个httpdpass文件、tom和jerry用户
[root@centos7data]#htpasswd -c /etc/httpd/conf.d/httpdpass tom 创建tom用户和httpdpass文件 New password: Re-type new password: Adding password for user tom [root@centos7data]#htpasswd -s /etc/httpd/conf.d/httpdpass jerry 创建jerry用户时,不要再创建文件,不然会覆盖httpdpass文件,因此可以用默认的-s选项加密 New password: Re-type new password: Adding password for user jerry
修改新创建的文件权限
[root@centos7data]#chmod 600 /etc/httpd/conf.d/httpdpass
只赋予apache账号一个读权限即可:
[root@centos7conf.d]#setfacl -m u:apache:r /etc/httpd/conf.d/httpdpass
修改新建的配置文件:
vim /etc/httpd/conf.d/test.conf 修改此配置文件 <directory /data/www/admin> AuthType Basic AuthName "welcome to login" AuthUserFile "/etc/httpd/conf.d/httpdpass" Require user tom 只允许tom访问此文件 </directory>

检查httpd服务的配置文件信息,并将httpd服务重启
[root@centos7www]#httpd -t AH00558: httpd: Could not reliably determine the server's fully qualified domain name, using fe80::20c:29ff:fe9d:204e. Set the 'ServerName' directive globally to suppress this message Syntax OK [root@centos7www]#systemctl restart httpd

验证网页效果,并登陆

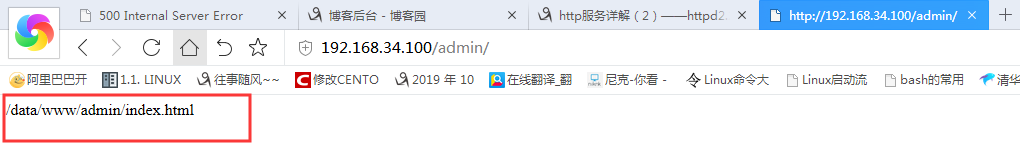
允许所有人登陆访问网页
第一种实现方法:
设置所有人都能登录,需要加入valid-user选项即可,然后重启httpd服务:
DocumentRoot "/data/www" <directory /data/www/admin> AuthType Basic AuthName "welcome to login" AuthUserFile "/etc/httpd/conf.d/httpdpass" #Require user tom Require valid-user # 在上面的基础上加入此选项,允许所有人登陆访问 </directory>

第二种实现方法:
vim /etc/httpd/conf.d/test.conf # 在配置文件中修改 DocumentRoot "/data/www" <directory /data/www/admin> allowoverride authconfig # 允许在/data/www/admin/.htaccess文件基于验证登陆访问网页 </directory> vim /data/www/admin/.htaccess # 在.htaccess文件中配置允许所有人访问 AuthType Basic AuthName "welcome to login" AuthUserFile "/etc/httpd/conf.d/httpdpass" #Require user tom Require valid-user # 在上面的基础上加入此选项,允许所有人登陆访问
删除用户名:
[root@centos7conf.d]#htpasswd -D /etc/httpd/conf.d/httpdpass jerry Deleting password for user jerry
基于组账号进行认证
(1) 定义安全域
<Directory “/path"> AuthType Basic AuthName "String“ AuthUserFile "/PATH/HTTPD_USER_PASSWD_FILE" AuthGroupFile "/PATH/HTTPD_GROUP_FILE" Require group grpname1 grpname2 ... </Directory>
(2) 创建用户账号和组账号文件
组文件:每一行定义一个组
GRP_NAME: username1 username2 ...
实现组认证登陆网页
在httpdgroup文件中配置两个用户组账号
[root@centos7conf.d]#vim /etc/httpd/conf.d/httpdgroup testgroup:tom jerry
在.htaccess中修改配置文件:
vim /data/www/.htaccess # 在 AuthType Basic AuthName "welcome to login" AuthUserFile "/etc/httpd/conf.d/httpdpass" AuthGroupFile "/etc/httpd/conf.d/httpdgroup" # 只有此组里边的用户名访问httpdpass文件 Require group testgroup # 允许分组进行登陆网页,与上面允许用户访问类似。
远程客户端和用户验证的控制
Satisfy ALL|Any
(1)ALL 客户机IP和用户验证都需要通过才可以
(2)Any客户机IP和用户验证,有一个满足即可
实现用户家目录的http共享
基于模块mod_userdir.so实现
SELinux: http_enable_homedirs
相关设置:
vim /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf <IfModule mod_userdir.c> #UserDir disabled UserDir public_html #指定共享目录的名称 </IfModule>
准备目录
su - wang;mkdir ~/public_html setfacl -m u:apache:x ~wang
访问
http://localhost/~wang/index.html
提问:我们如何将用户账号家目录的指定目录共享在网页上?
下来我介绍一下:
先在/etc/httpd/conf.d/目录下查看一个配置文件userdir.conf:
[root@centos7data]#ls /etc/httpd/conf.d autoindex.conf httpdgroup httpdpass manual.conf README test.conf userdir.conf welcome.conf

配置userdir.conf文件里边的内容:
vim /etc/httpd/conf.d/userdir.conf

重启httpd服务:systemctl restart httpd
此时切换至wang用户,然后创建一个public_html目录:
[root@centos7conf.d]#su - wang Last login: Sun Nov 24 22:07:47 CST 2019 on pts/0 [wang@centos7~]$pwd /home/wang [wang@centos7~]$mkdir public_html [wang@centos7~]$echo wanghome_public_html > public_html/index.html

给apache账号一个执行权限,可以切换到/home/wang目录下,并能查看信息:
[wang@centos7~]$setfacl -m u:apache:x /home/wang
查看此时的网页页面:
192.168.34.100/~wang

如果想将wang家目录加密让指定的用户访问,对家目录进行加密,怎么办?只需要修改配置文件,在最底部写入内容:
vim /etc/httpd/conf.d/userdir.conf
<directory /home/wang/public_html> authtype basic authname "wang home" authuserfile "/etc/httpd/conf.d/httpdpass" require user tom </directory>

重启httpd服务:systemctl restart httpd
查看网页效果:

登陆tom账号才能看到家目录wang账号信息:

ServerSignature On | Off | EMail
(1)当客户请求的网页并不存在时,服务器将产生错误文档,缺省情况下由于打开了 ServerSignature选项,错误文档的最后一行将包含服务器的名字、Apache的版本等信息
(2)如果不对外显示这些信息,就可以将这个参数设置为Off,默认是关闭的。
(3)设置为Email,将显示ServerAdmin 的Email提示
status页面
这个功能需要status_module 模块
httpd -M | grep status 查询这个模块有没有被加载

LoadModule status_module modules/mod_status.so 模块总配置文件已经加载
为了安全起见,只能允许部分IP地址访问状态页:
<Location "/status"> 此处status只是文件夹的名称,访问时使用此名称访问即可 SetHandler server-status 系统自带的内部处理模块 <requireany> require all denied # 拒绝所有IP地址 require ip 192.168.7.0/24 # 允许IP地址段进行访问 </requireany> </Location>
ExtendedStatus On 显示扩展信息,默认是打开的
演示:我们可以查看apache是否有问题,可以将此配置写入到配置文件中,查看网页信息,然后确定apache是否正常
在vim /etc/httpd/conf.d/test.conf

重启httpd服务:systemctl restart httpd

状态的类型:
"-"等待连接 "S"启动 "R"处于读取状态 "W"发送应答 "K"保持长连接 "D"dns查询 "C"正处于关闭状态 "L"记录日志 "G"优雅的终止,温柔的断开 "r"把空闲的worker进程清理 "."没有正常的进程
虚拟主机
站点标识: socket
IP相同,但端口不同 IP不同,但端口均为默认端口,此方式用的不多 FQDN不同: 请求报文中首部 Host: www.magedu.com 用法最多
有三种实现方案:
基于ip:为每个虚拟主机准备至少一个ip地址 基于port:为每个虚拟主机使用至少一个独立的port 基于FQDN:为每个虚拟主机使用至少一个FQDN
虚拟主机的配置方法:
<VirtualHost IP:PORT> ServerName FQDN DocumentRoot “/path" </VirtualHost>
建议:上述配置存放在独立的配置文件中
其它可用指令:
ServerAlias:虚拟主机的别名;可多次使用 ErrorLog: 错误日志 CustomLog:访问日志 <Directory “/path"> </Directory> Alias
实验一:基于IP的多虚拟主机(不推荐)
(1)新建三个目录和三个index.html文件
[root@centos7conf.d]#mkdir /data/{a,b,c}site
[root@centos7conf.d]#echo www.a.com > /data/asite/index.html
[root@centos7conf.d]#echo www.b.com > /data/bsite/index.html
[root@centos7conf.d]#echo www.c.com > /data/csite/index.html
(2)由于本机器只有两个IP地址,此时再新加一个IP地址:
[root@centos7conf.d]#ip a a 192.168.34.100 dev ens33 [root@centos7conf.d]#ip a a 192.168.34.111 dev ens33 [root@centos7conf.d]#ip a a 192.168.34.112 dev ens33
(3)在/etc/httpd/conf.d/test.conf文件中修改配置:
<virtualhost 192.168.34.100:80> documentroot "/data/asite" <directory /data/asite> require all granted </directory> customlog /var/log/httpd/access_a.log combined </virtualhost> <virtualhost 192.168.34.111:80> documentroot "/data/bsite" <directory /data/bsite> require all granted </directory> customlog /var/log/httpd/access_b.log combined </virtualhost> <virtualhost 192.168.34.112:80> documentroot "/data/csite" <directory /data/csite> require all granted </directory> customlog /var/log/httpd/access_c.log combined </virtualhost>

重启httpd服务:systemctl restart httpd
配置DNS解析域名,此时我们不需要麻烦,直接将IP地址写入到hosts文件中即可
[root@centos7 httpd]# cat /etc/hosts 127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4 ::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6 192.168.34.100 www.a.com 192.168.34.111 www.b.com 192.168.34.112 www.c.com
查看当前IP地址分配的网址,此时都已经可以访问,此做法缺点就是需要大量的IP地址进行做网站。
[root@centos7 httpd]# curl www.a.com www.a.com [root@centos7 httpd]# curl www.b.com www.b.com [root@centos7 httpd]# curl www.c.com www.c.com
实验二:基于端口的多虚拟主机(不推荐)
此方法在用户输入每个网页的端口号,比较繁琐,不建议使用
修改配置文件/etc/httpd/conf.d/test.conf
listen 81 监听81端口 listen 82 监听82端口 listen 83 监听83端口 <virtualhost *:81> 将IP地址改为*,端口号改为81 documentroot "/data/asite" <directory /data/asite> require all granted </directory> customlog /var/log/httpd/access_a.log combined </virtualhost> <virtualhost *:82> 将IP地址改为*,端口号改为82 documentroot "/data/bsite" <directory /data/bsite> require all granted </directory> customlog /var/log/httpd/access_b.log combined </virtualhost> <virtualhost *:83> 将IP地址改为*,端口号改为83 documentroot "/data/csite" <directory /data/csite> require all granted </directory> customlog /var/log/httpd/access_c.log combined </virtualhost>

重启httpd服务,systemctl restart httpd
修改/etc/hosts域名解析文件,将所有域名都指向本机的一个IP地址。
[root@centos7 conf.d]# cat /etc/hosts 127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4 ::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6 192.168.7.100 www.a.com www.b.com www.c.com
验证结果,可以看出,只需要一个IP地址,指定端口就可以访问网页
[root@centos7www]#curl 192.168.34.100:81 www.a.com [root@centos7www]#curl 192.168.34.100:82 www.b.com [root@centos7www]#curl 192.168.34.100:83 www.c.com
实验三:基于主机头多虚拟主机(推荐)
A主机:192.168.34.100 提供网站
B主机:192.168.34.101 客户端,访问网页
注意:任意目录下的页面只有显式授权才能被访问
基于FQDN实现的方式原理:用户访问网站,在http内就会携带主机头,因此我们可以利用此特性,根据主机头来判断用户访问的是哪个网站,然后返回对应的页面。
(1)在A主机(网站)和B主机上(客户端)的/etc/hosts配置文件中写入相关的IP地址和网址,指向A主机的IP地址,域名解析代替DNS解析
vim /etc/hosts 127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4 centos7.localdomain ::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6 192.168.34.100 www.a.com www.b.net www.c.cn # 其中192.168.34.100是A主机的IP地址

(2)在A主机上修改/etc/httpd/conf.d/test.conf配置文件内容:
<virtualhost *:80> servername "www.a.com" # 将访问的网址写入到主机内 documentroot "/data/asite" <directory /data/asite> require all granted </directory> customlog /var/log/httpd/access_a.log testlog </virtualhost> <virtualhost *:80> servername "www.b.net" # 将访问的网页写入到主机内 documentroot "/data/bsite" <directory /data/bsite> require all granted </directory> customlog /var/log/httpd/access_b.log testlog </virtualhost> <virtualhost *:80> servername "www.c.cn" documentroot "/data/csite" <directory /data/csite> require all granted </directory> customlog /var/log/httpd/access_c.log testlog </virtualhost>

(3)在B主机上测试实现访问结果,此时三个网址都可以访问

mod_deflate压缩模块(生产中很重要,网页必须压缩)
使用mod_deflate模块压缩页面优化传输速度
适用场景:
(1) 节约带宽,额外消耗CPU;同时,可能有些较老浏览器不支持
[root@centos7 conf.modules.d]# pwd /etc/httpd/conf.modules.d [root@centos7 conf.modules.d]# cat 00-base.conf |grep deflate # 查看此模块是否加载,如果没有加载,就需要启动,此时我们看到此模块已经加载了。 LoadModule deflate_module modules/mod_deflate.so
(2) 压缩适于压缩的资源,例如文本文件
LoadModule deflate_module modules/mod_deflate.so SetOutputFilter DEFLATE SetOutputFilter DEFLATE # Restrict compression to these MIME types AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE text/plain # 压缩为纯文本 AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE text/html # 压缩html后缀的文件 AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE application/xhtml+xml AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE text/xml AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE application/xml AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE application/x-javascript AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE text/javascript AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE text/css
(3)Level of compression (Highest 9 - Lowest 1)
(4)DeflateCompressionLevel 9 压缩比
(5)排除特定旧版本的浏览器,不支持压缩
Netscape 4.x 只压缩text/html BrowserMatch ^Mozilla/4 gzip-only-text/html Netscape 4.06-08三个版本 不压缩 BrowserMatch ^Mozilla/4\.0[678] no-gzip Internet Explorer标识本身为“Mozilla / 4”,但实际上是能够处理请求的压缩。如果用户代理首部匹配字符串“MSIE”(“B”为单词边界”),就关闭之前定义的限制 BrowserMatch \bMSI[E] !no-gzip !gzip-only-text/html
实验:压缩网站页面
(1)在A主机上,将之前配置过的文件中进行修改,压缩指定的虚拟机中的网页
vim /etc/httpd/conf.d/test.conf
<virtualhost *:80> documentroot "/data/asite" servername www.a.com <directory /data/asite> require all granted </directory> customlog /var/log/httpd/access_a.log combined AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE text/plain # 将plain格式压缩为text格式 AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE text/html # 将html压缩为text格式 DeflateCompressionLevel 9 # 压缩比,9为最高压缩比 </virtualhost>

(2)重启服务:systemctl restart httpd
(3)将系统日志传到/data/asite目录下
[root@centos7asite]#cp /var/log/messages /data/asite/m.txt [root@centos7asite]#chmod +r /data/asite/m.txt
(4)在B主机上验证压缩后的网页结果,此时是以gzip压缩格式显示。
curl -I --compressed www.a.com/m.txt

(5)在网页上访问,查看头报文,可以看到此时的网站已经被压缩。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号