DHCP服务搭建
DHCP服务搭建
DHCP动态分配主机地址(Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)
动态主机配置协议(DHCP)是一种基于UDP协议且仅限于在局域网内部使用的网络协议,主要用于大型的局域网环境或者存在较多移动办公设备的局域网环境中,其主要用途是为局域网内部的设备或网络供应商自动分配IP地址等参数。
DHCP概念拓扑图:

DHCP(Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol,动态主机配置协议)是一个局域网的网络协议,使用UDP协议工作。它是一种流行的Client/Server协议,一般用于为主机或者为路由器等指定相关的配置信息。DHCP服务在企业和家庭中得到了大量的应用,它能够自动分配ip地址以及一些其他的相关信息,整个过程对客户透明。
DHCP分配方式
自动分配方式(Automatic Allocation),DHCP服务器为主机指定一个永久性的IP地址,一旦DHCP客户端第一次成功从DHCP服务器端租用到IP地址后,就可以永久性的使用该地址。
动态分配方式(Dynamic Allocation),DHCP服务器给主机指定一个具有时间限制的IP地址,时间到期或主机明确表示放弃该地址时,该地址可以被其他主机使用。
手工分配方式(Manual Allocation),客户端的IP地址是由网络管理员指定的,DHCP服务器只是将指定的IP地址告诉客户端主机。
DHCP工作过程
DHCP客户机在启动时,会搜寻网络中是否存在DHCP服务器。如果找到,则给DHCP服务器发送一个请求。DHCP服务器接到请求后,为DHCP客户机选择TCP/IP配置的参数,并把这些参数发送给客户端。 如果已配置冲突检测设置,则DHCP服务器在将租约中的地址提供给客户机之前会使用Ping测试作用域中每个可用地址的连通性。这可确保提供给客户的每个IP地址都没有被使用手动TCP/IP配置的另一台非DHCP计算机使用。
根据客户端是否第一次登录网络,DHCP的工作形式会有所不同。
初次登录
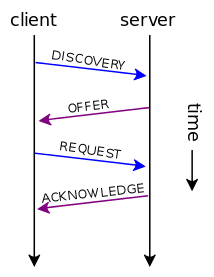
初次登录时DHCP工作包括四个步骤
1、寻找DHCP服务器
当DHCP客户端第一次登录网络的时候,计算机发现本机上没有任何IP地址设定,将以广播方式发送DHCP discover发现信息来寻找DHCP服务器,即向255.255.255.255发送特定的广播信息。网络上每一台安装了TCP/IP协议的主机都会接收这个广播信息,但只有DHCP服务器才会做出响应。
2、分配IP地址
在网络中接收到DHCP discover发现信息的DHCP服务器就会做出响应,它从尚未分配的IP地址池中挑选一个分配给DHCP客户机,并向DHCP客户机发送一个包含分配的IP地址和其他设置的DHCP offer提供信息。
3、接受IP地址
DHCP客户端接受到DHCP offer提供信息之后,选择第一个接收到的提供信息,然后以广播的方式回答一个DHCP request请求信息,该信息包含向它所选定的DHCP服务器请求IP地址的内容。
4、IP地址分配确认
当DHCP服务器收到DHCP客户端回答的DHCP request请求信息之后,便向DHCP客户端发送一个包含它所提供的IP地址和其他设置的DHCP ack确认信息,告诉DHCP客户端可以使用它提供的IP地址。然后,DHCP客户机便将其TCP/IP协议与网卡绑定,另外,除了DHCP客户机选中的DHCP服务器外,其他的DHCP服务器将收回曾经提供的IP地址。
网络配置
- 静态指定
- 动态获取: bootp:boot protocol MAC与IP一一静态对应dhcp:增强的bootp,动态
DHCP: (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)
- 动态主机配置协议
- 局域网协议,UDP协议
主要用途:
- 用于内部网络和网络服务供应商自动分配IP地址给用户
- 用于内部网络管理员作为对所有电脑作集中管理的手段
使用场景
- 自动化安装系统
- 解决IPV4资源不足问题
一:DHCP共有八种报文
DHCP DISCOVER:客户端到服务器
DHCP OFFER :服务器到客户端
DHCP REQUEST:客户端到服务器
DHCP ACK :服务器到客户端
DHCP NAK:服务器到客户端,通知用户无法分配合适的IP地址
DHCP DECLINE :客户端到服务器,指示地址已被使用
DHCP RELEASE:客户端到服务器,放弃网络地址和取消剩余的租约时间
DHCP INFORM:客户端到服务器, 客户端如果需要从DHCP服务器端获取更为详细的配置信息,则发送Inform报文向服务器进行请求,极少用到
DHCP相关文件信息:
cat > /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0
<<EOF
TYPE=Ethernet
BOOTPROTO=dhcp
NAME=eth0
DEVICE=eth0
ONBOOT=yes
IPADDR=10.0.0.200
PREFIX=24
GATEWAY=10.0.0.2
DNS1=223.5.5.5
EOF
systemctl restart network
[root@centos7x86_64]#cd /var/lib/dhclient
[root@centos7dhclient]#cat dhclient.leases
lease {
interface "eth0";
fixed-address 10.0.0.200;
option subnet-mask 255.255.255.0;
option routers 10.0.0.200;
option dhcp-lease-time 1800;
option dhcp-message-type 5;
option domain-name-servers 223.5.5.5; 获取的DNS
option dhcp-server-identifier 192.168.34.254; 获取的DHCP地址
option broadcast-address 192.168.34.255;
option domain-name "localdomain";
renew 2 2019/10/29 12:15:35; 续租时间
rebind 2 2019/10/29 12:27:37;
expire 2 2019/10/29 12:31:22; 可以看到当前dhcp的有效期
}
续租
1)50% :租赁时间达到50%时来续租,刚向DHCP服务器发向新的DHCPREQUEST请求。如果dhcp服务没有拒绝的理由,则回应DHCPACK信息。当DHCP客户端收到该应答信息后,就重新开始新的租用周期
2)87.5%:如果之前DHCP Server没有回应续租请求,等到租约期的7/8时,主机会再发送一次广播请求
同网段多DHCP服务
1)DHCP服务必须基于本地
2)先到先得的原则
跨网段
1)RFC 1542 Compliant Routers
2)dhcrelay: 中继 用户通过ARP广播到达DHCP时,如果中间有路由器阻挡,可以通过中继进行传递,返回时也可以通过中继到达用户的过程
相关协议
Arp 用户通过ARP广播到达DHCP
rarp
DHCP服务器会自动把IP地址、子网掩码、网关、DNS地址等网络信息分配给有需要的客户端,而且当客户端的租约时间到期后还可以自动回收所分配的IP地址,以便交给新加入的客户端。
二:搭建DHCP服务器
服务器的DHCP端口是67
客户端的DHCP端口是68
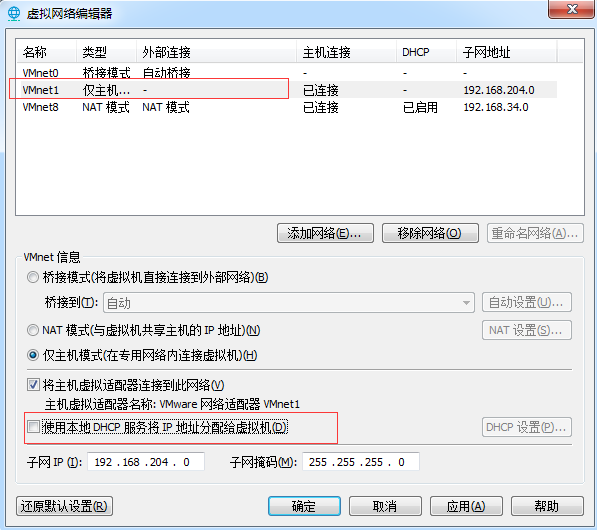
2)将VMnet1仅主机模式的使用本地DHCP服务那栏去掉对勾
服务端
[root@centos6~]#yum install dhcp -y
DHCP的相关配置文件:
[root@centos6~]#rpm -ql dhcp
/etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf DHCP配置文件
/var/lib/dhcpd DHCP主程序
/var/lib/dhcpd/dhcpd.leases 租出去的DHCP地址信息
启动DHCP服务:
[root@centos7~]#systemctl start dhcpd 无法启动
Job for dhcpd.service failed because the control process exited with error code. See "systemctl status dhcpd.service" and "journalctl -xe" for details.
[root@centos7~]#systemctl status dhcpd 查看为何不能启动
dhcpd.service - DHCPv4 Server Daemon
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/dhcpd.service; disabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: failed (Result: exit-code) since Tue 2019-10-29 20:42:01 CST; 1s ago
Docs: man:dhcpd(8)
man:dhcpd.conf(5)
Process: 7572 ExecStart=/usr/sbin/dhcpd -f -cf /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf -user dhcpd -group dhcpd --no-pid (code=exited, status=1/FAILURE)
Main PID: 7572 (code=exited, status=1/FAILURE)
Oct 29 20:42:01 centos7.localdomain dhcpd[7572]: Internet Systems Consortium DHCP Server 4.2.5
Oct 29 20:42:01 centos7.localdomain dhcpd[7572]: Copyright 2004-2013 Internet Systems Consortium.
Oct 29 20:42:01 centos7.localdomain dhcpd[7572]: All rights reserved.
Oct 29 20:42:01 centos7.localdomain dhcpd[7572]: For info, please visit https://www.isc.org/software/dhcp/
Oct 29 20:42:01 centos7.localdomain dhcpd[7572]: Not searching LDAP since ldap-server, ldap-port and ldap-base-...file
Oct 29 20:42:01 centos7.localdomain dhcpd[7572]: Wrote 0 leases to leases file.
Oct 29 20:42:01 centos7.localdomain systemd[1]: dhcpd.service: main process exited, code=exited, status=1/FAILURE
Oct 29 20:42:01 centos7.localdomain systemd[1]: <strong>Failed to start DHCPv4 Server Daemon</strong>. 有一个错误提示
Oct 29 20:42:01 centos7.localdomain systemd[1]: Unit dhcpd.service entered failed state.
Oct 29 20:42:01 centos7.localdomain systemd[1]: dhcpd.service failed.
Hint: Some lines were ellipsized, use -l to show in full.
vim /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf 查看DHCP里边的配置文件
# DHCP Server Configuration file.
# see /usr/share/doc/dhcp*/dhcpd.conf.example
# see dhcpd.conf(5) man page
[root@centos7~]#cp /usr/share/doc/dhcp*/dhcpd.conf.example /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf
修改DHCP里边的配置文件:
[root@centos7~]#vim /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf
# option definitions common to all supported networks...
# Use this to send dhcp log messages to a different log file (you also
# have to hack syslog.conf to complete the redirection).
log-facility local7;
# No service will be given on this subnet, but declaring it helps the
# DHCP server to understand the network topology.
subnet 10.0.0.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 { #声明IP地址段和子网掩码
option domain-name "dhcp";
default-lease-time 86400; #设置当前的IP地址有效期,单位s
max-lease-time 864000; #设置申请最大有效期
range 10.0.0.20 10.0.0.200; #地址池:设置一个地址段
option routers 10.0.0.1; #指定网关:
option domain-name-servers 114.114.114.114,180.76.76.76;
获取DNS:114.114.114.114,180.76.76.76
next-server 192.168.34.101; #tftp服务IP地址,搭建DHCP服务可不写
filename "dhcp"; #安装系统的引导计算机的文件,搭建DHCP服务可不写
}
host passacaglia {
hardware ethernet 0:0:c0:5d:bd:95; #输入客户端的MAC地址
filename-adress 192.168.34.66 #固定给用户一个IP地址,当用户连接时给一个固定的IP地址,固定地址不能使用地址池分配的地址
}
host test {
hardware ethernet 08:00:07:26:c0:a5;
fixed-address 192.168.7.200;
}
# You can declare a class of clients and then do address allocation
# based on that. The example below shows a case where all clients
# in a certain class get addresses on the 10.17.224/24 subnet, and all
# other clients get addresses on the 10.0.29/24 subnet.
class "foo" {
match if substring (option vendor-class-identifier, 0, 4) = "SUNW";
}
shared-network 224-29 {
subnet 10.17.224.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 {
option routers rtr-224.example.org;
}
subnet 10.0.29.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 {
option routers rtr-29.example.org;
}
pool {
allow members of "foo";
range 10.17.224.10 10.17.224.250;
}
pool {
deny members of "foo";
range 10.0.29.10 10.0.29.230;
}
}
[root@centos7~]#tee /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf <<-EOD
# option definitions common to all supported networks...
subnet 10.152.187.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 {
}
# Use this to send dhcp log messages to a different log file (you also
# have to hack syslog.conf to complete the redirection).
log-facility local7;
# No service will be given on this subnet, but declaring it helps the
# DHCP server to understand the network topology.
subnet 10.0.0.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 {
option domain-name "dhcp";
default-lease-time 86400;
max-lease-time 864000;
range 10.0.0.20 10.0.0.200;
option routers 10.0.0.1;
option domain-name-servers 114.114.114.114,180.76.76.76;
next-server 10.0.0.100;
filename "dhcp";
}
host passacaglia {
hardware ethernet 0:0:c0:5d:bd:95;
filename-adress 10.0.0.66;
}
host test {
server-name "toccata.fugue.com";
fixed-address 10.0.0.50;
}
# You can declare a class of clients and then do address allocation
# based on that. The example below shows a case where all clients
# in a certain class get addresses on the 10.17.224/24 subnet, and all
# other clients get addresses on the 10.0.29/24 subnet.
class "foo" {
match if substring (option vendor-class-identifier, 0, 4) = "SUNW";
}
shared-network 224-29 {
subnet 10.17.224.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 {
option routers rtr-224.example.org;
}
subnet 10.0.29.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 {
option routers rtr-29.example.org;
}
pool {
allow members of "foo";
range 10.17.224.10 10.17.224.250;
}
pool {
deny members of "foo";
range 10.0.29.10 10.0.29.230;
}
}
EOF
重启服务
[root@centos7~]#systemctl restart dhcpd
[root@centos7~]#ss -nulp
客户端
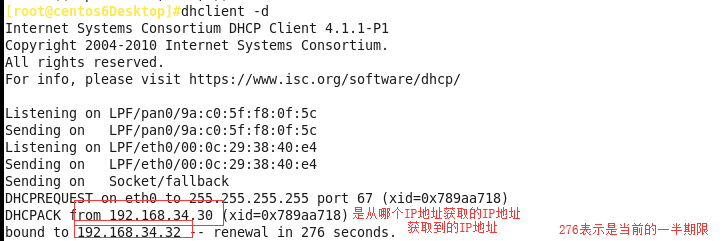
dhclient -d
#服务端
cd /var/lib/dhcpd
cat dhcpd.leases
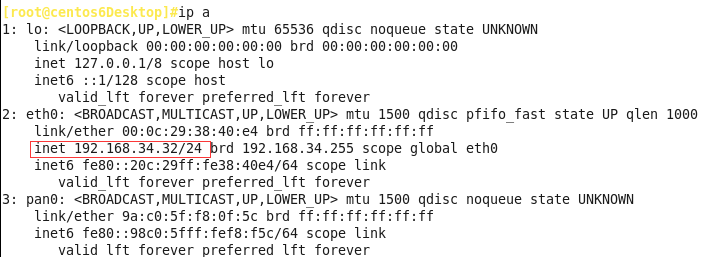
DHCPACK from 192.168.34.30 #获取的IP地址来自哪里
bound to 192.168.34.32 renewal in 276 seconds #客户端获取的IP地址是192.168.34.32, #有效期的一半是276s
启动客户端的网卡:
service network start
可以看到当前的IP地址和我们自己获取跟踪的IP地址192.168.34.32一样,DHCP服务搭建完毕。