SpringMVC源码分析之一个请求的处理
前言
这里我们以SpringBoot项目为例,Spring会帮我们自动配置DispatcherServlet和RequestMappingHandlerMapping及RequestMappingHandlerAdapter。
具体可以查看DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration和WebMvcAutoConfiguration。
简单例子
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/test")
public class TestController {
@GetMapping("/testName")
@ResponseBody
public String testName(String name) {
return "hello " + name;
}
}
@Controller注解表示这是一个Bean。@RequestMapping注解用来配置请求路径。
原理分析
RequestMappingHandlerMapping
进入其父类AbstractHandlerMethodMapping的afterPropertiesSet()方法,此方法会在当前Bean初始化时执行
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
// 初始化处理器方法
initHandlerMethods();
}
继续跟进去
protected void initHandlerMethods() {
// 获取容器中所有Bean的名称
for (String beanName : getCandidateBeanNames()) {
// 不能是代理对象
if (!beanName.startsWith(SCOPED_TARGET_NAME_PREFIX)) {
// 依次处理每一个Bean
processCandidateBean(beanName);
}
}
}
具体处理每一个Bean
protected void processCandidateBean(String beanName) {
Class<?> beanType = null;
try {
// 根据Bean名称获取到Bean类型
beanType = obtainApplicationContext().getType(beanName);
}
// Bean所属Class必须包含@Controller注解或者@RequestMapping注解
if (beanType != null && isHandler(beanType)) {
// 探测处理器方法
detectHandlerMethods(beanName);
}
}
探测方法处理器
protected void detectHandlerMethods(Object handler) {
Class<?> handlerType = (handler instanceof String ?
obtainApplicationContext().getType((String) handler) : handler.getClass());
if (handlerType != null) {
Class<?> userType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(handlerType);
// 过滤出所有包含@RequestMapping注解的方法
Map<Method, T> methods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(userType,
(MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup<T>) method -> {
try {
return getMappingForMethod(method, userType);
}
});
// 将所有方法及对应的请求路径注册到MappingRegistry对象中
methods.forEach((method, mapping) -> {
Method invocableMethod = AopUtils.selectInvocableMethod(method, userType);
registerHandlerMethod(handler, invocableMethod, mapping);
});
}
}
至此,我们在项目中定义的或者第三方库定义的Controller中的处理器(包含@RequestMapping注解的方法)都已经被探测到并保存到MappingRegistry中了。
RequestMappingHandlerAdapter
进入其afterPropertiesSet()方法
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
// 初始化所有Class包含@ControllerAdvice注解的Bean
initControllerAdviceCache();
// 初始化默认的和自定义的处理器方法参数解析器
if (this.argumentResolvers == null) {
List<HandlerMethodArgumentResolver> resolvers = getDefaultArgumentResolvers();
this.argumentResolvers = new HandlerMethodArgumentResolverComposite().addResolvers(resolvers);
}
// 初始化数据绑定的参数解析器,用的不多
if (this.initBinderArgumentResolvers == null) {
List<HandlerMethodArgumentResolver> resolvers = getDefaultInitBinderArgumentResolvers();
this.initBinderArgumentResolvers = new HandlerMethodArgumentResolverComposite().addResolvers(resolvers);
}
// 初始化默认的和自定义的处理器方法返回值处理器
if (this.returnValueHandlers == null) {
List<HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler> handlers = getDefaultReturnValueHandlers();
this.returnValueHandlers = new HandlerMethodReturnValueHandlerComposite().addHandlers(handlers);
}
}
我们以RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor为例来分析一下,它既是一个参数解析器,也是一个返回值处理器。
public class RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor extends AbstractMessageConverterMethodProcessor {
// 当前参数解析器是否支持该参数
@Override
public boolean supportsParameter(MethodParameter parameter) {
// 仅支持包含@RequestBody注解的参数
return parameter.hasParameterAnnotation(RequestBody.class);
}
// 当前返回值处理器是否支持该返回值
@Override
public boolean supportsReturnType(MethodParameter returnType) {
// 仅支持返回值所在方法的所在类包含@ResponseBody注解或返回值包含@ResponseBody注解
return (AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(returnType.getContainingClass(), ResponseBody.class) ||
returnType.hasMethodAnnotation(ResponseBody.class));
}
// 解析参数值
@Override
public Object resolveArgument(MethodParameter parameter, @Nullable ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,
NativeWebRequest webRequest, @Nullable WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory) throws Exception {
// 通过Http消息转换器从HTTP请求体中读取参数值
Object arg = readWithMessageConverters(webRequest, parameter, parameter.getNestedGenericParameterType());
String name = Conventions.getVariableNameForParameter(parameter);
if (binderFactory != null) {
WebDataBinder binder = binderFactory.createBinder(webRequest, arg, name);
if (arg != null) {
// 如果我们声明了@Validated注解或@Valid注解,会使用校验器校验参数,默认的校验器为HibernateValidator
validateIfApplicable(binder, parameter);
// 如果参数校验有问题,且我们当前参数的下一个参数不是Errors类型,就抛出异常
if (binder.getBindingResult().hasErrors() && isBindExceptionRequired(binder, parameter)) {
throw new MethodArgumentNotValidException(parameter, binder.getBindingResult());
}
}
if (mavContainer != null) {
mavContainer.addAttribute(BindingResult.MODEL_KEY_PREFIX + name, binder.getBindingResult());
}
}
return adaptArgumentIfNecessary(arg, parameter);
}
// 处理返回值
@Override
public void handleReturnValue(@Nullable Object returnValue, MethodParameter returnType,
ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, NativeWebRequest webRequest)
throws IOException, HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException, HttpMessageNotWritableException {
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(true);
ServletServerHttpRequest inputMessage = createInputMessage(webRequest);
ServletServerHttpResponse outputMessage = createOutputMessage(webRequest);
// 通过Http消息转换器将返回值写入到HTTP响应中
writeWithMessageConverters(returnValue, returnType, inputMessage, outputMessage);
}
}
使用最多的一个Http消息转换器为MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter,底层使用Jackson这个JSON解析器框架来进行普通对象和JSON字符串之间的转换。
在Http消息转换器读取前后,我们可以通过定义RequestBodyAdvice接口的实现类来对信息进行包装等处理,
在Http消息转换器写入之前,我们也可以通过定义ResponseBodyAdvice接口的实现类对数据进行处理。
DispatcherServlet
DispatcherServlet也是一个HttpServlet,默认监听的请求路径为/,表示处理所有请求。
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
// 从容器中获取文件解析器(文件上传相关),默认配置StandardServletMultipartResolver类型
initMultipartResolver(context);
// 从容器中获取区域解析器(国际化相关),如果没获取到,从DispatcherServlet.properties文件中获取默认值
initLocaleResolver(context);
// 从容器中获取主题解析器(不知道用来干嘛),如果没获取到,从DispatcherServlet.properties文件中获取默认值
initThemeResolver(context);
// 从容器中获取处理器映射,默认配置RequestMappingHandlerMapping
initHandlerMappings(context);
// 从容器中获取处理器适配器,默认配置RequestMappingHandlerAdapter
initHandlerAdapters(context);
// 从容器中获取异常解析器,默认配置HandlerExceptionResolverComposite,它是一个组合器,包含一系列其他的异常解析器
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
// 从容器中获取HTTP请求视图名称转换器(基本不用),如果没获取到,从DispatcherServlet.properties文件中获取默认值
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
// 从容器中获取视图解析器(响应为HTML页面),如果没获取到,从DispatcherServlet.properties文件中获取默认值
initViewResolvers(context);
// 在HTTP请求和Session之间管理属性(基本不用),如果没获取到,从DispatcherServlet.properties文件中获取默认值
initFlashMapManager(context);
}
initStrategies()方法在Servlet的init()方法调用过程中被执行,继续分析请求处理过程
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
// 判断是否为文件上传请求
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// 从处理器映射中根据请求路径找到对应的处理器(包含@RequestMapping注解的方法)
// 这里的处理器映射就是RequestMappingHandlerMapping,它内部的mappingRegistry对象存储着所有的请求路径和处理方法的对应关系
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null) {
// 如果没找到,返回404
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// 根据处理器找到合适的处理器适配器,这里就是RequestMappingHandlerAdapter
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// 执行拦截器的前置处理
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// 核心,处理器适配器执行处理器(包含@RequestMapping注解的方法),具体的业务逻辑
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
// 执行拦截器的后置处理
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
catch (Throwable err) {
dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err);
}
// 对处理器结果进行统一处理,如果出现异常,交给异常解析器来处理
// 如果没有异常,且结果包含视图,交给视图解析器渲染具体的视图页面
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
}
doDispatch()方法在Servlet的service()方法调用过程中被执行,相当于每一个请求都会经过这个流程。
整个过程最重要的就是处理器的执行,进入RequestMappingHandlerAdapter的handleInternal()方法
@Override
protected ModelAndView handleInternal(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception {
ModelAndView mav;
if(this.synchronizeOnSession) {
}
else {
// 核心,执行处理器方法,以上述示例代码为例,这里的handlerMethod就是testName()方法
mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
return mav;
}
@Nullable
protected ModelAndView invokeHandlerMethod(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception {
ServletWebRequest webRequest = new ServletWebRequest(request, response);
try {
WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory = getDataBinderFactory(handlerMethod);
ModelFactory modelFactory = getModelFactory(handlerMethod, binderFactory);
// 创建方法执行器
ServletInvocableHandlerMethod invocableMethod = createInvocableHandlerMethod(handlerMethod);
// 设置参数解析器
if (this.argumentResolvers != null) {
invocableMethod.setHandlerMethodArgumentResolvers(this.argumentResolvers);
}
// 设置返回值处理器
if (this.returnValueHandlers != null) {
invocableMethod.setHandlerMethodReturnValueHandlers(this.returnValueHandlers);
}
// 具体执行处理器方法
invocableMethod.invokeAndHandle(webRequest, mavContainer);
return getModelAndView(mavContainer, modelFactory, webRequest);
}
}
继续跟进去
public void invokeAndHandle(ServletWebRequest webRequest, ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,
Object... providedArgs) throws Exception {
// 通过参数解析器设置参数,通过反射来执行具体的方法
Object returnValue = invokeForRequest(webRequest, mavContainer, providedArgs);
try {
// 通过返回值处理器处理返回值
this.returnValueHandlers.handleReturnValue(
returnValue, getReturnValueType(returnValue), mavContainer, webRequest);
}
}
如果我们处理器的结果不是视图,而是一个普通对象,需要转成JSON字符串响应,经过这一步整个请求已经结束了。
总结
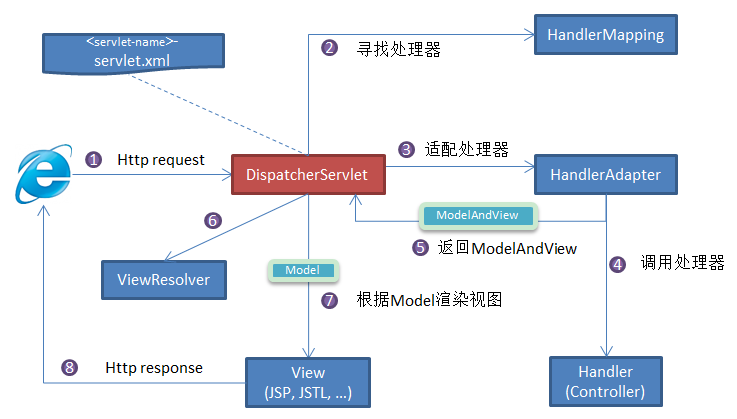
SpringMVC基本原理就是通过一个DispatcherServlet来处理所有请求,根据请求路径匹配到到指定Controller的指定方法,在执行方法前会根据不同的参数解析器来解析参数值,执行方法之后会根据方法返回值处理器来处理返回值类型。








 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号