设计模式之简单工厂
定义
提供一个创建对象实例的功能,而无需关心其具体实现,被创建实例的类型可以是接口,抽象类,也可以是具体的类。
结构
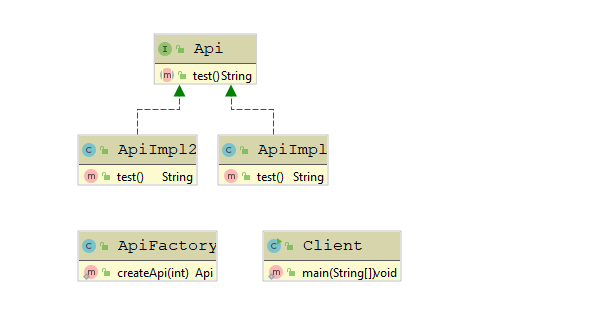
- Api,客户所需要的功能接口。
- ApiImpl,功能接口的实现,可以有多个。
- ApiFactory,工厂角色,来创建具体的功能对象,一般实现成一个工具类,直接使用静态方法。
- Client,客户端,通过工厂来创建功能对象,然后面向接口编程。
简单实现
Api接口
public interface Api {
String test();
}
Api实现
public class ApiImpl implements Api {
@Override
public String test() {
return "this is a impl";
}
}
另一个Api实现
public class ApiImpl2 implements Api {
@Override
public String test() {
return "this is a impl2";
}
}
Api工厂
public class ApiFactory {
private ApiFactory() {
}
public static Api createApi(int condition) {
if (condition == 1) {
return new ApiImpl();
} else {
return new ApiImpl2();
}
}
}
客户端
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Api api = ApiFactory.createApi(1);
System.out.println(api.test());
}
}
上述实现方式有一个缺点,在创建实例时需要传入选择的参数,这说明客户端必须知道每个参数值的含义以及每个参数对应功能的处理,这就要求在一定程度上,要向客户端暴露一些实现细节。
可配置的实现
这里使用properties文件配置
apiimpl=xxx.ApiImpl
和上一种的区别在于ApiFactory的实现
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.Properties;
public class ApiFactory {
private ApiFactory() {
}
public static Api createApi() {
Properties properties = new Properties();
InputStream inputStream = ApiFactory.class
.getClassLoader()
.getResourceAsStream("apifactory.properties");
try {
properties.load(inputStream);
return (Api) Class.forName(properties.getProperty("apiimpl")).getDeclaredConstructor()
.newInstance();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
}
客户端使用也不需要传入参数了。
简单工厂在jdk中的实现
java中的Calendar实现
/**
* Gets a calendar using the default time zone and locale. The
* <code>Calendar</code> returned is based on the current time
* in the default time zone with the default
* {@link Locale.Category#FORMAT FORMAT} locale.
* <p>
* If the locale contains the time zone with "tz"
* <a href="Locale.html#def_locale_extension">Unicode extension</a>,
* that time zone is used instead.
*
* @return a Calendar.
*/
public static Calendar getInstance()
{
Locale aLocale = Locale.getDefault(Locale.Category.FORMAT);
return createCalendar(defaultTimeZone(aLocale), aLocale);
}
private static Calendar createCalendar(TimeZone zone,
Locale aLocale)
{
CalendarProvider provider =
LocaleProviderAdapter.getAdapter(CalendarProvider.class, aLocale)
.getCalendarProvider();
if (provider != null) {
try {
return provider.getInstance(zone, aLocale);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException iae) {
// fall back to the default instantiation
}
}
Calendar cal = null;
if (aLocale.hasExtensions()) {
String caltype = aLocale.getUnicodeLocaleType("ca");
if (caltype != null) {
switch (caltype) {
case "buddhist":
cal = new BuddhistCalendar(zone, aLocale);
break;
case "japanese":
cal = new JapaneseImperialCalendar(zone, aLocale);
break;
case "gregory":
cal = new GregorianCalendar(zone, aLocale);
break;
}
}
}
if (cal == null) {
// If no known calendar type is explicitly specified,
// perform the traditional way to create a Calendar:
// create a BuddhistCalendar for th_TH locale,
// a JapaneseImperialCalendar for ja_JP_JP locale, or
// a GregorianCalendar for any other locales.
// NOTE: The language, country and variant strings are interned.
if (aLocale.getLanguage() == "th" && aLocale.getCountry() == "TH") {
cal = new BuddhistCalendar(zone, aLocale);
} else if (aLocale.getVariant() == "JP" && aLocale.getLanguage() == "ja"
&& aLocale.getCountry() == "JP") {
cal = new JapaneseImperialCalendar(zone, aLocale);
} else {
cal = new GregorianCalendar(zone, aLocale);
}
}
return cal;
}
根据不同的地区参数,返回不同的日历对象,Calendar自己作为一个工厂。
优缺点总结
优点
- 实现了客户端和具体实现类的解耦,可以面向接口编程。
缺点
- 客户端通过不同的参数来选择不同的实现,客户端就必须理解每个参数的具体功能和含义,一定程度上增加了客户端的复杂度。
- 系统扩展困难,增加新的实现就必须修改工厂逻辑,不利于维护。
本质
简单工厂的本质就是选择实现,以Calendar为例,不同的参数选择不同的实现,如JapaneseImperialCalendar,GregorianCalendar,难点在于如何选择的逻辑。
使用场景
- 工厂类创建的对象比较少,创建逻辑不太复杂。
- 客户端不需要知道具体实现。
参考
简单工厂模式(Simple Factory)
大战设计模式(第二季)【1】———— 从源码看工厂模式
设计模式的征途—2.简单工厂(Simple Factory)模式
研磨设计模式-书籍








 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号