java中的大端和小端存储
前言
- 字节序:
指多字节数据在计算机内存中存储或者网络传输时各字节的存储顺序,有大端和小端两种方式 - 大端:
指高位字节存放在内存的低地址端,低位字节存放在内存的高地址端。 - 小端:
指低位字节放在内存的低地址端,高位字节放在内存的高地址端。
以一个int值 0x01020304 为例
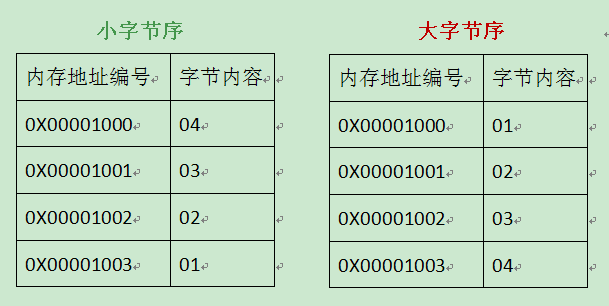
存储方式和CPU架构有关,IA架构(Intel、AMD)的CPU中是Little-Endian,而PowerPC 、SPARC和Motorola是Big-Endian
获取CPU使用的存储方式
在windows下
import java.nio.ByteOrder;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(ByteOrder.nativeOrder());
}
}
输出为
LITTLE_ENDIAN
java8中的实现原理为
public static ByteOrder nativeOrder() {
return Bits.byteOrder();
}
static ByteOrder byteOrder() {
if (byteOrder == null)
throw new Error("Unknown byte order");
return byteOrder;
}
static {
long a = unsafe.allocateMemory(8);
try {
unsafe.putLong(a, 0x0102030405060708L);
byte b = unsafe.getByte(a);
switch (b) {
case 0x01: byteOrder = ByteOrder.BIG_ENDIAN; break;
case 0x08: byteOrder = ByteOrder.LITTLE_ENDIAN; break;
default:
assert false;
byteOrder = null;
}
} finally {
unsafe.freeMemory(a);
}
}
java11中实现原理为
public static ByteOrder nativeOrder() {
return NATIVE_ORDER;
}
private static final ByteOrder NATIVE_ORDER
= Unsafe.getUnsafe().isBigEndian()
? ByteOrder.BIG_ENDIAN : ByteOrder.LITTLE_ENDIAN;
public final boolean isBigEndian() { return BE; }
private static final boolean BE = theUnsafe.isBigEndian0();
private native boolean isBigEndian0();
修改java中的存储方式
java中默认使用大端
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.ByteOrder;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x = 0x01020304;
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(new byte[4]);
byteBuffer.asIntBuffer().put(x);
String before = Arrays.toString(byteBuffer.array());
System.out.println("默认字节序:" + byteBuffer.order().toString() + "," + "内存数据:" + before);
byteBuffer.order(ByteOrder.LITTLE_ENDIAN);
byteBuffer.asIntBuffer().put(x);
String after = Arrays.toString(byteBuffer.array());
System.out.println("小端字节序:" + byteBuffer.order().toString() + "," + "内存数据:" + after);
}
}
输出为
默认字节序:BIG_ENDIAN,内存数据:[1, 2, 3, 4]
小端字节序:LITTLE_ENDIAN,内存数据:[4, 3, 2, 1]
源码实现为
public IntBuffer asIntBuffer() {
int size = this.remaining() >> 2;
long addr = address + position();
return (bigEndian
? (IntBuffer)(new ByteBufferAsIntBufferB(this,
-1,
0,
size,
size,
addr))
: (IntBuffer)(new ByteBufferAsIntBufferL(this,
-1,
0,
size,
size,
addr)));
}
public IntBuffer put(int x) {
int y = (x);
UNSAFE.putIntUnaligned(bb.hb, byteOffset(nextPutIndex()), y,
true);
return this;
}
/** @see #putLongUnaligned(Object, long, long, boolean) */
public final void putIntUnaligned(Object o, long offset, int x, boolean bigEndian) {
putIntUnaligned(o, offset, convEndian(bigEndian, x));
}
核心在于
private static int convEndian(boolean big, int n) { return big == BE ? n : Integer.reverseBytes(n) ; }








