Comparator.reversed()编译类型推断失败
错误描述
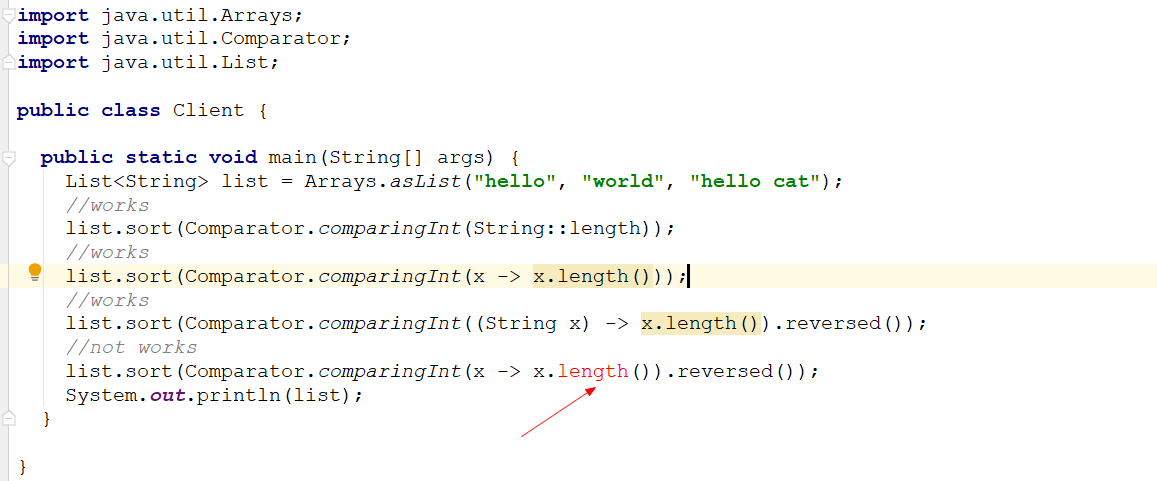
复制import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("hello", "world", "hello cat");
//works
list.sort(Comparator.comparingInt(String::length));
//works
list.sort(Comparator.comparingInt(x -> x.length()));
//works
list.sort(Comparator.comparingInt((String x) -> x.length()).reversed());
//not works
list.sort(Comparator.comparingInt(x -> x.length()).reversed());
System.out.println(list);
}
}
复制/**
* Returns a comparator that imposes the reverse ordering of this
* comparator.
*
* @return a comparator that imposes the reverse ordering of this
* comparator.
* @since 1.8
*/
default Comparator<T> reversed() {
return Collections.reverseOrder(this);
}
前面几种情况可以正常编译,第四种情况编译不通过,这种情况编译器不能推断出字符串类型,只能当做Object类型。
解决方法
复制import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("hello", "world", "hello cat");
//works
list.sort(Comparator.comparingInt((String x) -> x.length()).reversed());
//works
list.sort(Collections.reverseOrder(Comparator.comparingInt(x -> x.length())));
//works
list.sort(Comparator.comparing(x -> x.length(), Comparator.reverseOrder()));
System.out.println(list);
}
}
显式声明类型或者使用Collections.reverseOrder()方法。
参考
Comparator.reversed() does not compile using lambda
Comparator.reversed() should be usable in static context









【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本
· Manus爆火,是硬核还是营销?
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 单元测试从入门到精通