图的广度优先遍历及应用
简介
上一篇 我们实现了图的深度优先遍历及各种应用,使用广度优先遍历也是可以实现的。

从顶点0开始遍历,结果为0->1->3->2->6->4->5。
代码实现
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Queue;
/**
* 图的广度优先遍历
*/
public class GraphBFS {
/**
* 每个顶点是否已访问过
*/
private boolean[] visited;
/**
* 要遍历的图
*/
private Graph graph;
/**
* 遍历结果
*/
private List<Integer> levelOrder;
public GraphBFS(Graph graph) {
this.graph = graph;
int v = graph.V();
visited = new boolean[v];
levelOrder = new ArrayList<>();
bfs();
}
private void bfs() {
//图中可能有多个联通子图,所有顶点都需要遍历
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < graph.V(); i++) {
queue.add(i);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int poll = queue.poll();
if (visited[poll]) {
continue;
}
visited[poll] = true;
levelOrder.add(poll);
graph.adj(poll).forEach(queue::add);
}
}
}
public Iterable<Integer> levelOrder() {
return levelOrder;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
GraphBFS graphDFS = new GraphBFS(new AdjSet("g.txt"));
System.out.println(graphDFS.levelOrder());
}
}
深度优先遍历是通过递归实现的,当然也可以通过栈实现,广度优先遍历只能通过队列来实现,类似二叉树的层序遍历。
应用
联通分量
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Queue;
/**
* 求一个图的连通分量和每个连通子图的具体顶点(迭代实现)
*/
public class GraphCC {
/**
* 每个顶点是否已访问过
*/
private boolean[] visited;
/**
* 每个顶点所在的连通分量索引 两个顶点的索引相等表示在同一个连通子图中
*/
private int[] connectedComponents;
private Graph graph;
/**
* 连通分量
*/
private int connectedComponentCount;
public GraphCC(Graph graph) {
this.graph = graph;
int v = graph.V();
visited = new boolean[v];
connectedComponents = new int[v];
for (int i = 0; i < v; i++) {
if (!visited[i]) {
bfs(i);
connectedComponentCount++;
}
}
}
private void bfs(int rootV) {
Queue<Pair> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(new Pair(rootV, connectedComponentCount));
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Pair pair = queue.poll();
int v = pair.v;
if (visited[v]) {
continue;
}
visited[v] = true;
connectedComponents[v] = pair.connectedComponentCount;
graph.adj(v).forEach(w -> queue.add(new Pair(w, pair.connectedComponentCount)));
}
}
private static class Pair {
private int v;
private int connectedComponentCount;
Pair(int v, int connectedComponentCount) {
this.v = v;
this.connectedComponentCount = connectedComponentCount;
}
}
public int connectedComponentCount() {
return connectedComponentCount;
}
public Iterable<Iterable<Integer>> connectedComponentList() {
List<Iterable<Integer>> connectedComponentList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < connectedComponentCount; i++) {
connectedComponentList.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
for (int i = 0; i < connectedComponents.length; i++) {
((List<Integer>) connectedComponentList.get(connectedComponents[i])).add(i);
}
return connectedComponentList;
}
public boolean isConnected(int v, int w) {
graph.validateVertex(v);
graph.validateVertex(w);
return connectedComponents[v] == connectedComponents[w];
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
GraphCC graphCC = new GraphCC(new AdjSet("g.txt"));
System.out.println(graphCC.connectedComponentCount());
System.out.println(graphCC.connectedComponentList());
System.out.println(graphCC.isConnected(4, 6));
System.out.println(graphCC.isConnected(3, 5));
System.out.println(graphCC.isConnected(3, 7));
}
}
使用一个新的数据结构 Pair 来保存当前节点和当前节点的连通分量索引。
环检测

import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
/**
* 图中检测环(迭代实现)
*/
public class GraphCircle {
private boolean[] visited;
private Graph graph;
/**
* 是否存在环
*/
private boolean existsCircle;
public GraphCircle(Graph graph) {
this.graph = graph;
int v = graph.V();
visited = new boolean[v];
existsCircle = existsCircle();
}
public boolean isExistsCircle() {
return existsCircle;
}
private boolean existsCircle() {
int v = graph.V();
//多个连通子图有一个存在环就可以
for (int i = 0; i < v; i++) {
if (!visited[i]) {
if (existsCircle(i)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
private boolean existsCircle(int rootV) {
Queue<Pair> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(new Pair(rootV, rootV));
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Pair pair = queue.poll();
int v = pair.v;
if (visited[v]) {
continue;
}
visited[v] = true;
for (Integer w : graph.adj(v)) {
if (w != pair.preV && visited[w]) {
return true;
}
queue.add(new Pair(w, v));
}
}
return false;
}
private static class Pair {
private int v;
private int preV;
Pair(int v, int preV) {
this.v = v;
this.preV = preV;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
GraphCircle graphCircle = new GraphCircle(new AdjSet("g.txt"));
System.out.println(graphCircle.isExistsCircle());
}
}
二分图检测
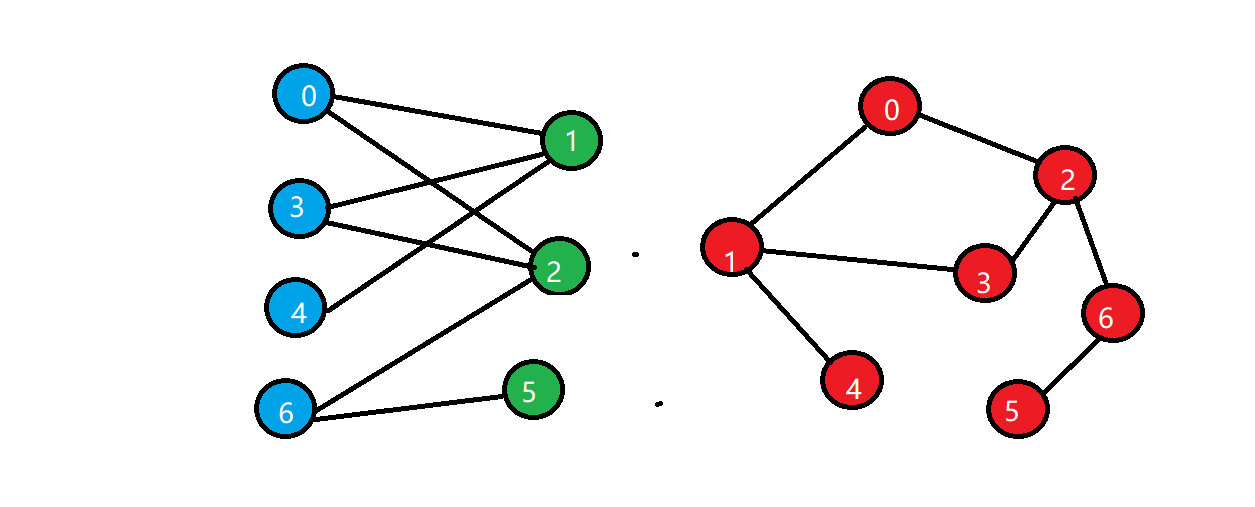
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
/**
* 检测图是否为二分图(将图中顶点分为两个不相交子集,每条边都分别连接两个集合中的顶点),迭代实现
*/
public class GraphHalf {
private boolean[] visited;
//每个顶点的颜色 -1未染色 0蓝色 1绿色
private int[] colors;
private Graph graph;
/**
* 是否为二分图
*/
private boolean half;
public GraphHalf(Graph graph) {
this.graph = graph;
int v = graph.V();
visited = new boolean[v];
colors = new int[v];
Arrays.fill(colors, -1);
half = half();
}
private boolean half() {
int v = graph.V();
for (int i = 0; i < v; i++) {
if (!visited[i]) {
if (!half(i)) {
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
private boolean half(int rootV) {
Queue<Pair> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(new Pair(rootV, -1));
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Pair pair = queue.poll();
int v = pair.v;
if (visited[v]) {
continue;
}
visited[v] = true;
colors[v] = getColor(pair.preColor);
for (Integer w : graph.adj(v)) {
if (isSameColor(v, w)) {
return false;
}
queue.add(new Pair(w, colors[v]));
}
}
return true;
}
private static class Pair {
private int v;
private int preColor;
Pair(int v, int preColor) {
this.v = v;
this.preColor = preColor;
}
}
public boolean isHalf() {
return half;
}
/**
* 根据前一个顶点的颜色获取当前顶点的颜色
*/
private int getColor(int preColor) {
//前一个顶点为蓝色,此顶点为绿色,前一个顶点未染色或为绿色,此顶点为蓝色
if (preColor == 0) {
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
/**
* 判断顶点v和顶点w颜色是否相同
*/
private boolean isSameColor(int v, int w) {
//如果顶点未染色也表示颜色不相同
if (colors[v] == -1 || colors[w] == -1) {
return false;
}
return colors[v] == colors[w];
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
GraphHalf graphCircle = new GraphHalf(new AdjSet("g.txt"));
System.out.println(graphCircle.isHalf());
}
}
路径问题
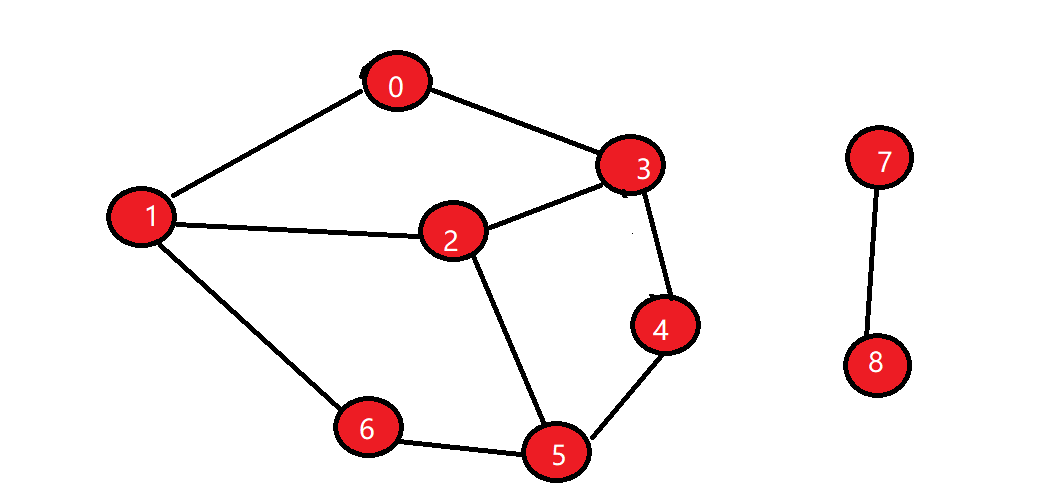
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Queue;
/**
* 图中两个顶点的路径(单源,不适用任意两点),迭代实现
*/
public class GraphRoute {
private boolean[] visited;
//源顶点
private int source;
private Graph graph;
//记录每个顶点的上一个顶点
private int[] pre;
public GraphRoute(Graph graph, int source) {
graph.validateVertex(source);
this.source = source;
this.graph = graph;
int v = graph.V();
visited = new boolean[v];
pre = new int[v];
Arrays.fill(pre, -1);
bfs();
}
private void bfs() {
Queue<Pair> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(new Pair(source, source));
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Pair pair = queue.poll();
int v = pair.v;
if (visited[v]) {
continue;
}
visited[v] = true;
pre[v] = pair.preV;
graph.adj(v).forEach(w -> queue.add(new Pair(w, v)));
}
}
private static class Pair {
private int v;
private int preV;
Pair(int v, int preV) {
this.v = v;
this.preV = preV;
}
}
public boolean isConnectTo(int w) {
graph.validateVertex(w);
return visited[w];
}
public Iterable<Integer> route(int w) {
graph.validateVertex(w);
List<Integer> route = new ArrayList<>();
if (!isConnectTo(w)) {
return route;
}
int preV = w;
while (true) {
route.add(preV);
if (preV == source) {
break;
}
preV = pre[preV];
}
Collections.reverse(route);
return route;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
GraphRoute graphRoute = new GraphRoute(new AdjSet("g.txt"), 0);
System.out.println(graphRoute.route(6));
System.out.println(graphRoute.route(7));
}
}
通过组合单源路径可以实现求任意两点之间的路径
/**
* 图中两个顶点的路径(多源,适用任意两点),最短路径
*/
public class MultiGraphRoute {
private Graph graph;
private GraphRoute[] graphRoutes;
public MultiGraphRoute(Graph graph) {
int v = graph.V();
this.graph = graph;
graphRoutes = new GraphRoute[v];
for (int i = 0; i < v; i++) {
graphRoutes[i] = new GraphRoute(graph, i);
}
}
/**
* 从v到w的路径
*/
public Iterable<Integer> route(int v, int w) {
graph.validateVertex(v);
graph.validateVertex(w);
return graphRoutes[v].route(w);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MultiGraphRoute graphRoute = new MultiGraphRoute(new AdjSet("g.txt"));
System.out.println(graphRoute.route(0, 6));
System.out.println(graphRoute.route(5, 2));
System.out.println(graphRoute.route(2, 5));
System.out.println(graphRoute.route(8, 5));
}
}
以求顶点0到顶点6之间的路径为例,深度优先遍历结果为0->1->2->3->4->5->6。
广度优先遍历结果为0->2->6。广度优先遍历求的路径就是两点之间的最短路径,
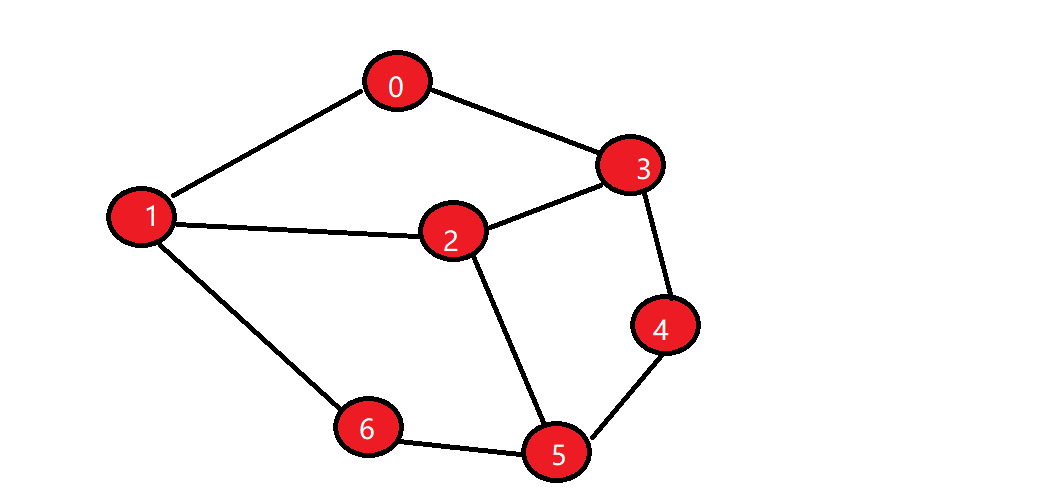
- 离顶点0的距离为0的顶点:0
- 离顶点0的距离为1的顶点:1,3
- 离顶点0的距离为2的顶点:6,2,4
- 离顶点0的距离为3的顶点:5
广度优先遍历就是按照距离来遍历的,先遍历的顶点距离肯定更小。








 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号