图的深度优先遍历及应用
简介
每种数据结构,都有自己的遍历方式,对于二叉树,有前序遍历,中序遍历,后序遍历,对于图,有深度优先遍历和广度优先遍历,今天先看深度优先遍历。

我们从0顶点开始遍历,深度遍历结果0-1->2->3->4->5->6。因为图中可能存在环,所以我们需要记录已经访问过的顶点。
代码实现
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 图的深度优先遍历
*/
public class GraphDFS {
/**
* 每个顶点是否已访问过
*/
private boolean[] visited;
/**
* 要遍历的图
*/
private Graph graph;
/**
* 遍历结果
*/
private List<Integer> preOrder;
public GraphDFS(Graph graph) {
this.graph = graph;
int v = graph.V();
visited = new boolean[v];
preOrder = new ArrayList<>();
//图中可能有多个联通子图,所有顶点都需要遍历
for (int i = 0; i < v; i++) {
if (!visited[i]) {
dfs(i);
}
}
}
private void dfs(int v) {
if (visited[v]) {
return;
}
visited[v] = true;
preOrder.add(v);
graph.adj(v).forEach(this::dfs);
}
public Iterable<Integer> preOrder() {
return preOrder;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
GraphDFS graphDFS = new GraphDFS(new AdjSet("g.txt"));
System.out.println(graphDFS.preOrder());
}
}
代码依赖上一篇中图的邻接表实现。输出结果为
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
应用
求连通分量和每个连通子图包含的具体顶点
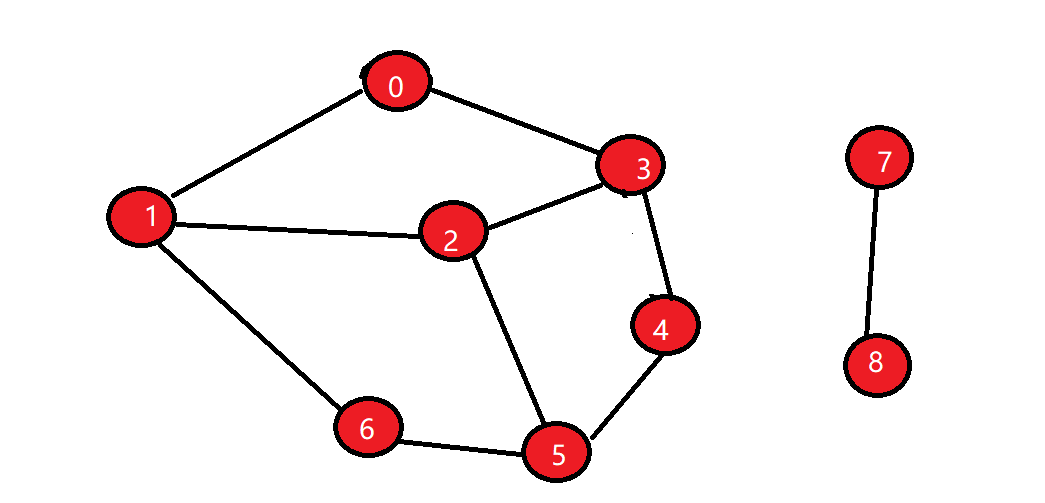
上图的连通分量为2,第一个连通子图包含顶点0,1,2,3,4,5,6,第二个连通子图包含顶点7,8。
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 求一个图的连通分量和每个连通子图的具体顶点
*/
public class GraphCC {
/**
* 每个顶点是否已访问过
*/
private boolean[] visited;
/**
* 每个顶点所在的连通分量索引 两个顶点的索引相等表示在同一个连通子图中
*/
private int[] connectedComponents;
private Graph graph;
/**
* 连通分量
*/
private int connectedComponentCount;
public GraphCC(Graph graph) {
this.graph = graph;
int v = graph.V();
visited = new boolean[v];
connectedComponents = new int[v];
for (int i = 0; i < v; i++) {
if (!visited[i]) {
dfs(i, connectedComponentCount);
connectedComponentCount++;
}
}
}
private void dfs(int v, int connectedComponentCount) {
if (visited[v]) {
return;
}
visited[v] = true;
connectedComponents[v] = connectedComponentCount;
graph.adj(v).forEach(vv -> dfs(vv, connectedComponentCount));
}
public int connectedComponentCount() {
return connectedComponentCount;
}
public Iterable<Iterable<Integer>> connectedComponentList() {
List<Iterable<Integer>> connectedComponentList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < connectedComponentCount; i++) {
connectedComponentList.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
for (int i = 0; i < connectedComponents.length; i++) {
((List<Integer>) connectedComponentList.get(connectedComponents[i])).add(i);
}
return connectedComponentList;
}
public boolean isConnected(int v, int w) {
graph.validateVertex(v);
graph.validateVertex(w);
return connectedComponents[v] == connectedComponents[w];
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
GraphCC graphCC = new GraphCC(new AdjSet("g.txt"));
System.out.println(graphCC.connectedComponentCount());
System.out.println(graphCC.connectedComponentList());
System.out.println(graphCC.isConnected(4, 6));
System.out.println(graphCC.isConnected(3, 5));
}
}
路径问题
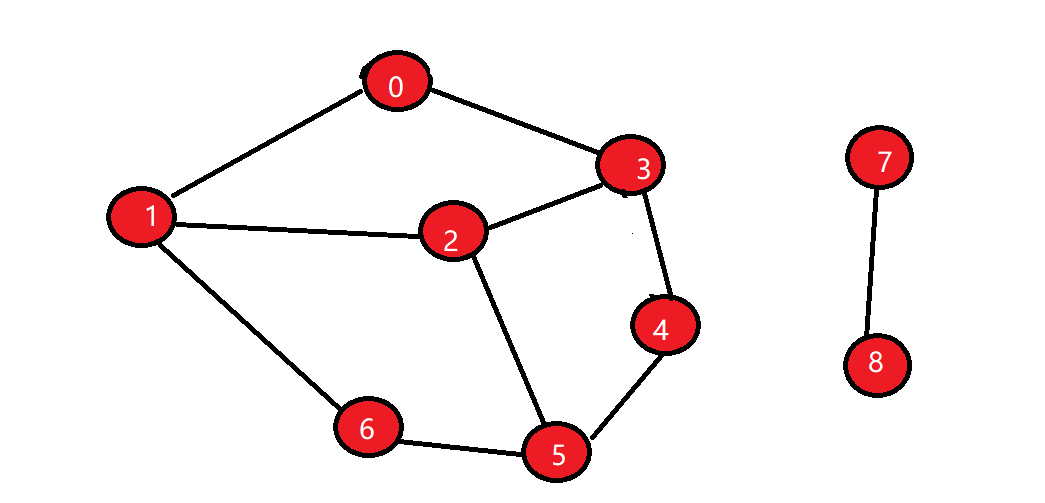
求两个顶点之间的路径,如顶点0和顶点5之间的路径0->1->2->3->4->5。
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 图中两个顶点的路径(单源,不适用任意两点)
*/
public class GraphRoute {
private boolean[] visited;
//源顶点
private int source;
private Graph graph;
//记录每个顶点的上一个顶点
private int[] pre;
public GraphRoute(Graph graph, int source) {
graph.validateVertex(source);
this.source = source;
this.graph = graph;
int v = graph.V();
visited = new boolean[v];
pre = new int[v];
Arrays.fill(pre, -1);
dfs(source, source);
}
private void dfs(int preV, int v) {
if (visited[v]) {
return;
}
visited[v] = true;
pre[v] = preV;
graph.adj(v).forEach(vv -> dfs(v, vv));
}
public boolean isConnectTo(int w) {
graph.validateVertex(w);
return visited[w];
}
public Iterable<Integer> route(int w) {
graph.validateVertex(w);
List<Integer> route = new ArrayList<>();
if (!isConnectTo(w)) {
return route;
}
int preV = w;
while (true) {
route.add(preV);
if (preV == source) {
break;
}
preV = pre[preV];
}
Collections.reverse(route);
return route;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
GraphRoute graphRoute = new GraphRoute(new AdjSet("g.txt"), 0);
System.out.println(graphRoute.route(6));
System.out.println(graphRoute.route(7));
}
}
上面的代码只能求每个顶点到一个固定顶点的路径,不支持任意两个顶点的路径。
/**
* 图中两个顶点的路径(多源,适用任意两点)
*/
public class MultiGraphRoute {
private Graph graph;
private GraphRoute[] graphRoutes;
public MultiGraphRoute(Graph graph) {
int v = graph.V();
this.graph = graph;
graphRoutes = new GraphRoute[v];
for (int i = 0; i < v; i++) {
graphRoutes[i] = new GraphRoute(graph, i);
}
}
/**
* 从v到w的路径
*/
public Iterable<Integer> route(int v, int w) {
graph.validateVertex(v);
graph.validateVertex(w);
return graphRoutes[v].route(w);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MultiGraphRoute graphRoute = new MultiGraphRoute(new AdjSet("g.txt"));
System.out.println(graphRoute.route(0, 6));
System.out.println(graphRoute.route(5, 2));
System.out.println(graphRoute.route(2, 5));
System.out.println(graphRoute.route(8, 7));
}
}
支持任意两个顶点之间的路径。
环检测
/**
* 图中检测环
*/
public class GraphCircle {
private boolean[] visited;
private Graph graph;
/**
* 是否存在环
*/
private boolean existsCircle;
public GraphCircle(Graph graph) {
this.graph = graph;
int v = graph.V();
visited = new boolean[v];
existsCircle = existsCircle();
}
public boolean isExistsCircle() {
return existsCircle;
}
private boolean existsCircle() {
int v = graph.V();
//多个连通子图有一个存在环就可以
for (int i = 0; i < v; i++) {
if (!visited[i]) {
if (existsCircle(i, i)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
private boolean existsCircle(int preV, int v) {
if (visited[v]) {
return false;
}
visited[v] = true;
for (Integer vv : graph.adj(v)) {
if (vv != preV && visited[vv]) {
return true;
}
if (existsCircle(v, vv)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
GraphCircle graphCircle = new GraphCircle(new AdjSet("g.txt"));
System.out.println(graphCircle.isExistsCircle());
}
}
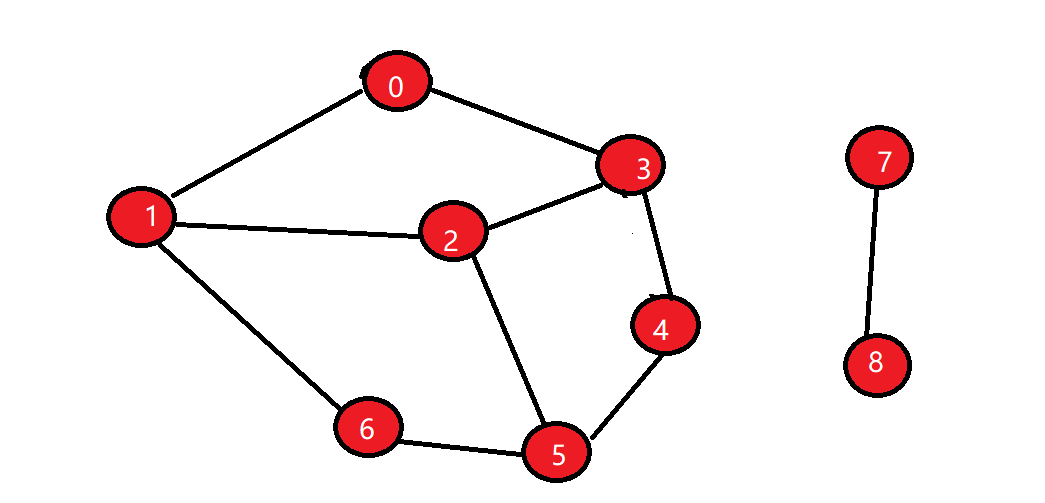
在遍历的过程中如果一个顶点的邻接顶点已经访问过且邻接顶点不是当前顶点的前一个顶点,就表示存在环,如上图,访问顺序为0->1->2->3->4->5->6,在访问顶点3时,3的邻接顶点有0,2,4,2已经访问过但2是3的前一个顶点,0也已经访问过且不是前一个顶点,这种情况表示存在环。
二分图检测
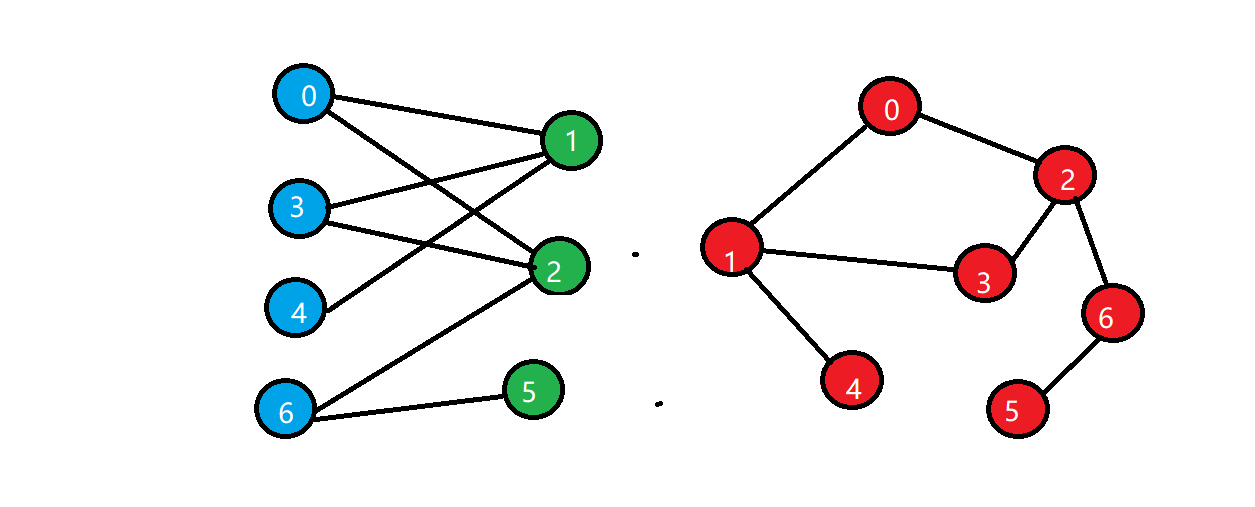
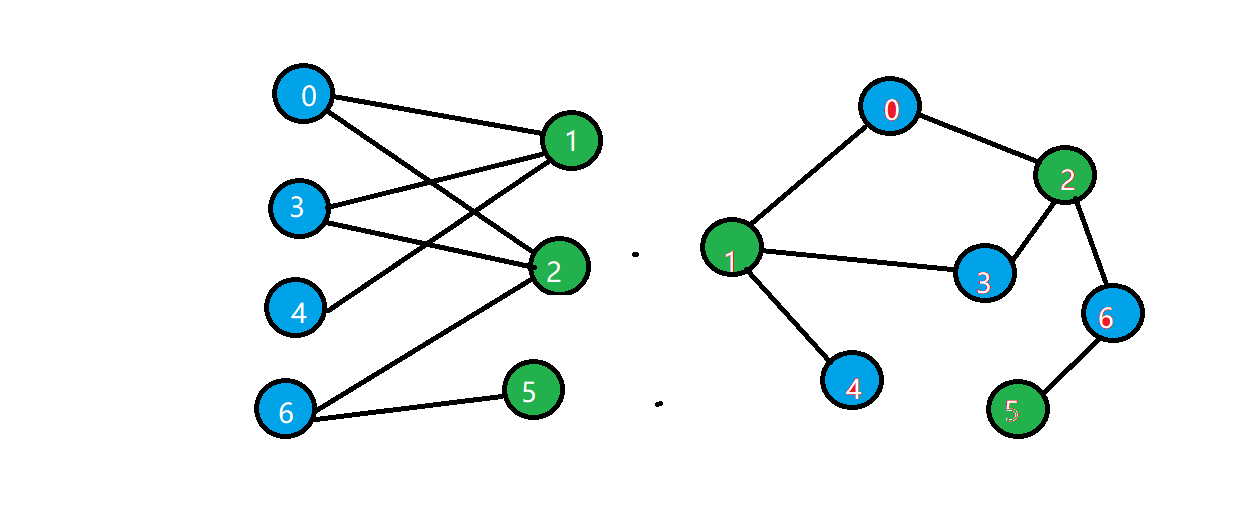
二分图:顶点可以分成不相交的两部分,所有边的两个端点隶属于不同的两部分。
上图中左右图是等价的,都是二分图。
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* 检测图是否为二分图(将图中顶点分为两个不相交子集,每条边都分别连接两个集合中的顶点)
*/
public class GraphHalf {
private boolean[] visited;
//每个顶点的颜色 -1未染色 0蓝色 1绿色
private int[] colors;
private Graph graph;
/**
* 是否为二分图
*/
private boolean half;
public GraphHalf(Graph graph) {
this.graph = graph;
int v = graph.V();
visited = new boolean[v];
colors = new int[v];
Arrays.fill(colors, -1);
half = half();
}
private boolean half() {
int v = graph.V();
for (int i = 0; i < v; i++) {
if (!visited[i]) {
if (!half(-1, i)) {
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
private boolean half(int preColor, int v) {
if (visited[v]) {
return true;
}
visited[v] = true;
colors[v] = getColor(preColor);
for (Integer vv : graph.adj(v)) {
if (isSameColor(v, vv)) {
return false;
}
if (!half(colors[v], vv)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public boolean isHalf() {
return half;
}
/**
* 根据前一个顶点的颜色获取当前顶点的颜色
*/
private int getColor(int preColor) {
//前一个顶点为蓝色,此顶点为绿色,前一个顶点未染色或为绿色,此顶点为蓝色
if (preColor == 0) {
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
/**
* 判断顶点v和顶点w颜色是否相同
*/
private boolean isSameColor(int v, int w) {
//如果顶点未染色也表示颜色不相同
if (colors[v] == -1 || colors[w] == -1) {
return false;
}
return colors[v] == colors[w];
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
GraphHalf graphCircle = new GraphHalf(new AdjSet("g.txt"));
System.out.println(graphCircle.isHalf());
}
}
在遍历过程中,给每个顶点染色,当前顶点染成蓝色,它的邻接顶点就染成绿色,如果遇到和邻接顶点颜色相同说明不是二分图。染色后的图为








 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号