图的基本表示-邻接矩阵和邻接表
简介
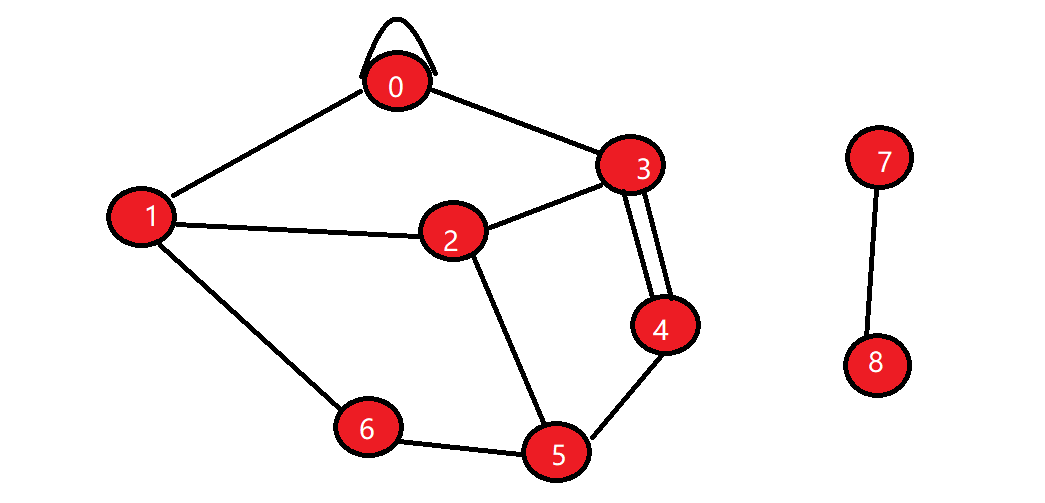
一个图主要包括顶点和边两部分。
- 自环边
自己到自己形成的边,如图中的0顶点 - 平行边
顶点3和顶点4这种情况就是平行边 - 简单图
没有自环边和平行边的图 - 连通图
图中任意两个顶点之间都有路径 - 连通分量
图中包含的连通子图的个数,如上图有2个连通分量 - 有环图
图中顶点之间可以形成环,上图0,1,2,3顶点之间存在环。
图根据边是否有方向和边是否有权重可以分为
- 无向无权图,如好友关系
- 有向无权图,如关注关系
- 无向有权图,如城市之间的关系,城市之间的距离就是权重
- 有向有权图,如一个城市的地铁线路
图的表示方式
以无向无权图且简单图为例。图有两种表示方式,邻接矩阵和邻接表。
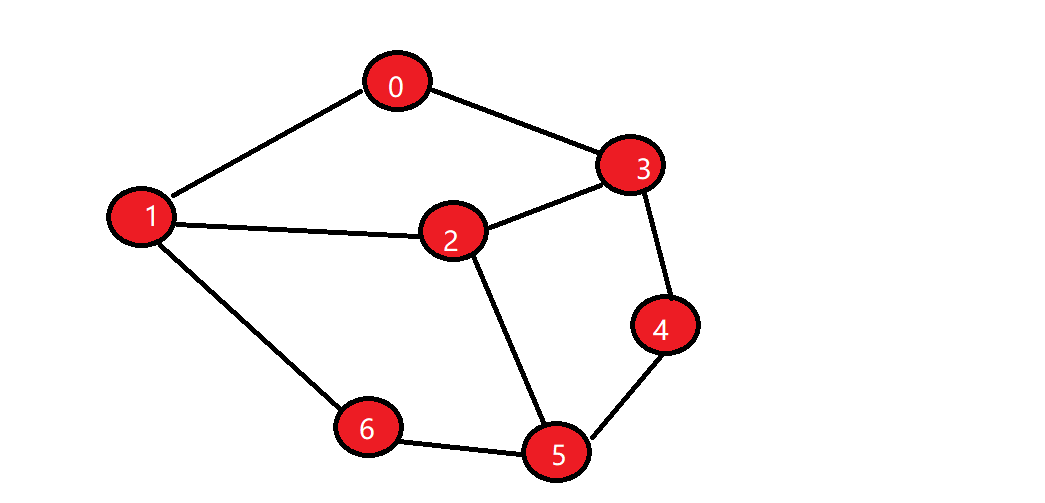
邻接矩阵
使用邻接矩阵表示为
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 3 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 5 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 6 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| A[i][j]=1表示顶点i和订单j相邻 |
代码实现
定义一个接口表示图的各种操作
public interface Graph {
/**
* 查询总顶点数
*/
int V();
/**
* 查询总边数
*/
int E();
/**
* 两个顶点之间是否有边
*/
boolean hasEdge(int v, int w);
/**
* 查询一个顶点的所有连接顶点
*/
Iterable<Integer> adj(int v);
/**
* 查询一个顶点的度(连接顶点的个数)
*/
int degree(int v);
/**
* 检查v顶点是否合法
*/
void validateVertex(int v);
}
邻接矩阵实现
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class AdjMatrix implements Graph {
/**
* 总顶点数
*/
private int V;
/**
* 总边数
*/
private int E;
/**
* 顶点之间的关系
*/
private int[][] adj;
public AdjMatrix(String fileName) {
try (InputStream is = AdjMatrix.class.getResourceAsStream(fileName);
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(is)) {
V = scanner.nextInt();
if (V < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("V must be non-negative");
}
adj = new int[V][V];
E = scanner.nextInt();
if (E < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("E must be non-negative");
}
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
int a = scanner.nextInt();
validateVertex(a);
int b = scanner.nextInt();
validateVertex(b);
if (a == b) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Self Loop is Detected!");
}
if (adj[a][b] == 1) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Parallel Edges are Detected!");
}
adj[a][b] = 1;
adj[b][a] = 1;
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void validateVertex(int v) {
if (v < 0 || v >= V) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("vertex " + v + "is invalid");
}
}
@Override
public int V() {
return V;
}
@Override
public int E() {
return E;
}
@Override
public boolean hasEdge(int v, int w) {
validateVertex(v);
validateVertex(w);
return adj[v][w] == 1;
}
@Override
public Collection<Integer> adj(int v) {
validateVertex(v);
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
if (adj[v][i] == 1) {
res.add(i);
}
}
return res;
}
@Override
public int degree(int v) {
return adj(v).size();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append(String.format("V = %d, E = %d\n", V, E));
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < V; j++) {
sb.append(String.format("%d ", adj[i][j]));
}
sb.append('\n');
}
return sb.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Graph graph = new AdjMatrix("g.txt");
System.out.println(graph);
System.out.println(graph.degree(0));
System.out.println(graph.adj(0));
}
}
g.txt为数据文件,内容如下
7 9
0 1
0 3
1 2
1 6
3 2
3 4
5 6
5 2
5 4
第一行表示顶点个数和边个数,后面行表示顶点和顶点之间的连接关系。
邻接矩阵空间复杂度为O(V^2),V表示顶点数,求相邻顶点时间复杂度为O(V),求两个顶点之间是否相邻时间复杂度为O(1)。对于稀疏图(边个数远小于顶点数的平方),邻接矩阵这种表示方式会造成大量的空间浪费,时间复杂度也比较高,我们可以使用邻接表来优化。
邻接表
0 : 1 3
1 : 0 2 6
2 : 1 3 5
3 : 0 2 4
4 : 3 5
5 : 6 2 4
6 : 1 5
每个顶点关联一个链表,表示邻接顶点
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class AdjList implements Graph {
private int V;
private int E;
private LinkedList<Integer>[] adj;
public AdjList(String fileName) {
try (InputStream is = AdjList.class.getResourceAsStream(fileName);
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(is)) {
V = scanner.nextInt();
if (V < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("V must be non-negative");
}
adj = new LinkedList[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
adj[i] = new LinkedList<>();
}
E = scanner.nextInt();
if (E < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("E must be non-negative");
}
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
int a = scanner.nextInt();
validateVertex(a);
int b = scanner.nextInt();
validateVertex(b);
if (a == b) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Self Loop is Detected!");
}
if (adj[a].contains(b)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Parallel Edges are Detected!");
}
adj[a].add(b);
adj[b].add(a);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void validateVertex(int v) {
if (v < 0 || v >= V) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("vertex " + v + "is invalid");
}
}
@Override
public int V() {
return V;
}
@Override
public int E() {
return E;
}
@Override
public boolean hasEdge(int v, int w) {
validateVertex(v);
validateVertex(w);
return adj[v].contains(w);
}
@Override
public Iterable<Integer> adj(int v) {
validateVertex(v);
return adj[v];
}
@Override
public int degree(int v) {
validateVertex(v);
return adj[v].size();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append(String.format("V = %d, E = %d\n", V, E));
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) {
sb.append(String.format("%d : ", v));
for (int w : adj[v]) {
sb.append(String.format("%d ", w));
}
sb.append('\n');
}
return sb.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
AdjList adjList = new AdjList("g.txt");
System.out.print(adjList);
}
}
这里使用LinkedList来保存顶点的邻接顶点,空间复杂度为O(V+E),V表示顶点数,E表示边数,求两个顶点是否相邻和求顶点的邻接顶点的时间复杂度都为O(degree(v)),degree(v)表示一个顶点的度,一般远远小于顶点数V。那么有没有更好的性能呢,我们可以使用TreeSet代替LinkedList,将时间复杂度降为O(logV)。
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.TreeSet;
public class AdjSet implements Graph {
private int V;
private int E;
private TreeSet<Integer>[] adj;
public AdjSet(String fileName) {
try (InputStream is = AdjSet.class.getResourceAsStream(fileName);
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(is)) {
V = scanner.nextInt();
if (V < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("V must be non-negative");
}
adj = new TreeSet[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
adj[i] = new TreeSet<Integer>();
}
E = scanner.nextInt();
if (E < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("E must be non-negative");
}
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
int a = scanner.nextInt();
validateVertex(a);
int b = scanner.nextInt();
validateVertex(b);
if (a == b) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Self Loop is Detected!");
}
if (adj[a].contains(b)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Parallel Edges are Detected!");
}
adj[a].add(b);
adj[b].add(a);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void validateVertex(int v) {
if (v < 0 || v >= V) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("vertex " + v + "is invalid");
}
}
@Override
public int V() {
return V;
}
@Override
public int E() {
return E;
}
@Override
public boolean hasEdge(int v, int w) {
validateVertex(v);
validateVertex(w);
return adj[v].contains(w);
}
@Override
public Iterable<Integer> adj(int v) {
validateVertex(v);
return adj[v];
}
@Override
public int degree(int v) {
validateVertex(v);
return adj[v].size();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append(String.format("V = %d, E = %d\n", V, E));
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) {
sb.append(String.format("%d : ", v));
for (int w : adj[v]) {
sb.append(String.format("%d ", w));
}
sb.append('\n');
}
return sb.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
AdjSet adjSet = new AdjSet("g.txt");
System.out.print(adjSet);
}
}
方式比较
| 空间 | 建图时间 | 查看两点是否相邻 | 查找点的所有相邻顶点 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 邻接矩阵 | O(V^2) | O(E) | O(1) | O(V) |
| 邻接表(LinkedList) | O(V+E) | O(E*V) | O(degree(v)) | O(degree(v)) |
| 邻接表(TreeSet) | O(V+E) | O(ElogV) | O(logV) | O(degree(v)) |
| 综合比较,邻接表(TreeSet)性能更好。 |








 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号