注解与反射
注解和反射
1、内置注解
重写注解
//@Override 重写注解
@Override
public String toString() {
return super.toString();
}
package annotation;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Test01 {
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public static void main(String[] args) {
test();
}
//@Override 重写注解
@Override
public String toString() {
return super.toString();
}
//Deprecated 不推荐程序员使用,但是可以使用,或则存在更好的方式
@Deprecated
public static void test(){
System.out.println("Deprecated");
}
public void test02(){
List list = new ArrayList();
}
}
2、元注解
package annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
//测试元注解
@MyAnnotation
public class Test02 {
public void test(){
}
}
//定义一个注解
//Target 表示我们的注解可以用在哪些地方
@Target( value = {ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE})
//Retention 表示我们的注解在什么地方都有效
// runtime >class>sources
@Retention(value = RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
//Documented 表示是否将我们的注解生成在JavaDoc中
@Documented
//Inherited 子类可以继承父类的注解
@Inherited
@interface MyAnnotation{
}
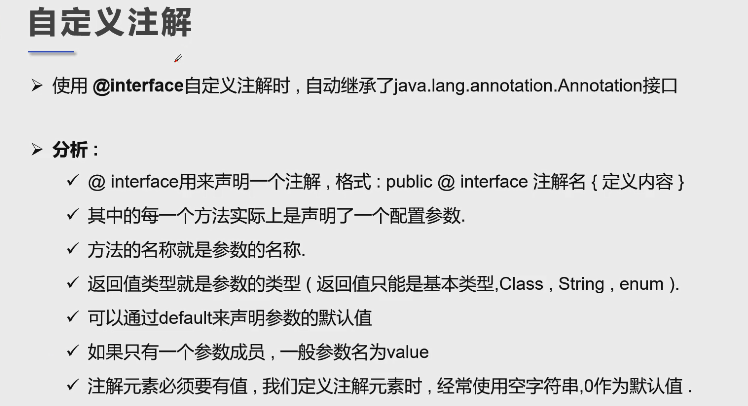
3、自定义注解
package annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
//自定义注解
public class Test03 {
//注解可以显示赋值 , 如果没有默认值,我们就必须给注解赋值
@MyAnnotation2(age = 21 ,name = "HLX")
public void test(){ }
@MyAnnotation3(value = "shoumi")
public void test2(){
}
}
@Target(value = {ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@interface MyAnnotation2{
//注解的参数:参数类型 + 参数名();
String name() default"";
int age();
int id() default -1;//如果默认值为-1,代表不存在。
String[] schools() default{"冲", "收"};
}
@Target(value = {ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@interface MyAnnotation3{
String value();
}
4、反射(Reflection)


反射的优缺点
优点:可以实现动态创建对象和编译,体现出很大的灵活性
缺点:对性能有影响;使用反射基本上是一种解释操作,我么可以告诉JVM,我们希望做什么并且它满足我们的要求;这类操作总是慢于直接执行相同的操作。

在Object类中定义了一下的方法,此方法将被所有子类继承

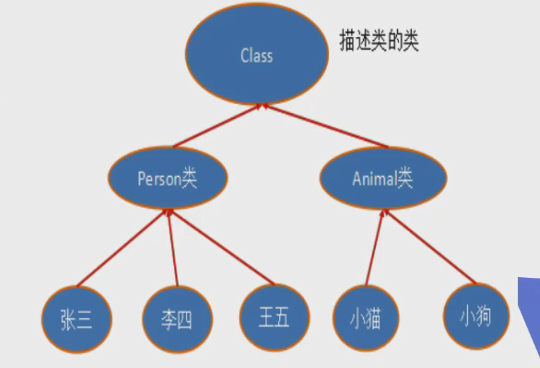
以上的方法返回值都是一个class类,此类是Java反射的源头,实际上所谓反射从程序的运行结果来看也很好理解,,即:可以通过反射求出类的名称。

package flection;
//测试class类的创建方式有哪些
public class Test02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
Person person = new Student();
System.out.println("这个人是:" + person.name);
//方式一:通过对象获得
Class c1 = person.getClass();
System.out.println(c1.hashCode());
//方式二:forName获得
Class c2 = Class.forName("flection.Student");
System.out.println(c2.hashCode());
//方式三:通过类名 .clas获得
Class c3 = Student.class;
System.out.println(c3.hashCode());
//方式四:基本内置类型的包装类都有一个Type属性
Class c4 = Integer.TYPE;
System.out.println(c4);
//获得父类类型
Class c5 = c1.getSuperclass();
System.out.println(c5);
}
}
class Person{
public String name;
public Person() {
}
public Person(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
class Student extends Person {
public Student(){
this.name = "学生";
}
}
class Teacher extends Person {
public Teacher(){
this.name = "老师";
}
}
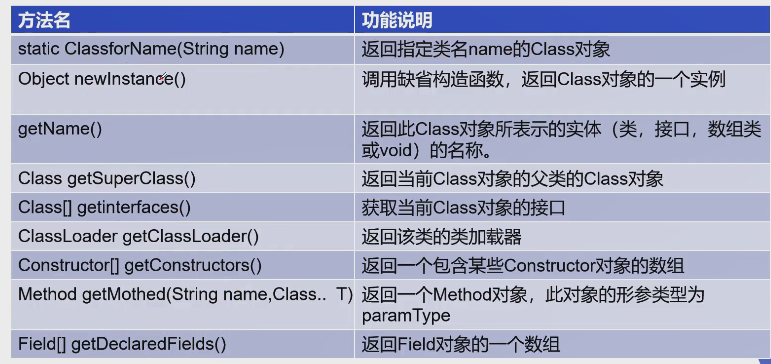
哪些类型可以有Class对象?

package flection;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
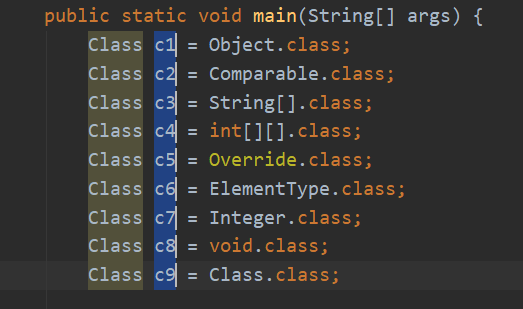
public class Test03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Class c1 = Object.class;
Class c2 = Comparable.class;
Class c3 = String[].class;
Class c4 = int[][].class;
Class c5 = Override.class;
Class c6 = ElementType.class;
Class c7 = Integer.class;
Class c8 = void.class;
Class c9 = Class.class;
System.out.println(c1);
System.out.println(c2);
System.out.println(c3);
System.out.println(c4);
System.out.println(c5);
System.out.println(c6);
System.out.println(c7);
System.out.println(c8);
System.out.println(c9);
//只要元素类型与维度一样,就是同一个Class。
int [] a = new int[10];
int [] b = new int[100];
System.out.println(a.getClass().hashCode());
System.out.println(b.getClass().hashCode());
}
}
IDEA操作小技巧
1.按住alt,用鼠标选择想要复制的
2.Ctrl + D:复制出相同的语句块
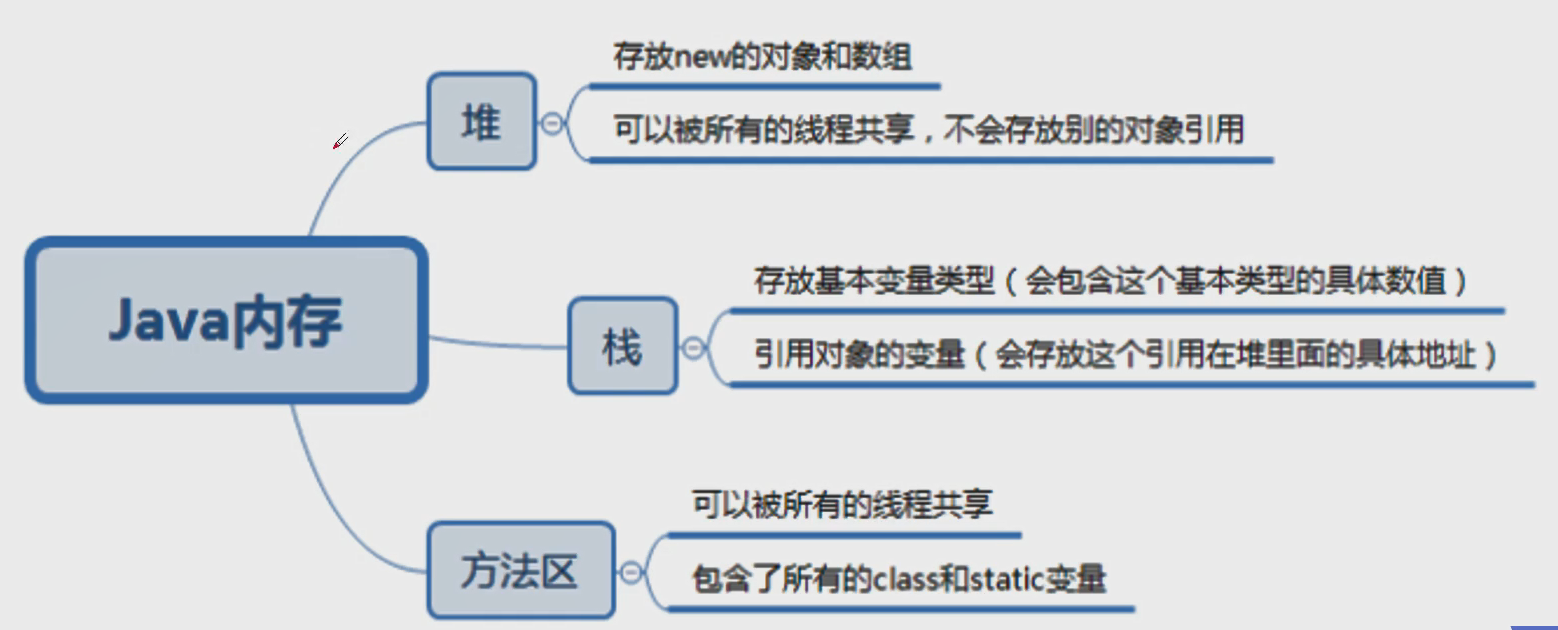
5、Java内存分析
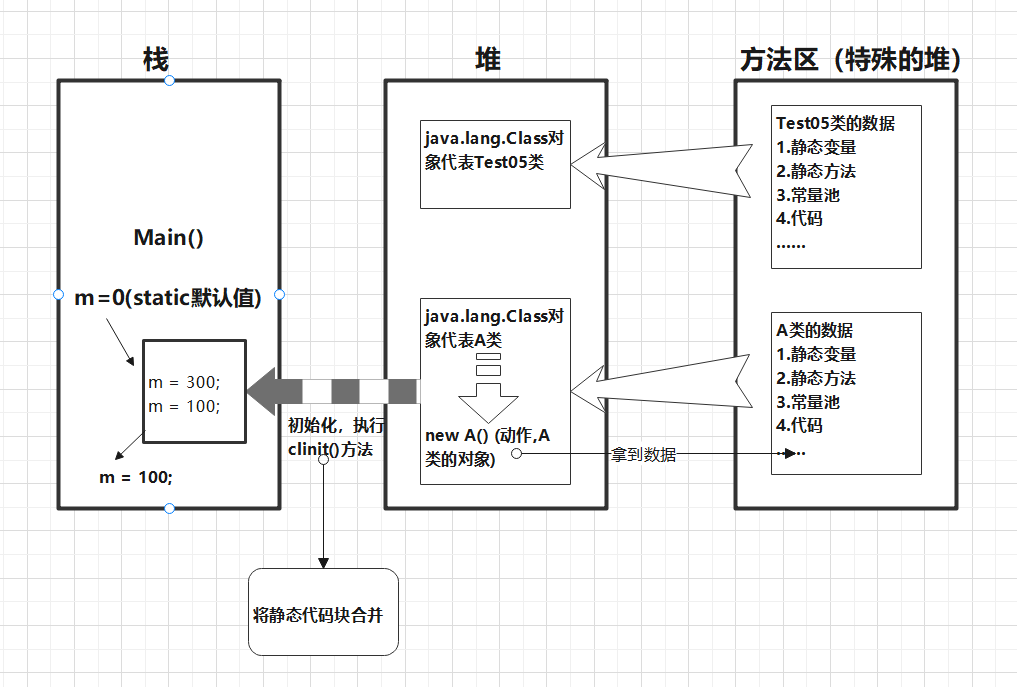
6、类的加载

package flection;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
A a = new A();
System.out.println((A.m));
/*
1.加载到内存,会产生一个类对应的class对象
2.链接,链接结束后m = 0
3.初始化
<clinit>(){
System.out.println("A类静态代码块初始化")
m = 300;
m = 100;
}
m = 100;
* */
}
}
class A{
static {
System.out.println("A类静态代码块初始话");
m = 300;
}
/*
* m = 300
* m = 100
* */
static int m = 100;
public A(){
System.out.println("A类的无参构造初始话");
}
}
7、什么时候会发生类初始化?

package flection;
//测试类什么时候会初始化
public class Test05 {
static {
System.out.println("Main类被加载");
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
// // 1.主动引用
// Son son = new Son();
// // 2.反射也会产生主动引用
// Class.forName("flection.Son");
//
// //不会产生类的引用的方法
// System.out.println(Son.b);
// Son[] array = new Son[5];
System.out.println(Son.M);
}
}
class Father{
static int b = 2;
static{
System.out.println("父类被加载");
}
}
class Son extends Father{
static{
System.out.println("子类被加载");
m = 300;
}
static int m = 100;
static final int M = 1;
}
8、类加载器的作用

package flection;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
//获得类的信息
public class Test07 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException, NoSuchMethodException {
Class c1 = Class.forName("flection.User");
//获取类的名字
System.out.println(c1.getName()); //获得包名 + 类名
System.out.println(c1.getSimpleName()); //获得类名
//获得类的属性
System.out.println("==============================");
//两个区别
Field[] fields = c1.getFields(); // 只能找到public属性
fields = c1.getDeclaredFields(); //获得全部的属性
for (Field field : fields) { //找到全部的属性
System.out.println(field);
}
//获得指定的属性的值
Field name = c1.getDeclaredField("name");
System.out.println(name);
//获取类的方法
System.out.println("==========================");
Method[] methods = c1.getMethods();//获得本类及其父类的全部public方法
for (Method method:methods) {
System.out.println("正常的" + method);
}
methods = c1.getDeclaredMethods(); //获得本类的所有方法
for(Method method :methods){
System.out.println("getDeclaredMethods" + method);
}
//获得指定的方法
//重载
Method getName = c1.getMethod("getName",null);
Method setName = c1.getMethod("setName", String.class);
System.out.println(getName);
System.out.println(setName);
//获得指定的构造器
System.out.println("================");
//获得public方法
Constructor[] constructors = c1.getConstructors();
for (Constructor constructor : constructors) {
System.out.println(constructor);
}
//获得本类的所有方法
constructors = c1.getDeclaredConstructors();
for (Constructor constructor : constructors) {
System.out.println("getDeclaredConstructors"+constructor);
}
//获得指定的构造器
Constructor declaredConstructor = c1.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class, int.class, int.class);
System.out.println("DeC指定:"+declaredConstructor);
}
}
9、有了Class对象,我们能做什么???

调用指定的方法-->invoke


package flection;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class Test08 {
//动态创建的对象,通过反射
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, NoSuchFieldException {
//获得class对象
Class c1 = Class.forName("flection.User");
//构造一个对象
// User user = (User)c1.newInstance(); //本质是调用了类的无参构造器
// System.out.println(user);
//通过构造器创建对象
// Constructor constructor = c1.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class, int.class, int.class);
// User user2 = (User) constructor.newInstance("流星", 001, 18);
// System.out.println(user2);
// //通过反射调用普通方法
// User user3 = (User)c1.newInstance();
// //通过反射获取一个方法
// Method setName = c1.getDeclaredMethod("setName", String.class);
//
// //invoke :激活的意思
// //(对象 , "方法的值")
// setName.invoke(user3,"帅哥");
// System.out.println(user3.getName());
//通过反射操作属性
System.out.println("=============================");
User user4 = (User)c1.newInstance();
Field name = c1.getDeclaredField("name");
//不能直接操作私有属性,我们需要关闭程序的安全检测,属性或方法的setAccessible(true);
name.setAccessible(true);
name.set(user4,"星冰乐");
System.out.println(user4.getName());
}
}
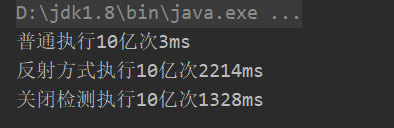
setAccessible性能检测对比
package flection;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
//分析性能问题
public class Test93 {
//普通方式调用
public static void test01(){
User user = new User();
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000000; i++) {
user.getName();
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("普通执行10亿次" + (endTime - startTime) + "ms");
}
//反射方式调用
public static void test02() throws NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
User user = new User();
Class c1 = user.getClass();
Method getName = c1.getDeclaredMethod("getName", null);
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000000; i++) {
getName.invoke(user,null);
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("反射方式执行10亿次" + (endTime - startTime) + "ms");
}
//反射方式调用 关闭检测
public static void test03() throws NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
User user = new User();
Class c1 = user.getClass();
Method getName = c1.getDeclaredMethod("getName", null);
getName.setAccessible(true);
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000000; i++) {
getName.invoke(user,null);
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("关闭检测执行10亿次" + (endTime - startTime) + "ms");
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException {
test01();
test02();
test03();
}
}
通过反射获取注解
package flection;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
public class Test10 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException {
Class<?> c1 = Class.forName("flection.student2");
//通过反射获得注解
Annotation[] annotations = c1.getAnnotations();
for (Annotation annotation : annotations) {
System.out.println(annotation);
}
//获得注解value的值
TableHuang tableHuang = (TableHuang) c1.getAnnotation(TableHuang.class);
String value = tableHuang.value();
System.out.println(value);
//获得类指定的注解
Field f = c1.getDeclaredField("name");
FieldHuang annotation = f.getAnnotation(FieldHuang.class);
System.out.println(annotation.columnName());
System.out.println(annotation.type());
System.out.println(annotation.length());
}
}
@TableHuang("db_student")
class student2 {
@FieldHuang(columnName = "db_id",type = "int",length = 10)
private int id ;
@FieldHuang(columnName = "db_age",type = "int",length = 10)
private int age;
@FieldHuang(columnName = "db_name",type = "varchar",length = 12)
private String name;
public student2() {
}
public student2(int id, int age, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "student2{" +
"id=" + id +
", age=" + age +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
//类名的注解
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@interface TableHuang{
String value();
}
//属性的注解
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@interface FieldHuang{
String columnName();
String type();
int length();
}




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· Manus的开源复刻OpenManus初探
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· 三行代码完成国际化适配,妙~啊~
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?