win32 - 匿名管道的使用
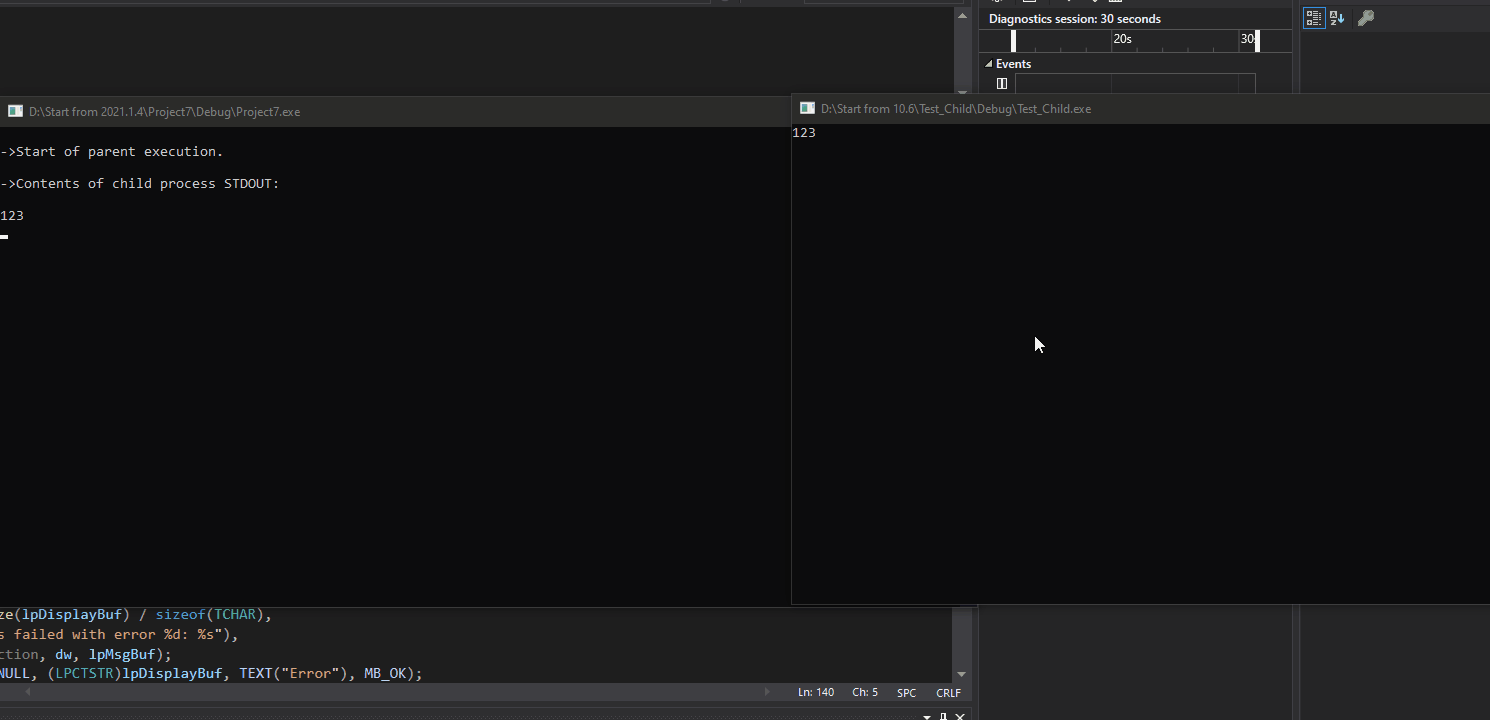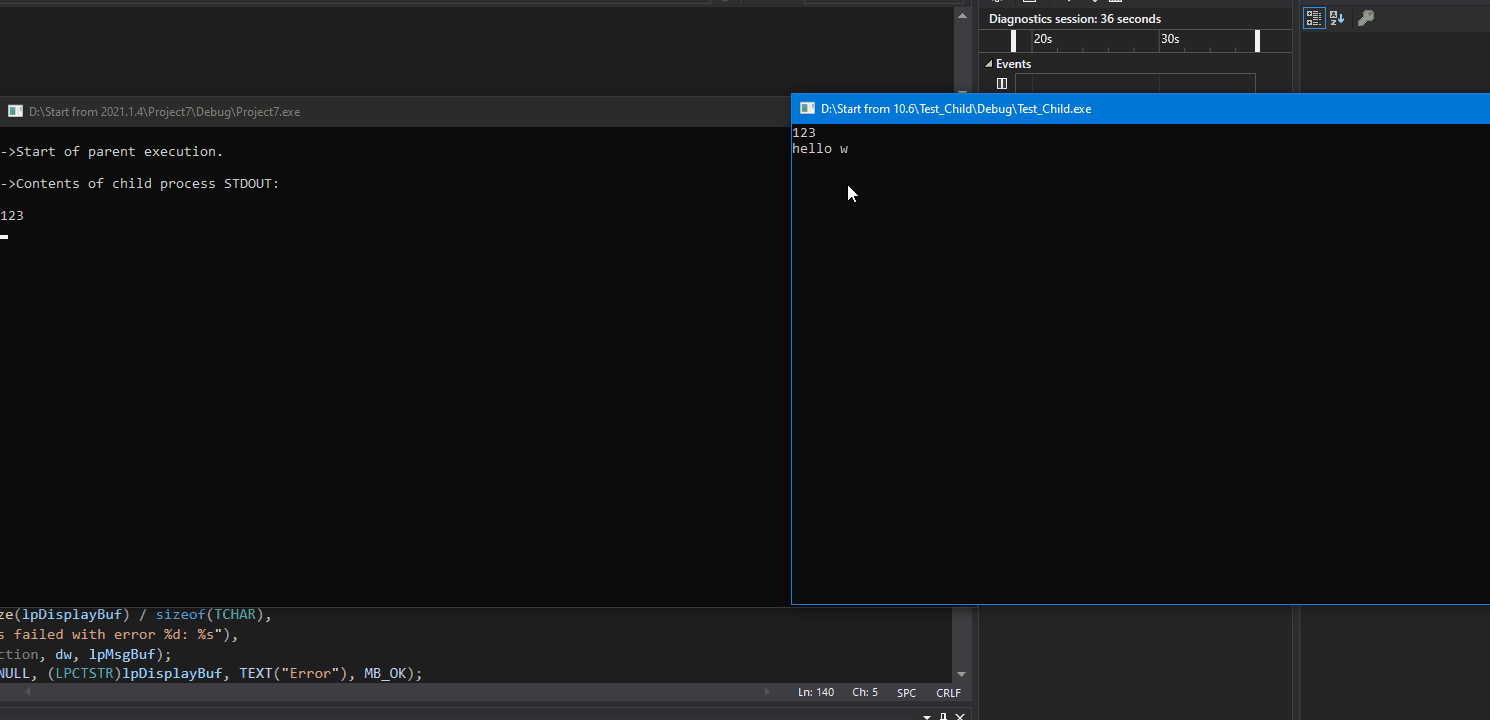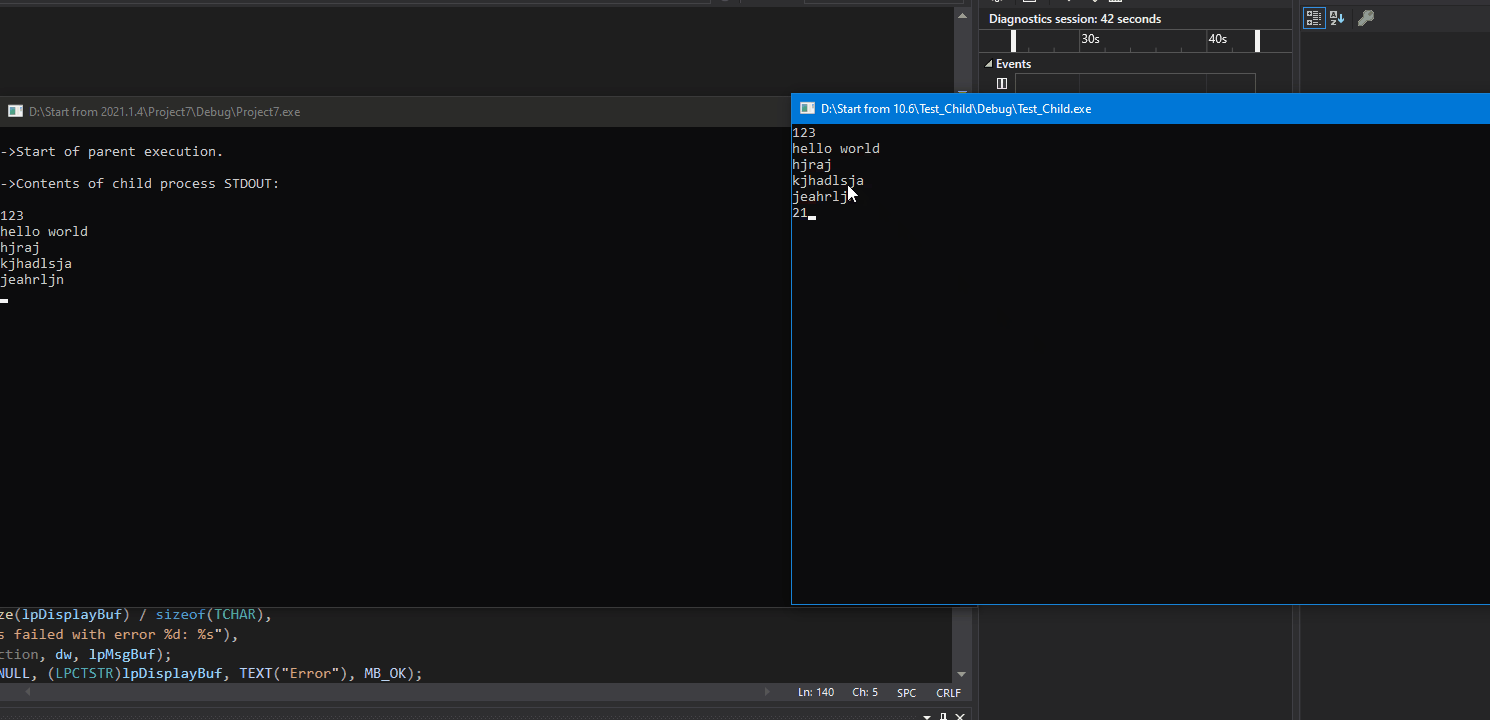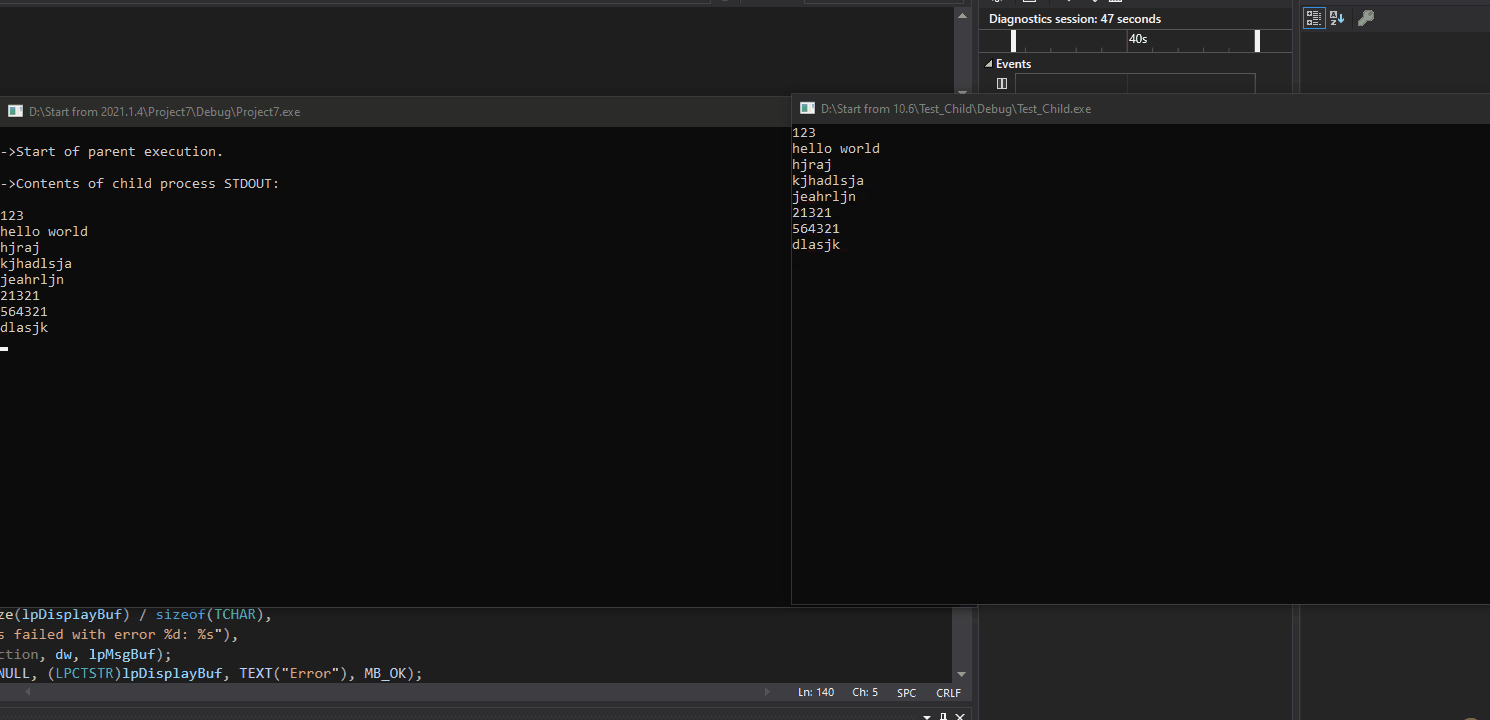
目标: 创建一个父进程和子进程,在子进程的控制台窗口输入数据,数据通过管道发送给父进程,父进程的控制台窗口读取数据,最后将数据打印出来。
Parent.cpp
//CMD.exe #include <windows.h> #include <tchar.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <strsafe.h> #define BUFSIZE 4096 HANDLE g_hChildStd_Rd = NULL; HANDLE g_hChildStd_Wr = NULL; HANDLE g_hInputFile = NULL; void CreateChildProcess(void); void ReadFromPipe(void); void ErrorExit(LPCWSTR); int _tmain(int argc, TCHAR* argv[]) { SECURITY_ATTRIBUTES saAttr; printf("\n->Start of parent execution.\n"); // Set the bInheritHandle flag so pipe handles are inherited. saAttr.nLength = sizeof(SECURITY_ATTRIBUTES); saAttr.bInheritHandle = TRUE; saAttr.lpSecurityDescriptor = NULL; // Create a pipe for the child process's STDOUT. if (!CreatePipe(&g_hChildStd_Rd, &g_hChildStd_Wr, &saAttr, 0)) ErrorExit(L"StdoutRd CreatePipe"); // Ensure the read handle to the pipe for STDOUT is not inherited. if (!SetHandleInformation(g_hChildStd_Rd, HANDLE_FLAG_INHERIT, 0)) ErrorExit(L"Stdout SetHandleInformation"); CreateChildProcess(); // Read from pipe that is the standard output for child process. printf("\n->Contents of child process STDOUT:\n\n"); ReadFromPipe(); printf("\n->End of parent execution.\n"); return 0; } void CreateChildProcess() { TCHAR szCmdline[] = TEXT("Child.exe"); PROCESS_INFORMATION piProcInfo; STARTUPINFO siStartInfo; BOOL bSuccess = FALSE; // Set up members of the PROCESS_INFORMATION structure. ZeroMemory(&piProcInfo, sizeof(PROCESS_INFORMATION)); ZeroMemory(&siStartInfo, sizeof(STARTUPINFO)); siStartInfo.cb = sizeof(STARTUPINFO); siStartInfo.hStdError = g_hChildStd_Wr; siStartInfo.hStdOutput = g_hChildStd_Wr; siStartInfo.dwFlags |= STARTF_USESTDHANDLES; // Create the child process. bSuccess = CreateProcess(NULL, szCmdline, // command line NULL, // process security attributes NULL, // primary thread security attributes TRUE, // handles are inherited CREATE_NEW_CONSOLE, // creation flags NULL, // use parent's environment NULL, // use parent's current directory &siStartInfo, // STARTUPINFO pointer &piProcInfo); // receives PROCESS_INFORMATION // If an error occurs, exit the application. if (!bSuccess) ErrorExit(L"CreateProcess"); else { CloseHandle(piProcInfo.hProcess); CloseHandle(piProcInfo.hThread); CloseHandle(g_hChildStd_Wr); } } void ReadFromPipe(void) // Read output from the child process's pipe for STDOUT // and write to the parent process's pipe for STDOUT. // Stop when there is no more data. { DWORD dwRead, dwWritten; CHAR chBuf[BUFSIZE]; BOOL bSuccess = FALSE; HANDLE hParentStdOut = GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE); for (;;) { bSuccess = ReadFile(g_hChildStd_Rd, chBuf, BUFSIZE, &dwRead, NULL); if (!bSuccess || dwRead == 0) break; bSuccess = WriteFile(hParentStdOut, chBuf, dwRead, &dwWritten, NULL); if (!bSuccess) break; } } void ErrorExit(LPCWSTR lpszFunction) // Format a readable error message, display a message box, // and exit from the application. { LPVOID lpMsgBuf; LPVOID lpDisplayBuf; DWORD dw = GetLastError(); FormatMessage( FORMAT_MESSAGE_ALLOCATE_BUFFER | FORMAT_MESSAGE_FROM_SYSTEM | FORMAT_MESSAGE_IGNORE_INSERTS, NULL, dw, MAKELANGID(LANG_NEUTRAL, SUBLANG_DEFAULT), (LPTSTR)&lpMsgBuf, 0, NULL); lpDisplayBuf = (LPVOID)LocalAlloc(LMEM_ZEROINIT, (lstrlen((LPCTSTR)lpMsgBuf) + lstrlen((LPCTSTR)lpszFunction) + 40) * sizeof(TCHAR)); StringCchPrintf((LPTSTR)lpDisplayBuf, LocalSize(lpDisplayBuf) / sizeof(TCHAR), TEXT("%s failed with error %d: %s"), lpszFunction, dw, lpMsgBuf); MessageBox(NULL, (LPCTSTR)lpDisplayBuf, TEXT("Error"), MB_OK); LocalFree(lpMsgBuf); LocalFree(lpDisplayBuf); ExitProcess(1); }
Child.cpp
#include <windows.h> #include <stdio.h> #define BUFSIZE 4096 #pragma warning(disable:4996) int main(void) { CHAR chBuf[BUFSIZE] = {}; DWORD dwRead, dwWritten; HANDLE hStdin, hStdout; BOOL bSuccess; hStdout = GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE); hStdin = GetStdHandle(STD_INPUT_HANDLE); if ( (hStdout == INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE) || (hStdin == INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE) ) ExitProcess(1); // Send something to this process's stdout using printf. printf("\n ** This is child process. ** \n"); // This simple algorithm uses the existence of the pipes to control execution. // It relies on the pipe buffers to ensure that no data is lost. // Larger applications would use more advanced process control. for (;;) { ReadFile(hStdin, chBuf, strlen(chBuf) + 2, &dwRead, NULL); // Write to standard output and stop on error. bSuccess = WriteFile(hStdout, chBuf, strlen(chBuf)+2, &dwWritten, NULL); memset(chBuf, NULL, BUFSIZE); if (!bSuccess) break; } return 0; }
效果:



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号